- Databases›
- Amazon DynamoDB›
- Global tables
Amazon DynamoDB global tables
What is global tables?
DynamoDB global tables is a fully managed, serverless, multi-Region, and multi-active database. Global tables provide you up to 99.999% availability, increased application resiliency, and improved business continuity. As global tables replicate your tables automatically across your choice of AWS Regions, you can achieve fast, local read and write performance.
If your application processing is interrupted in one Region, there is no need for a database failover, as global tables’ multi-active architecture allows customers to read and write to any replica table. Global tables also remove the difficult work of resolving update conflicts for multi-Region workloads.
Global tables supports both strong and eventual modes for multi-Region consistency. Multi-Region strong consistency gives you the highest level of application resilience, and enables customers’ applications to be always available and always read the latest data from any Region. You can now build applications with a recovery point objective of zero. With multi-Region eventual consistency, you can create replicas within a single AWS account or across multiple AWS accounts.
How it works
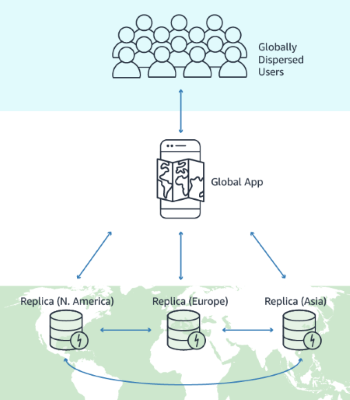
A DynamoDB global table is comprised of multiple replica tables. Each replica table exists in a different Region, but all replicas share the same primary key schema. When data is written to any replica table, DynamoDB automatically replicates that data to all other replica tables in the global table.
For example, suppose that your application serves a large customer base spread across three geographic areas—the US East Coast, Canada, and Western Europe. Without global tables, you would need to create a table in each AWS Region and write code to replicate data changes across each table in each Region.
With global tables, you can create a global table with a replica table in the three Regions closest to each geographic area. DynamoDB will automatically replicate changes from any replica to the replicas in the other Regions.
Global tables allows users of your application to have low-latency access to the data no matter where they are located. If your application processing is interrupted in one Region, your customers can still access the replica tables in the other Regions.
While creating a global table, you can choose either strong consistency or eventual consistency. A global table configured for multi-Region strong consistency provides the ability to perform a strongly consistent read across multiple Regions. The default setting is multi-Region eventual consistency.
For global tables configured using multi-Region eventual consistency mode, you can create replicas within a single AWS account or across multiple AWS accounts. Multi-account global tables automatically replicate tables across multiple accounts and Regions, delivering enhanced resiliency, security, and governance. They are ideal for customers that adopt multi-account strategies or use AWS Organizations to improve security isolation, enforce data perimeter guardrails, implement disaster recovery, or separate workloads by business unit.
Getting started with global tables is easy, as it uses the same DynamoDB APIs as single-Region tables. There are no upfront costs or commitments to use global tables, and you pay only for the resources you use. You can configure global tables in the AWS Management Console with the AWS CLI or with AWS CloudFormation. It's also easy to convert your single Region table to global tables.
Benefits of global tables
Global tables is designed for 99.999% availability. If a single Region becomes isolated or degraded, your application can shift traffic to a different Region and perform reads and writes against a different replica table. You can apply custom business logic to determine when to redirect requests to other Regions. In addition, with multi-Region strong consistency mode, your application will always read the latest data from any Region.
Global tables eliminate the complexity and operational burden of deploying and managing multi-active, multi-Region replication in DynamoDB. You can select the Regions where you need your data replicated and DynamoDB handles the rest. You can choose either eventual consistency or strong consistency for replication between table replicas across Regions. With multi-Region strong consistency, you never have to think about data consistency or data recovery during failover operation.
You can also choose to create replicas within a single AWS account or across multiple AWS accounts. With multi-account global tables, you can build applications across accounts for stronger isolation, better security and governance, and improved operational resiliency, which is aligned with the AWS Well-Architected Framework. Applications access global tables by using existing DynamoDB APIs and endpoints.
Global tables is now configurable for both strong consistency and eventual consistency. Strong consistency guarantees that strongly consistent reads will reflect the most recent write, while eventual consistency will have a short period before all replicas reflect the latest update in exchange for lower- latency local reads and writes.
In multi-Region strong consistency mode, DynamoDB ensures a successfully acknowledged write to any replica in any Region is immediately available for reads from any other replica. If a write operation were to modify an item that is already being modified in another Region, that write operation would fail with a retryable exception.
In multi-Region eventual consistency mode, DynamoDB replicates a write to any replica in any Region to all other replicas, usually within one to two seconds. If the same item is modified in multiple Regions, DynamoDB will resolve the conflict by using a last-writer-wins resolution method.
Global tables enable you to read and write your data locally, providing single-digit millisecond latency for your globally distributed application at any scale. This can boost the performance for massively scaled global applications.