AWS News Blog
How The Healthcare of Tomorrow is Being Delivered Today
|
|
My colleagues Jessica Beegle and Angel Pizarro wrote the guest post below to introduce you to an exciting new approach to healthcare!
— Jeff;
Precision Medicine is an emerging approach for disease prevention and treatment that takes into account a person’s individual variation in genes, lifestyle, and environment.
At AWS, we are proud to support the White House Precision Medicine Initiative and will continue our work to accelerate innovation and reduce time to translate research into clinical practice by providing a highly secure platform which can connect researchers and clinicians across the globe, making high-value healthcare datasets such as the 1,000 Genomes, The Cancer Genome Atlas (“TCGA”), and the International Cancer Genome Consortium (“ICGC”) available for use by qualified researchers free-of-charge, and supporting innovative global challenges such as the Qualcomm Tricorder XPRIZE and the Digital Mammography DREAM Challenge.
AWS has worked with many leading global enterprises, innovative startups, and top regulators over the past few years and below are a few highlights from our ecosystem of partners who are bringing precision medicine out of the lab and into clinical care, all with the aim of delivering the healthcare of tomorrow, today.
NCI-MATCH Clinical Trial and Thermo Fisher Scientific
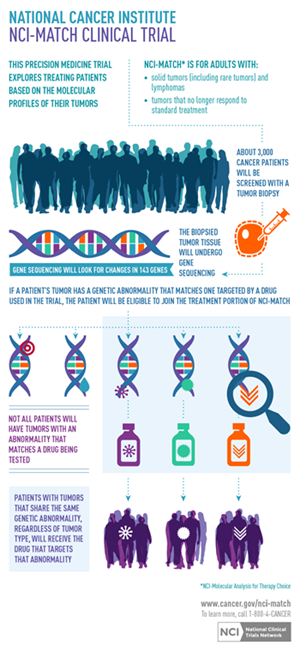 The National Cancer Institute Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice (NCI-MATCH) program is defining a new paradigm for how cancer could be addressed in the era of personalized medicine. The NCI-MATCH program is the first nation-wide trial in which targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology is being used to screen tumor samples for multiple genetic mutations simultaneously in an effort to place patients in one of up to 20 treatment arms that are part of this study.
The National Cancer Institute Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice (NCI-MATCH) program is defining a new paradigm for how cancer could be addressed in the era of personalized medicine. The NCI-MATCH program is the first nation-wide trial in which targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology is being used to screen tumor samples for multiple genetic mutations simultaneously in an effort to place patients in one of up to 20 treatment arms that are part of this study.
Multi-arm trial designs like NCI-MATCH allow researchers to cast a wider net, which helps take into account relatively rare tumor mutations and can drive the development of promising new therapies. The leaders of the program selected AWS partner Thermo Fisher Scientific’s Ion Torrent NGS system and complementary Oncomine reagents for its ability to deliver robust data from limited amounts of starting material derived from formalin fixed paraffin-embedded samples.
Mark Stevenson (Executive Vice President and President, Life Sciences Solutions, for Thermo Fisher) told us:
A study of this scale would not be feasible using the traditional one-sample, one-biomarker testing approach. It is the first national oncology trial of its kind being conducted in the spirit of President Obama’s Precision Medicine Initiative, which has the potential to transform the future of cancer care.
Led by the NCI, the trial is a first-of-its-kind collaboration with multiple pharmaceutical companies. More than 3,000 samples are being screened at four sites across the country using a standardized sequencing protocol on the NGS system to ultimately enroll up to 1,000 patients in the trail.
The sequencing sites participating in the program include:
- NCI Molecular Characterization Laboratory (Frederick, Maryland)
- The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center (Houston, Texas)
- Massachusetts General Hospital
- Yale University (New Haven, Connecticut)
Using the sequencing results, the study’s leads assign program participants, if eligible, to one of several trial arms based on the genetic alterations associated with their tumor, rather than their cancer type.
Precision Medicine Software Makes Genomic Data Actionable: Syapse
The use of genomic and molecular data has become common practice in the diagnosis of disease subtypes and in determining appropriate therapeutic treatment paths, yet clinicians are often unprepared to use these data for clinical decision-making. Traditional Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and other IT systems lack the capability to handle the scale and complexity of genomic and molecular data, and make the data useful for physicians.
To solve this problem facing many health systems and clinicians, Syapse created a software platform that integrates patients’ clinical, treatment, and outcomes data with genomic and molecular data. Using the Syapse Precision Medicine Platform, physicians can derive actionable insights from genomics and molecular data at the point-of-care. Syapse has been adopted by many leading healthcare organizations including Intermountain Healthcare, Providence Health and Services, Sarah Cannon, UCSF, Stanford University, and Sanford Health.
A recent study performed by Intermountain Healthcare produced evidence that their precision medicine program, supported by Syapse software. Here’s what it said:
Precision cancer medicine appears to significantly improve survival for patients with advanced cancer when compared to control patients who received conventional chemotherapy. The additional survival is not associated with increased costs. While the results of this study warrant further investigation in the setting of a prospective randomized control trial, this genomics-based approach appears to be a viable, and perhaps superior, option for patients with advanced or metastatic cancer.
You can watch this video to learn more about how Intermountain and Syapse worked together:
iHART: Decoding the Causes of Autism
AWS and Illumina partnered with researchers from the Hartwell Autism Research and Technology Initiative (iHART) to establish the largest open-access repository of bioinformatics data on autism spectrum disorders through Illumina’s cloud-based platform, BaseSpace. The collaborative research effort includes researchers from Stanford University, the University of California Los Angeles, and the New York Genome Center, who will be granted access to 5,000 genomes of both individuals with autism and those of their family members from the National Institute of Mental Health. Researchers will be able to access BaseSpace and Amazon Redshift to quickly analyze this valuable data to determine genomic variations across the samples.
Dr. Dennis Wall is Associate Professor of Pediatrics at the Stanford University School of Medicine and iHART’s principal investigator. He told us:
We believe this landmark collaboration and open initiative will set the stage for major, clinically useful discoveries in the near future. The complexity of autism requires big data scientific initiatives like this that are openly accessible and act as a sandbox in which all qualified researchers can play. Ultimately, we hope our effort will help define the forms of autism and bring sufficient clarity for marker development and much more.
PrecisionFDA: Advancing Innovation Through Collaboration
President Obama envisioned individualizing a diagnosis, treatment or even a cure for a person based on their genes when he announced his Precision Medicine Initiative a year ago. FDA’s precisionFDA is a step closer to achieving that vision. PrecisionFDA offers an online, cloud-based portal which creates a sandbox for scientists, academia, government and others across the genomics community to experiment, share data and tools, collaborate on projects, and define new standards for evaluating analytical software.
PrecisionFDA was created by the FDA’s Office of Health Informatics (OHI) under FDAs’ Chief Health Informatics Officer, Taha Kass-Hout, MD, MS, and OHI’s Deputy Director, Elaine Johanson, and is being developed under a contract with DNAnexus. The goal of precisionFDA is to help advance the regulatory science needed to assess the accuracy of genome testing and software. The creation of a secure cloud-based platform which is both open and transparent allows members of the genomics community at large to test, develop, and explore next-generation sequencing (“NGS”) methodologies to spur innovation needed to develop necessary standards. In addition, the creation of new reference datasets will unite the genomics community around common standard resources for the industry, and in doing so, will advance consumer safety.
Since it debuted on Dec 15, 2015, more than 900 members representing over 430 organizations worldwide have joined precisionFDA. Significantly, more than 130 members have shared software or reference genome material with the rest of the precisionFDA community. While U.S. members account for approximately 2/3 of the membership, almost half come from Silicon Valley. In addition, precisionFDA’s source code was publicly released on GitHub in January 2016.
Richard Daly (CEO of DNAnexus) told us:
DNAnexus is proud to be delivering precisionFDA and creating a community around open-source genomic analysis pipelines, reference data, and analytical processing resources. The FDA has taken a leadership position in making President Obama’s Precision Medicine Initiative a reality, and the DNAnexus platform will enable the managing and sharing of genomic data at an unprecedented level.
Here’s a video with more information about DNAnexus and their participation in precisionFDA:
NCI Cancer Genomics Cloud Pilot & Seven Bridges Genomics
This pilot aims to increase biomedical discovery by democratizing access to the world’s largest cancer genomics datasets.
Seven Bridges Genomics was selected as a winner of the National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Genomics Cloud Pilot, an initiative to develop a cloud-based infrastructure for data sets such as the Cancer Genome Atlas, which will exceed 2.5 PB, with the goal of increasing the speed of discovery through the democratization of access to some of the world’s most valuable cancer genomic datasets. While the quantity of genomic data has increased dramatically over the last few years, researchers lack the proper resources and methods to access, disseminate, share, and mine data at this scale today. The NCI Cancer Genomics Cloud is being created to solve these challenges and support co-localized data and computation in order to more effectively integrate the big data of cancer genomics.
Deniz Kural (Founder and CEO of Seven Bridges Genomics) told us:
With more than 14 million people in the US living with cancer, it is critical that we build a solution that matches the scale of the challenge. The NCI Cancer Genomics Cloud will enable cancer researcher to utilize genomic data and work towards making personalized medicine a reality. Our platform democratized genomics research and allows anyone with an Internet connection to access and analyze these massive datasets.
Learn More
We hope that you have enjoyed this review of some of the ways that our partners are using the AWS Cloud to solve some of today’s toughest and most critical healthcare challenges. To learn more, please visit our Genomics in the Cloud page and our Healthcare Providers and Insurers in the Cloud page.
— Jessica Beegle , Global Leader, Healthcare and Life Science Partner Ecosystem, AWS
— Angel Pizarro, Global Technical Business Development, Scientific Computing, AWS


