AWS News Blog
New EC2 Run Command – Remote Instance Management at Scale
When you move from a relatively static and homogeneous computing environment where you have a small number of persistent, well-known servers (or instances, using Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) terminology) to a larger and more dynamic and heterogeneous environment, you may need to think about managing and controlling those instances in a new way.
New EC2 Run Command
 Today we are introducing EC2 Run Command. This new feature will help you to administer your instances (no matter how many you have) in a manner that is both easy and secure. This feature was designed to support a wide range of enterprise scenarios including installing software, running ad hoc scripts or Microsoft PowerShell commands, configuring Windows Update settings, and more. It is accessible from the AWS Management Console, the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI), the AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell, and the AWS SDKs. If you currently administer individual Windows instances by running PS1 scripts or individual PowerShell commands, you can now run them on one or more instances.
Today we are introducing EC2 Run Command. This new feature will help you to administer your instances (no matter how many you have) in a manner that is both easy and secure. This feature was designed to support a wide range of enterprise scenarios including installing software, running ad hoc scripts or Microsoft PowerShell commands, configuring Windows Update settings, and more. It is accessible from the AWS Management Console, the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI), the AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell, and the AWS SDKs. If you currently administer individual Windows instances by running PS1 scripts or individual PowerShell commands, you can now run them on one or more instances.
We built this feature after talking to many users about their management needs. Here are some of the themes that came about as a result of these conversations:
- A need to implement configuration changes across their instances on a consistent yet ad hoc basis.
- A need for reliable and consistent results across multiple instances.
- Control over who can perform changes and what can be done.
- A clear audit path of what actions were taken.
- A desire to be able to do all of the above without the need for full remote desktop (RDP) access.
Command execution is secure, reliable, convenient, and scalable. You can create your own commands and exercise fine-grained control over execution privileges by using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). For example, you can specify that administrative commands can be run on a specific set of instances by a tightly controlled group of trusted users. All of the commands are centrally logged to AWS CloudTrail for easy auditing.
Run Command Benefits
The new Run Command feature was designed to provide you with the following benefits:
Control / Security – You can use IAM policies and roles to regulate access to commands and to instances. This allows you to reduce the number of users who have direct access to the instances.
Reliability – You can increase the reliability of your system by creating templates for your configuration changes. This will give you more control while also increasing predictability and reducing configuration drift over time.
Visibility – You will have more visibility into configuration changes because Run Command supports command tracking and is also integrated with CloudTrail.
Ease of Use – You can choose from a set of predefined commands, run them, and then track their progress using the Console, CLI, or API.
Customizability – You can create custom commands to tailor Run Command to the needs of your organization.
Exercising Run Command from the EC2 Console
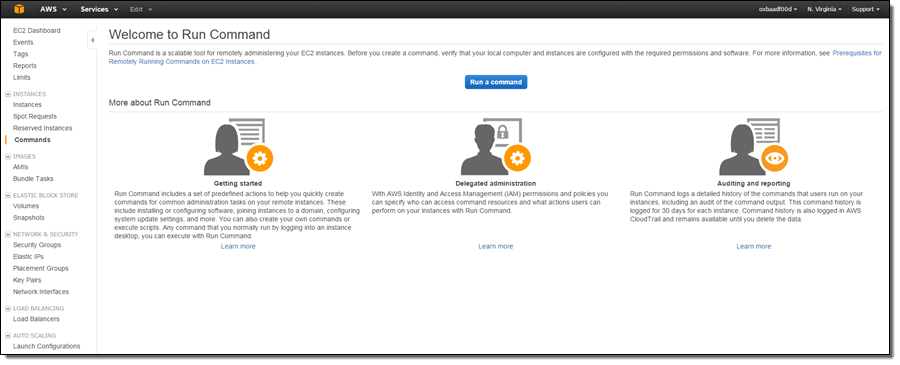
Run Command works across all of your Windows instances and uses the existing EC2Config agent on the instances. Open the Console, select Commands, and review the prerequisites for using Run Command:
Click on Run a command to take you to the main Run Command screen. You’ll see your existing runs (if any) and the Run a command button:
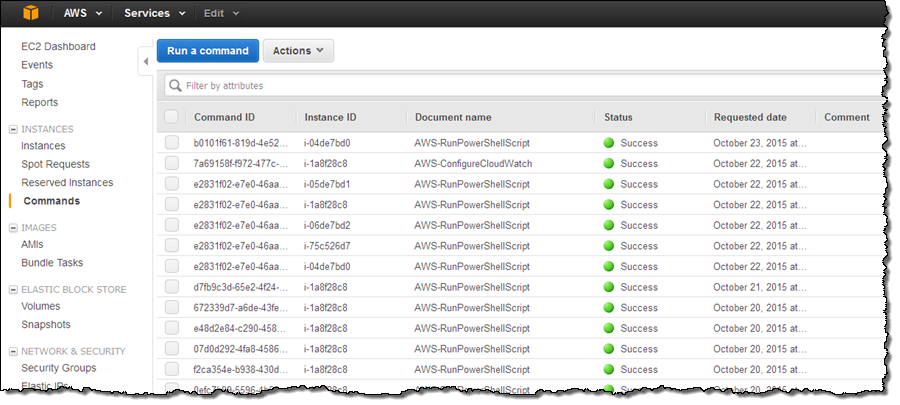
Each row on the display represents a command that has been executed on an instance. Click on Run a command to start a new command:
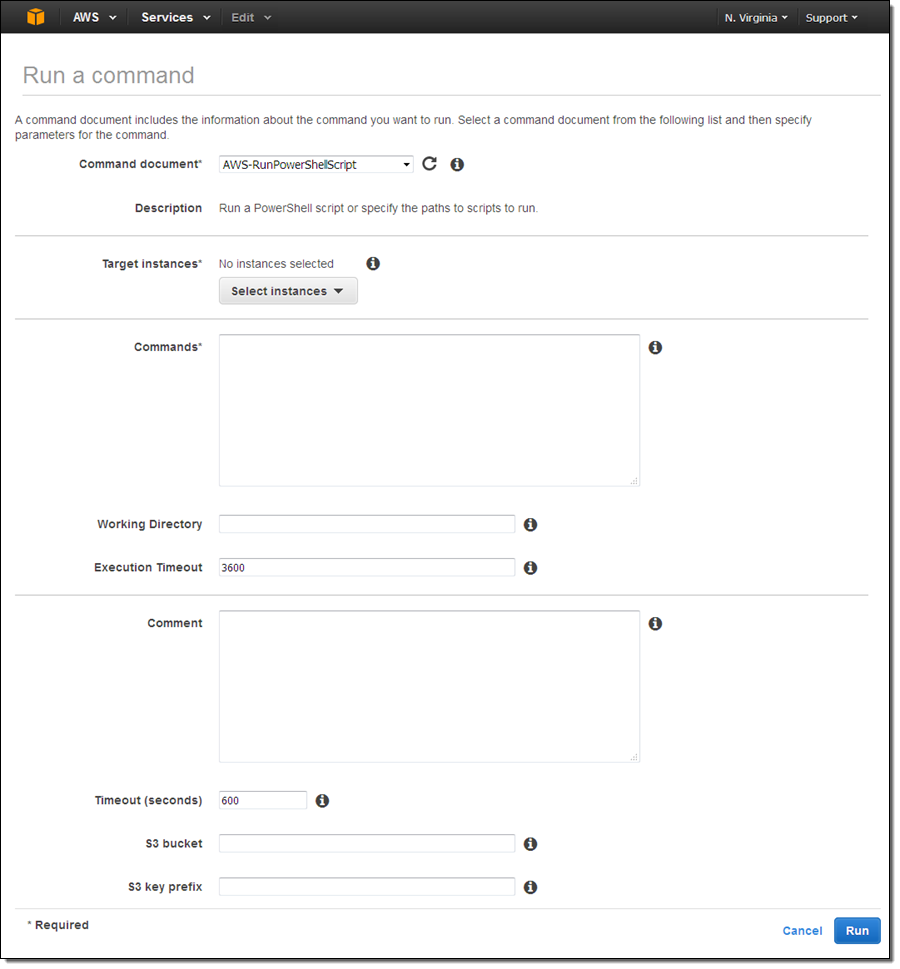
The Command document menu contains seven predefined commands, along with any custom commands that you have created for your account:
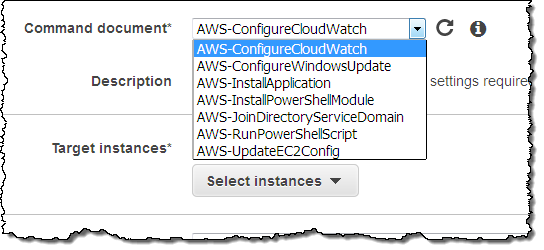
Choose the appropriate document based on your use case and the change that you want to make to the target instance(s). Each document has a description and an explanation that will help you to make the right choice. For common administrative tasks, use the AWS-RunPowerShellScript document. This will allow you to run any PowerShell command or to call an existing PowerShell script.
After choosing the document, fill in the command (I used ipconfig), and choose the instances of interest (you can filter by attributes, tags, or keywords):
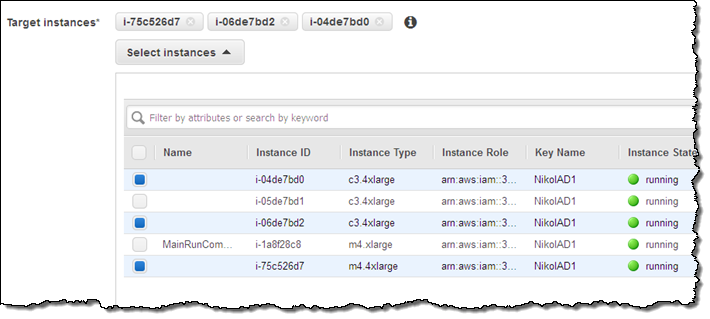
If you are running a command or script that will generate a lot of output on StdOut, you can specify an S3 bucket and a key prefix and the output will be routed there. If you don’t do this, Run Command will capture and display the first 2500 characters of console output.
When you are ready to proceed, click on Run. The Console will display a confirmation message:
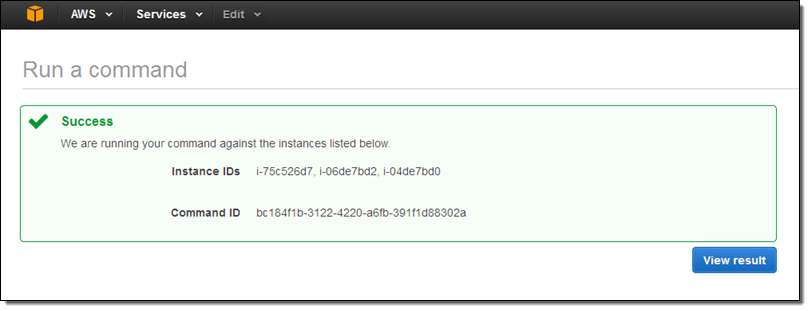
Return to the command history and inspect it to find the results:
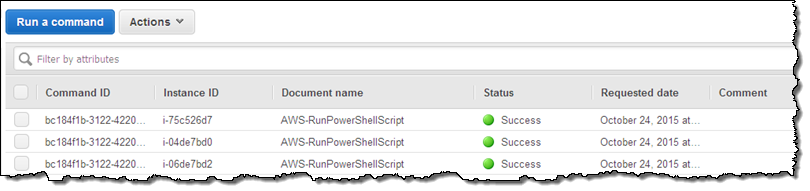
Select the desired command, and click on the Output tab:
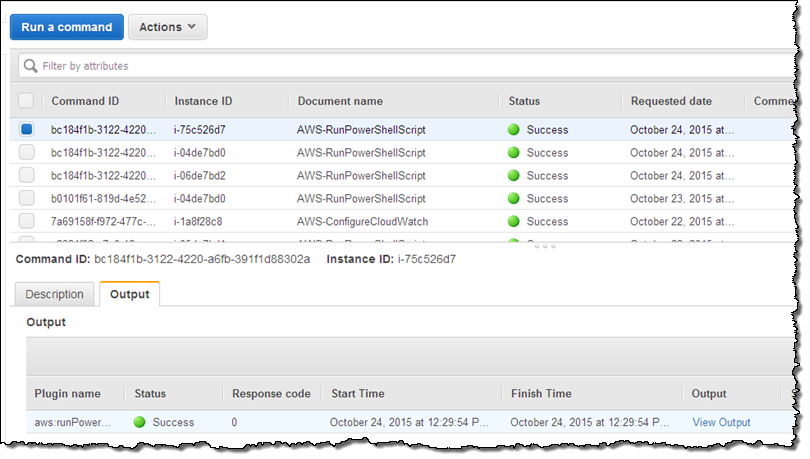
Then click on View Output:
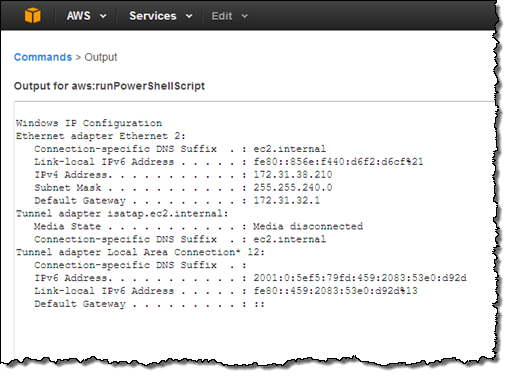
Using Run Command in Production
Here are some of the ways that you can make use of Run Command in your AWS environment:
- Install and configure third-party agents and software.
- Manage local groups and users.
- Check for installed software or patches, and act on the results.
- Restart a Windows service or service.
- Update a scheduled task.
Available Now
You can use Run Command today in the US East (N. Virginia), US West (Oregon), and Europe (Ireland) regions. Simply open the Run Command Console or use the latest AWS Tools for Windows PowerShell, AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI). There is no charge for this this feature; you pay only for the AWS resources that you consume.
— Jeff;
PS – We plan to provide similar functionality for instances that run Linux. Stay tuned to the blog for more info!