前言
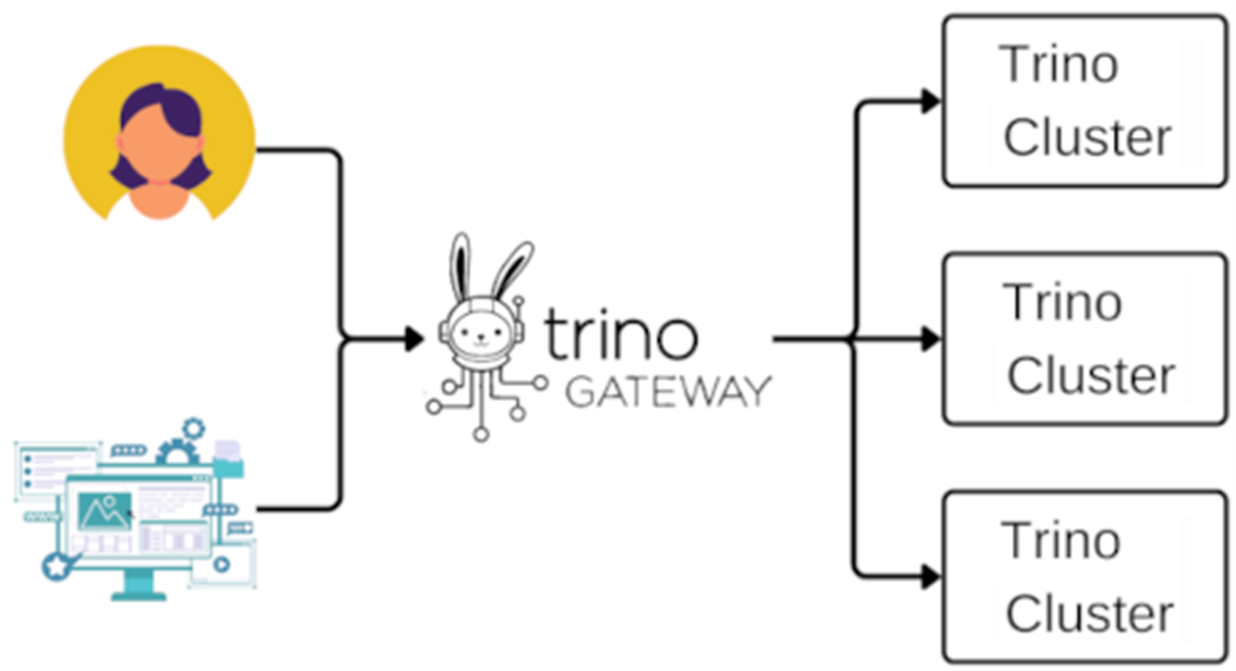
作為當前最流行的開源分散式 SQL 查詢引擎之一,Trino 憑藉其高速的平行度和聯邦查詢(Federated Query)能力,成為現代化數據平台的核心組件。然而,Trino 原生的架構設計存在明顯的痛點 — 單一 Coordinator 節點,在實際生產環境中,這意味著 Coordinator 既是效能瓶頸,也是單點故障(SPOF)的風險所在,一旦它過載或當機,整個集群的服務將完全中斷,這對於追求高可用(High Availability)的企業級應用來說是難以接受的。
為了解決這個難題, Trino Gateway 逐漸展露頭角。Trino Gateway 在2023年正式納入Trino Software Foundation ,是一個專門為 Trino 設計的負載均衡器(Load Balancer)與代理服務,它位於客戶端與多個後端 Trino 集群之間,扮演著「指揮官」的角色,對外提供統一入口,對內則負責管理多個集群的連線與分流,藉此達到高可用性,更支援了藍綠部署(Blue/Green Deployment)模式,實現後端Trino集群的無縫升級。
本文將聚焦於 Trino Gateway 的幾個核心功能的實戰—包括加入後端 Trino 集群,配置路由規則,根據不同的使用者場景(如 Ad-hoc 查詢或 ETL 任務),將 Query 自動導向至指定的後端 Trino 集群,從而實現資源隔離與負載優化。
本篇部落格將細探 Trino Gateway 的核心功能,從零開始教你配置高可用的動態路由策略。
架構
全部開啟以Trino Community提供的Trino和Trino Gateway Helm charts為基礎,在EKS上建立一個簡單的架構:一個Trino Gateway集群,一個Trino A集群和Trino B集群,作為後續配置的演示。除了這三個集群以外,Trino Gateway會需要後端資料庫來保留操作設定, 由MySQL、PostgreSQL 或 Oracle擇一。本文選擇以bitnami的Helm chart repo安裝Postgresql作為資料庫,當 Trino Gateway 服務啟動時,會自動完成資料庫初始化,並利用 Flyway 工具自動處理 Schema 的版本遷移。
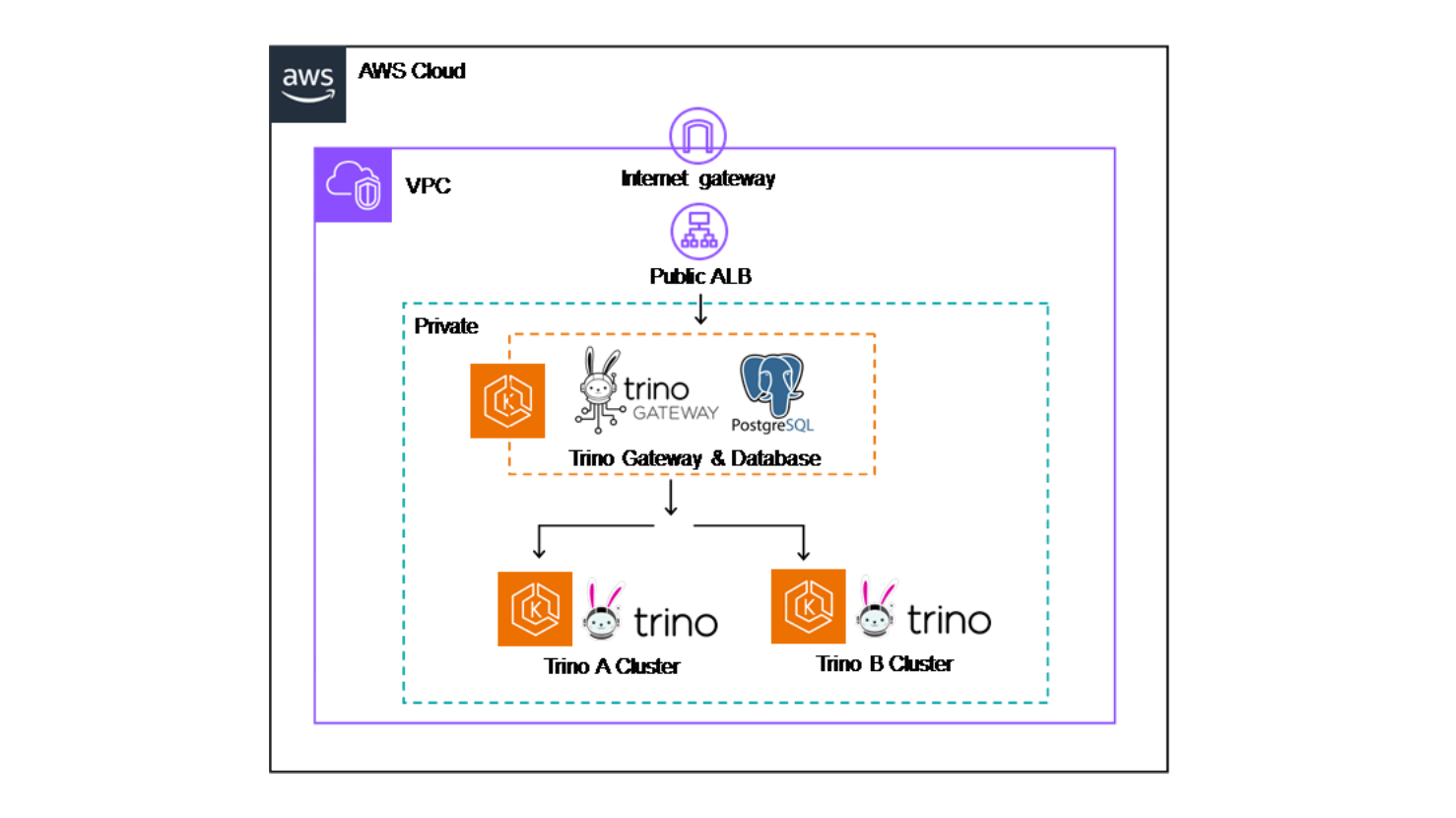
Figure 2: POC architecture diagram
加入後端 Trino 集群到 Trino Gateway
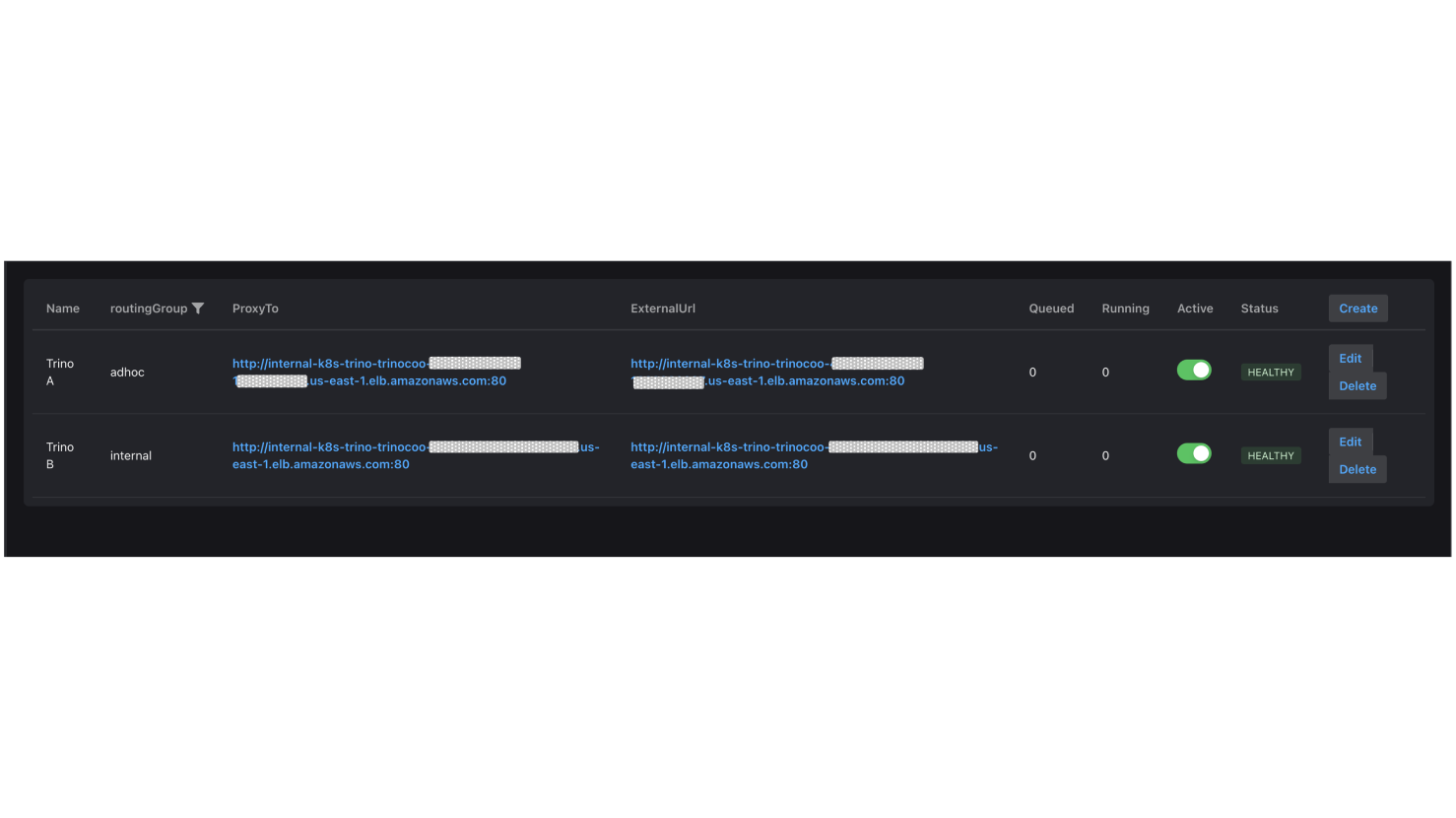
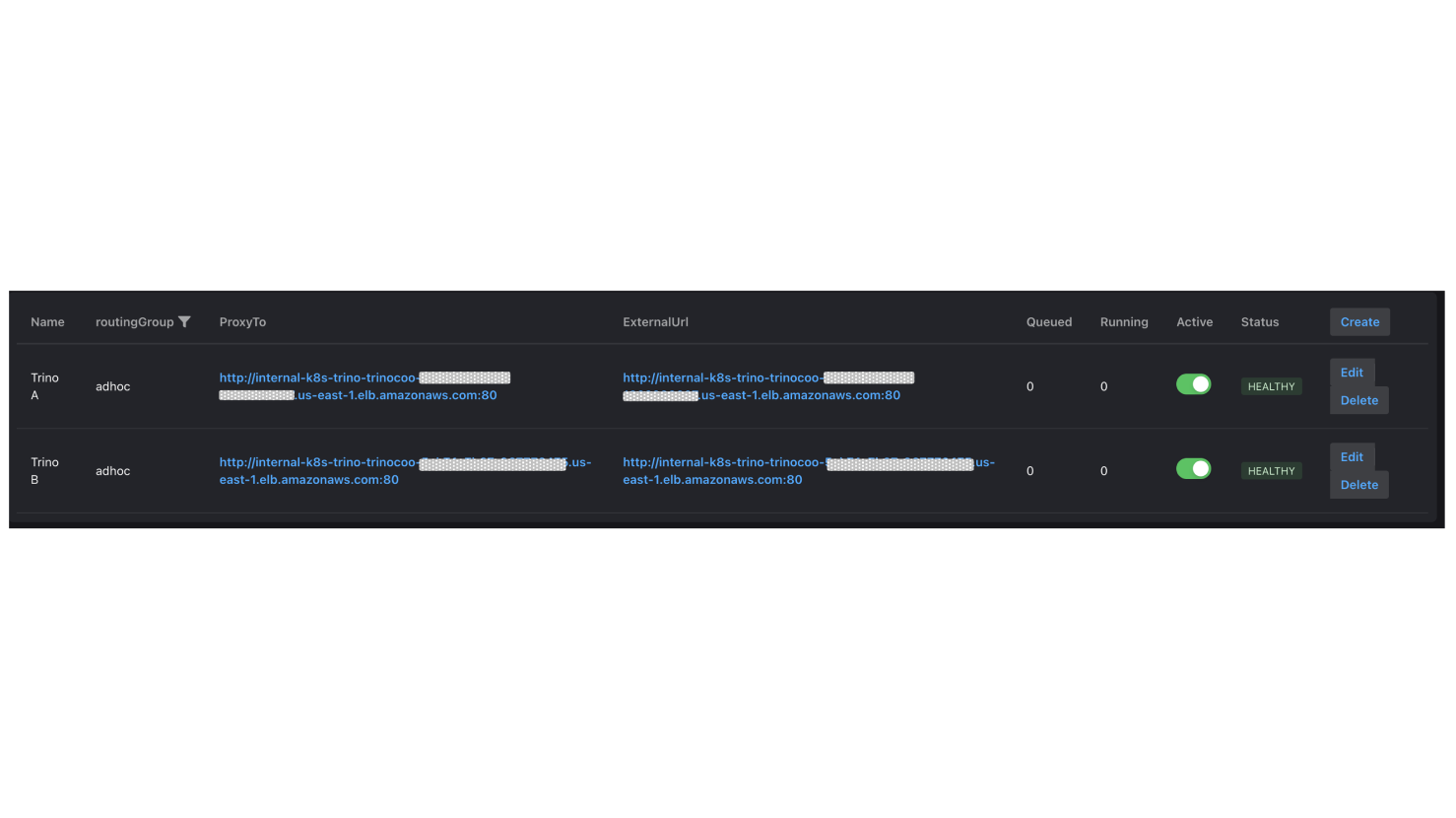
全部開啟1.Trino Gateway提供一個Cluster 管理介面,主要用於設定後端的多個 Trino 集群,以下操作將Trino A和Trino B加入後端集群:
點選左側選單的 "Cluster"。
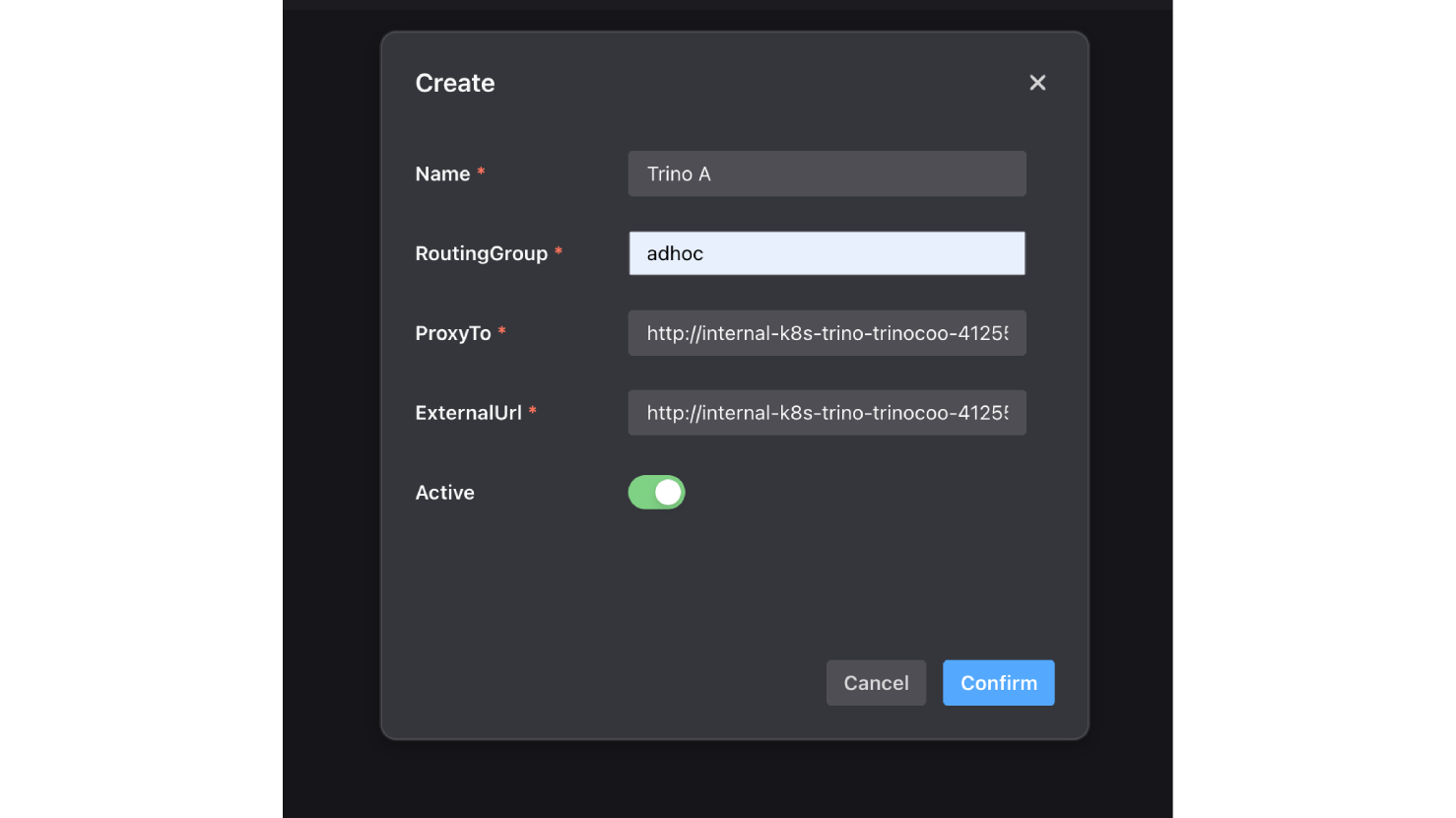
2.再次點擊 "Create",並為外部的adhoc查詢新增一個路由群組 (Routing Group )—adhoc,將Trino A的URL設至ProxyTo和ExternalUrl,設定完畢按下確認。此時,會在 UI 上看到 1個顯示狀態健康(Healthy)的路由群組。
3.接著,加入另一個提供內部查詢使用的路由群組—internal,將Trino B的URL設至ProxyTo和ExternalUrl,設定完畢按下確認。
4.UI 上 顯示狀態健康(Healthy)的2個路由群組加入成功。
預設Trino Gateway會讀取 X-Trino-Routing-Group Header 來決定將查詢(Query)導向哪個路由群組,如果請求中沒有帶這個 Header,系統就會啟用 defaultRoutingGroup 設定作為備案(Fallback);而這個備案的預設目的地是 adhoc 群組,你也可以修改它:
# /etc/trino-gateway/config.yaml
routing:
defaultRoutingGroup: "test-group"
當你維持 defaultRoutingGroup ,Client 端也沒有傳 Header,所有的查詢都會被導轉進 adhoc 這個群組裡,如 figure 3。每個路由群組內至少必須包含一個 Trino 集群,查詢進到路由群組後,預設的路由器會以*隨機(Randomly)*的方式選擇其中一個集群來執行查詢。
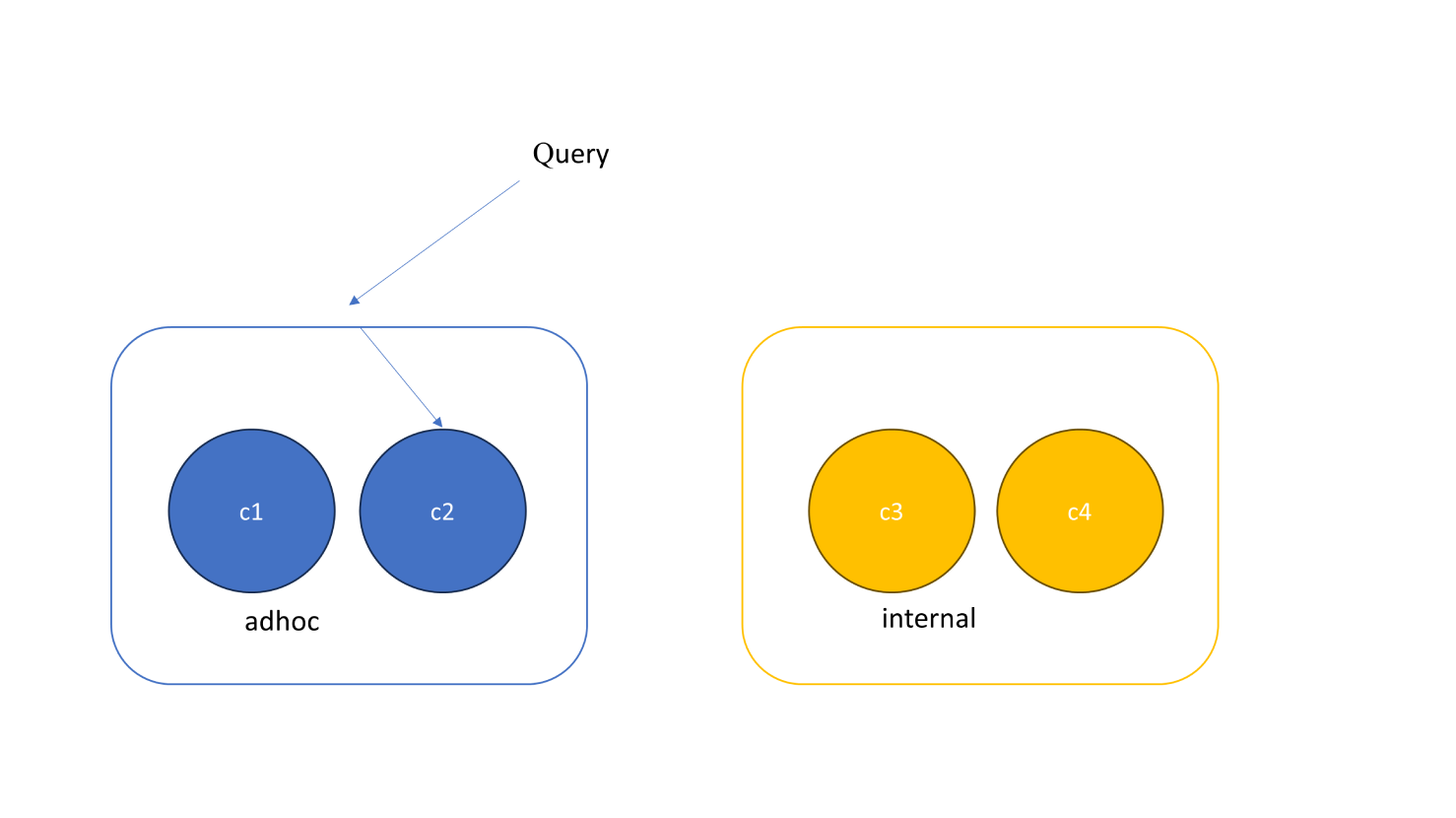
Figure 3: 每個Routing group 必須至少包含一個Trino集群
如果你希望將查詢導向路由群組內,負載最低的集群(Least Loaded Cluster),也就是當下『執行中』或『排隊中』查詢數量最少的那個集群,而不是隨機分配,你可以使用 QueryCountBasedRouter。要啟用這項功能,請將該模組名稱加入設定檔 (config.yaml)的 modules 區塊中:
modules:
- io.trino.gateway.ha.module.QueryCountBasedRouterProvider
驗證後端路由
全部開啟指定X-Trino-Routing-Group: adhoc並確認查詢確實進入Trino A,指令如下:
curl -v -X POST \
-H "X-Trino-Routing-Group: adhoc" \
-H "X-Trino-User: admin" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "X-Trino-Catalog: iceberg" \
-H "X-Trino-Schema: xxxxx_db" \
http://k8s-trino-trinogat-xxxxxxxx-xxxxxxxx.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com/v1/statement \
-d "SELECT * FROM xxxxx_table LIMIT 5"
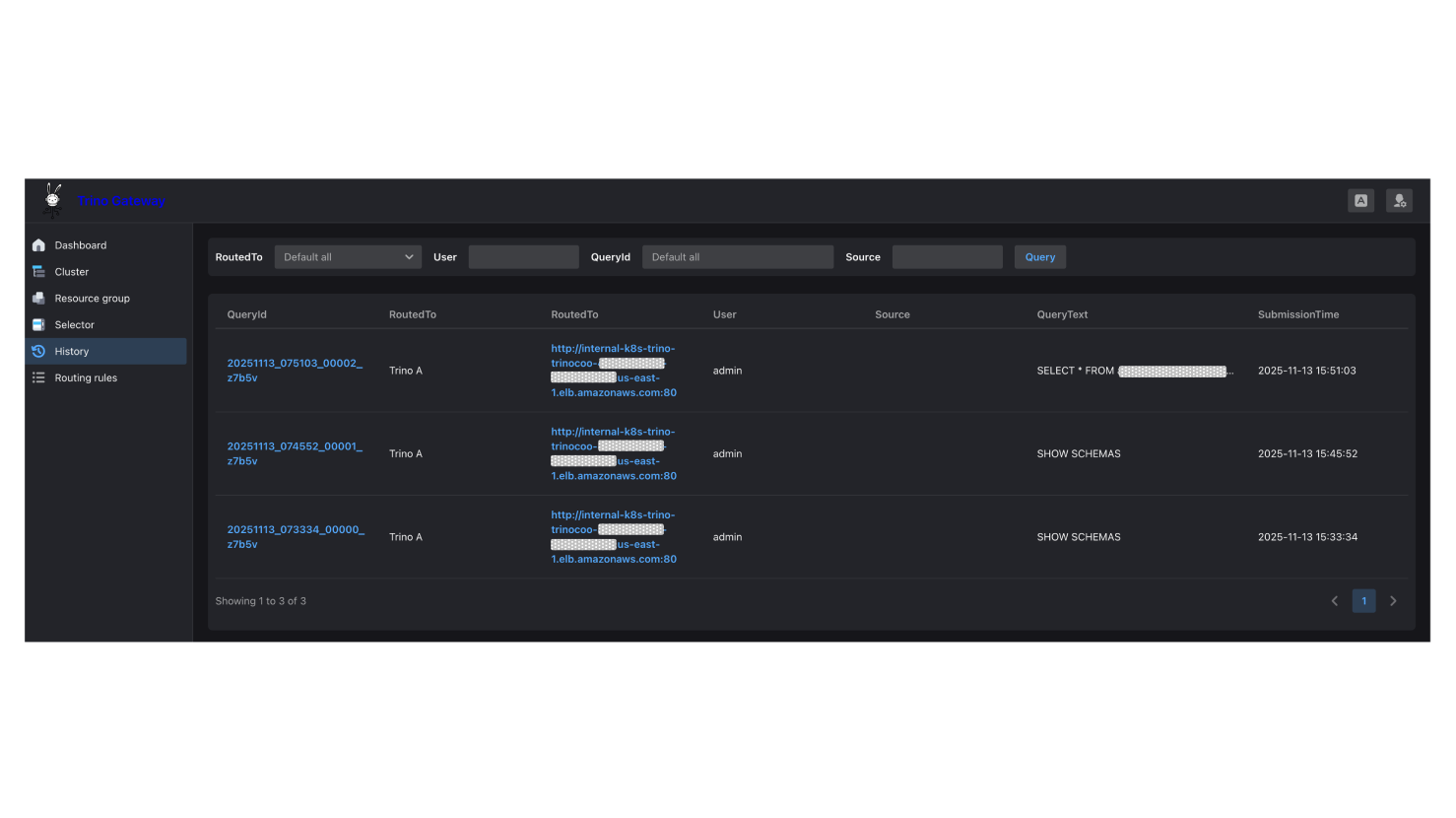
發送完畢後,進到Trino Gateway的History頁面確認查詢路由到Trino A:
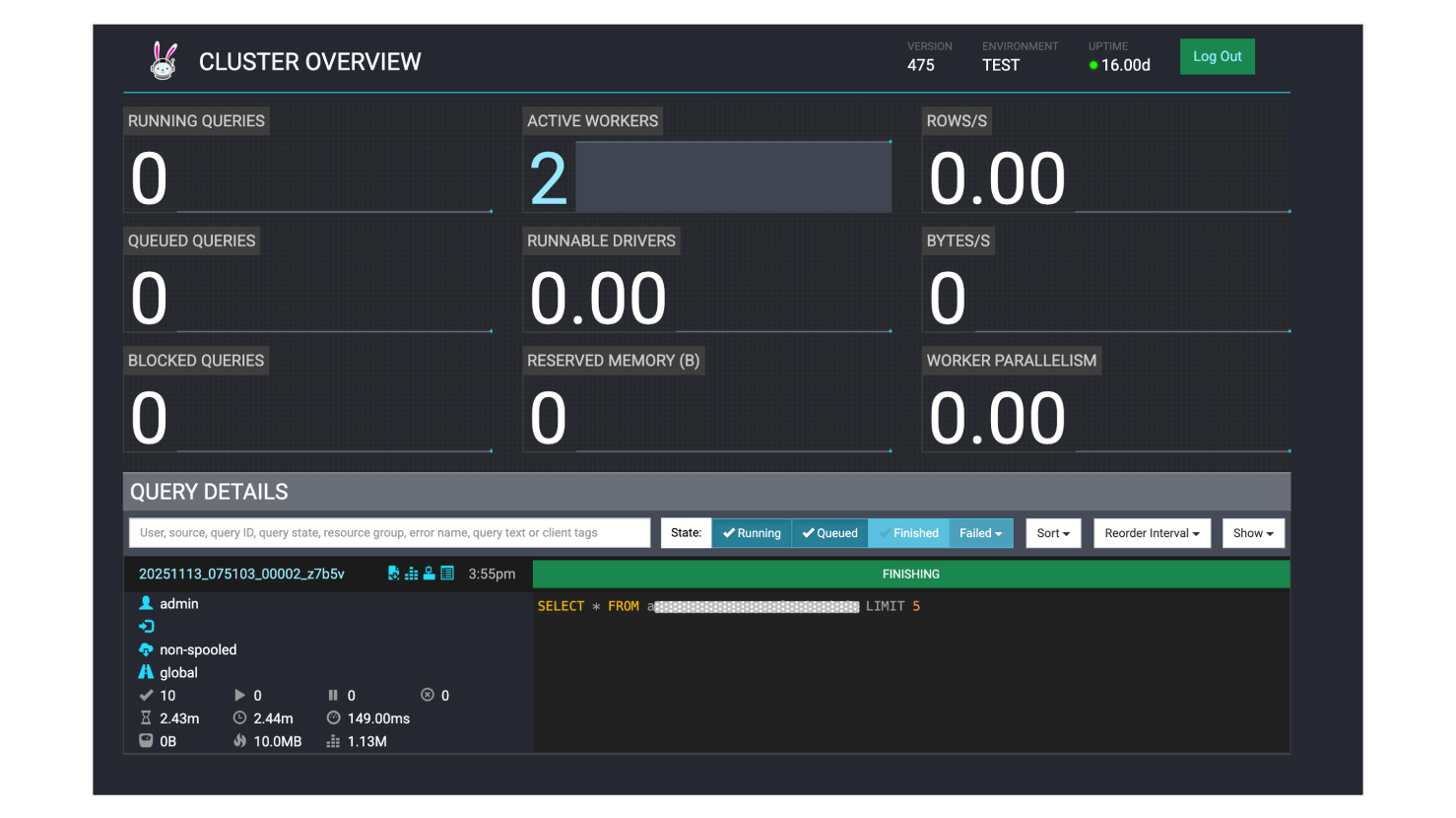
登入Trino A集群的Trino UI確認查詢正確執行完畢:
驗證 QueryCountBasedRouter
全部開啟驗證啟用 QueryCountBasedRouter 是否生效,首先需要將 Trino B 集群也改放置到 adhoc 路由群組,讓它至少有兩個集群可以分配查詢:
測試以20個併發發送50個查詢,期待Trino Gateway每次會選擇比較少負載的那座集群發送:
|
> python client/http_client.py --load-test --num-queries 50 --max-workers 20 |
|
http_client.py snippet: |
|
def load_test(num_queries=50, max_workers=10): """ Send multiple concurrent queries to test QueryCountBasedRouter load balancing
Args: num_queries: Total number of queries to send max_workers: Maximum concurrency """ gateway_host = os.getenv('TRINO_GATEWAY_HOST', 'your_gw_host') gateway_port = int(os.getenv('TRINO_GATEWAY_PORT', 'your_port')) catalog = os.getenv('TRINO_CATALOG', 'your_catalog') schema = os.getenv('TRINO_SCHEMA', 'your_db') user = os.getenv('TRINO_USER', 'admin') … … # Test query query = "SELECT * FROM your_table LIMIT 1"
results = [] start_time = time.time()
# Execute concurrently using ThreadPoolExecutor with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=max_workers) as executor: # Submit all queries futures = { executor.submit( execute_single_query, i, gateway_host, gateway_port, catalog, schema, user, query, extra_credential ): i for i in range(1, num_queries + 1) }
… … return results
if __name__ == "__main__": import argparse parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Trino Gateway Client') parser.add_argument('--load-test', action='store_true', help='Run load test') parser.add_argument('--num-queries', type=int, default=50, help='Number of queries for load test') parser.add_argument('--max-workers', type=int, default=10, help='Max concurrent workers')
args = parser.parse_args()
if args.load_test: load_test(num_queries=args.num_queries, max_workers=args.max_workers)
|
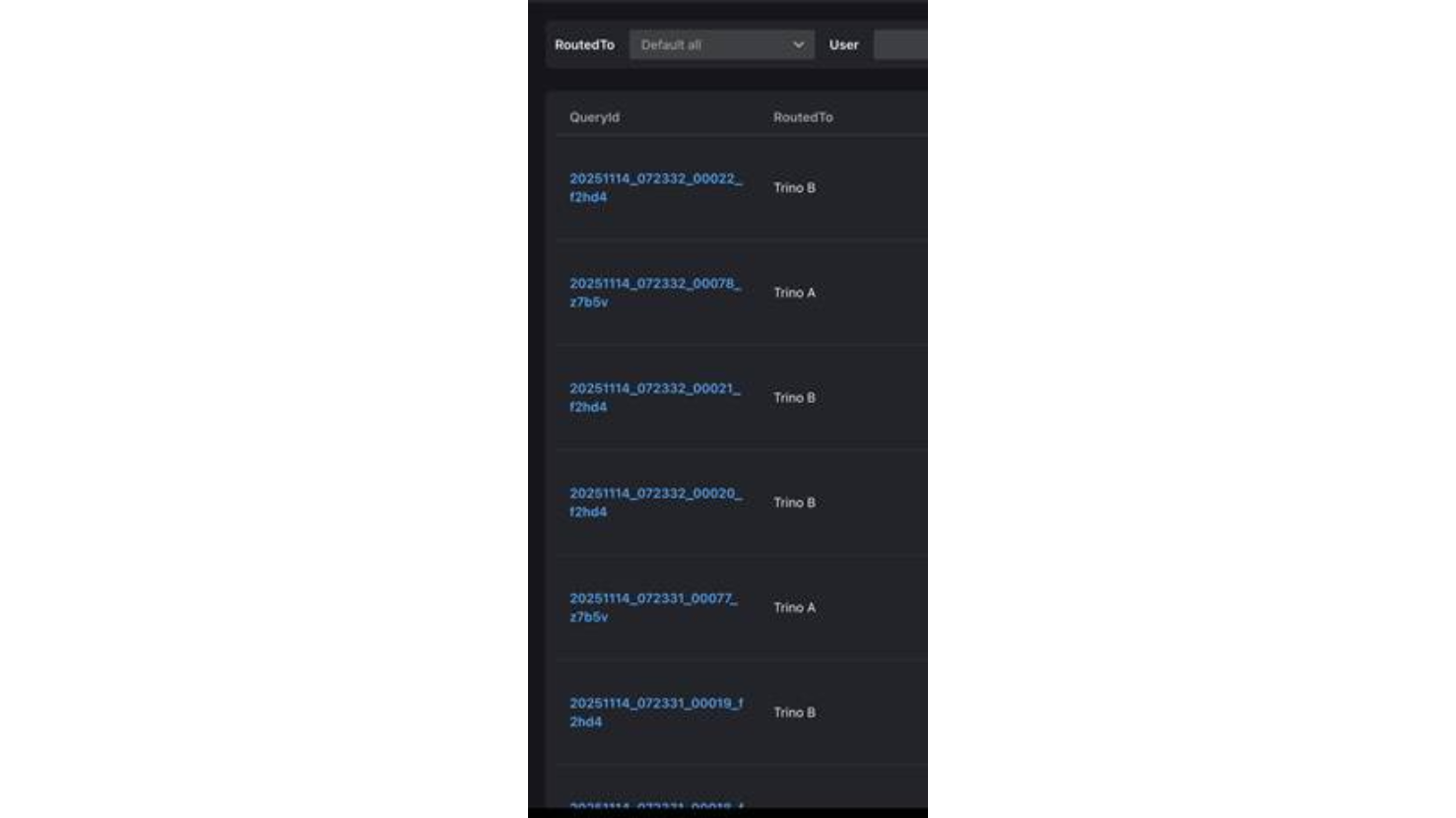
發送完畢後到History頁面,確認Trino Gateway 每次都選擇較輕負載的集群來平衡負載。
創建自定義的路由規則
全部開啟除了使用X-Trino-Routing-Group Header路由,你當然也可以自定義其它路由規則(Routing Rules)。在下圖的範例中定義了規則 #1和#2:
- #1:當 Header X-Trino-Source 為 customers 時,請求導向 adhoc 後端。
- #2:當Header X-Trino-Source 為 collegues時,請求導向 internal 後端。
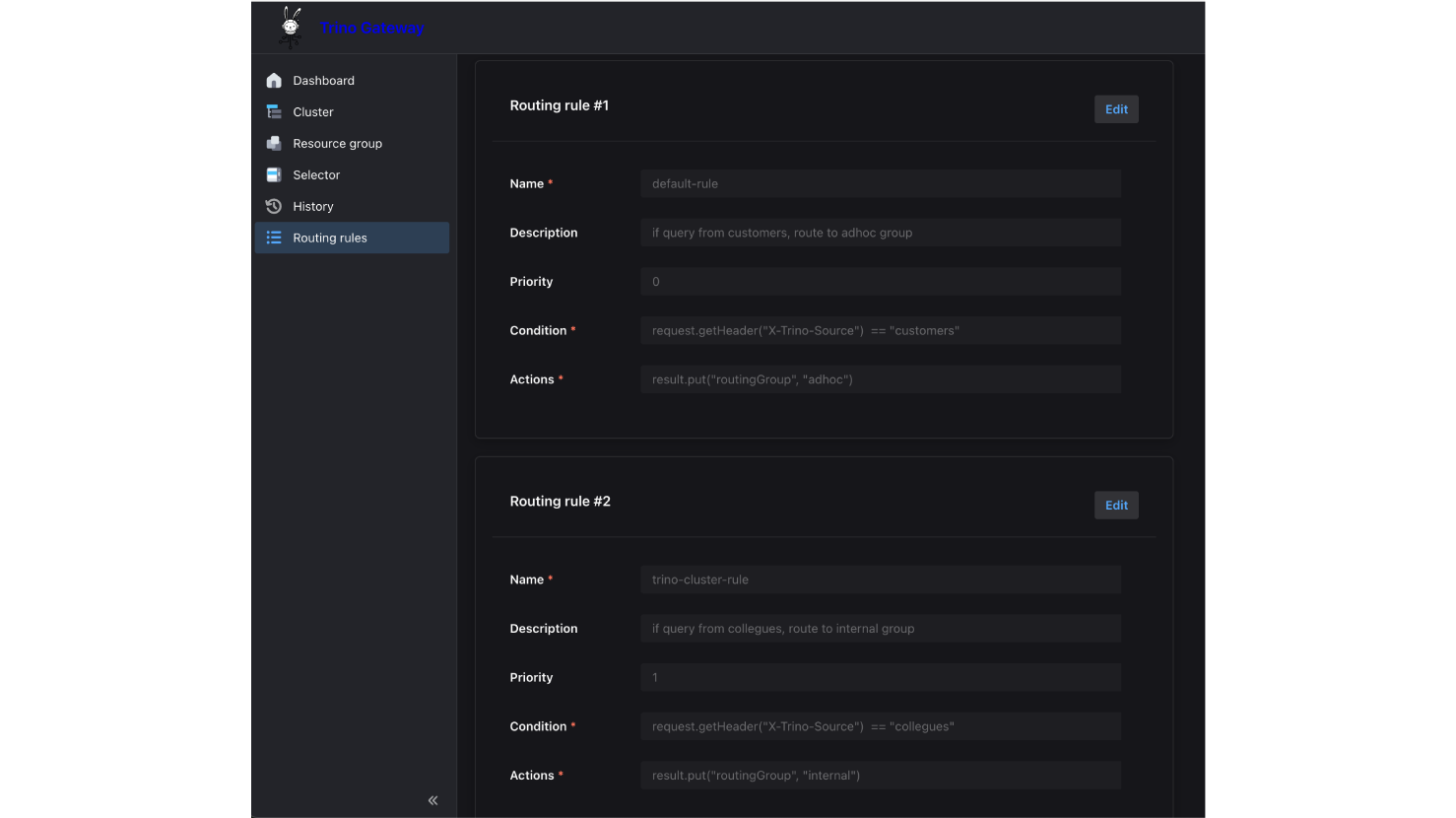
注意,規則#1和#2分別將優先級(Priority)設為 0和1,優先級的設定是「數值越小越早評估」。如果未指定優先級,則預設為 INT_MAX(最後評估)。在自定義的路由規則中,所有的規則都會按優先級評估。舉例來說,假設加入一個新的規則#3:
- Condition:request.getHeader("X-Trino-Tag") == "smallCluster"
- Action:導向 internal
- Priority:2
當一個請求同時滿足以下條件時:
X-Trino-Source = customers # 符合規則 #1 (Priority 0) -> 設為 adhoc
X-Trino-Tag = smallCluster # 符合規則 #3 (Priority 2) -> 改為 internal
這個請求最終會被導向 internal,而不是 adhoc,路由規則採取後發先至(Last Write Wins)的邏輯。因此,越特有或例外的規則,越該設定較大的優先級數值,以便它們能在最後階段覆蓋掉前面的通用設定被執行。
驗證自定義路由規則
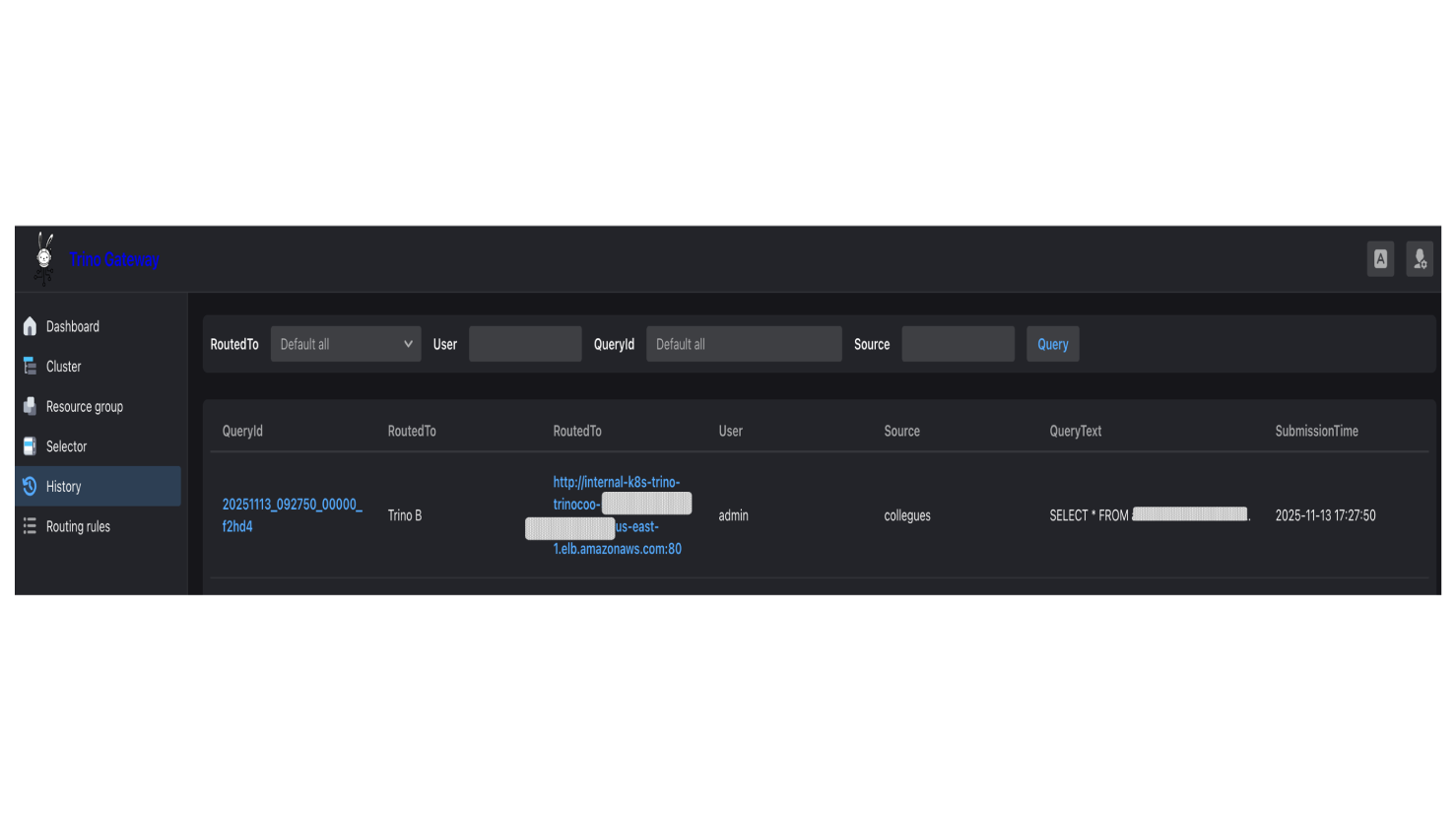
全部開啟發送以下指令,注意這裡並沒有攜帶X-Trino-Routing-Group Header,照預設路由,這則查詢會被導向adhoc群組,但因為我們設定了自定義規則,滿足X-Trino-Source: collegues 則導向internal群組:
|
curl -v -X POST \ -H "X-Trino-Source: collegues" \ -H "X-Trino-User: admin" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -H "X-Trino-Catalog: iceberg" \ -H "X-Trino-Schema: xxxxx_db" \ http://k8s-trino-trinogat-xxxxxxxx-xxxxxxxx.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com/v1/statement \ -d "SELECT * FROM xxxxx_table LIMIT 1" |
確認這則查詢正確被導向 internal 群組:
配置資源群組和選擇器
全部開啟在 Trino 中,資源群組(Resource Groups) 是控制資源配額的核心,它能設定 CPU/Memory 上限、排隊機制,甚至將資源切分給子群組。而選擇器 (Selectors) 就像是內部的交通警察,負責決定一個 查詢該進入哪個資源群組。
雖然 Trino 本身就可以用檔案(File Resource Group Manager)或數據庫(Database Resource Group Manager)來配置資源群組,但Trino Gateway提供的集中式 Database Resource Group Manager 簡化了跨多個 Trino 集群的資源群組管理。
這表示你可以將所有的 資源群組都設定在 Trino Gateway 的資料庫裡,隨時熱更新(Hot-reload),不需要重新部署或重啟後端 Trino 集群。
|
實戰案例: 我有一個對外的路由群組adhoc,後端只有Trino A集群,我希望為『大型客戶』保留較多的專屬資源,並讓其他所有客戶共享Trino A剩餘的資源。同時我不希望因為資源緊繃導致有查詢一直等待不到被分配,產生飢餓(Starvation)的現象。 |
資源群組配置操作步驟:
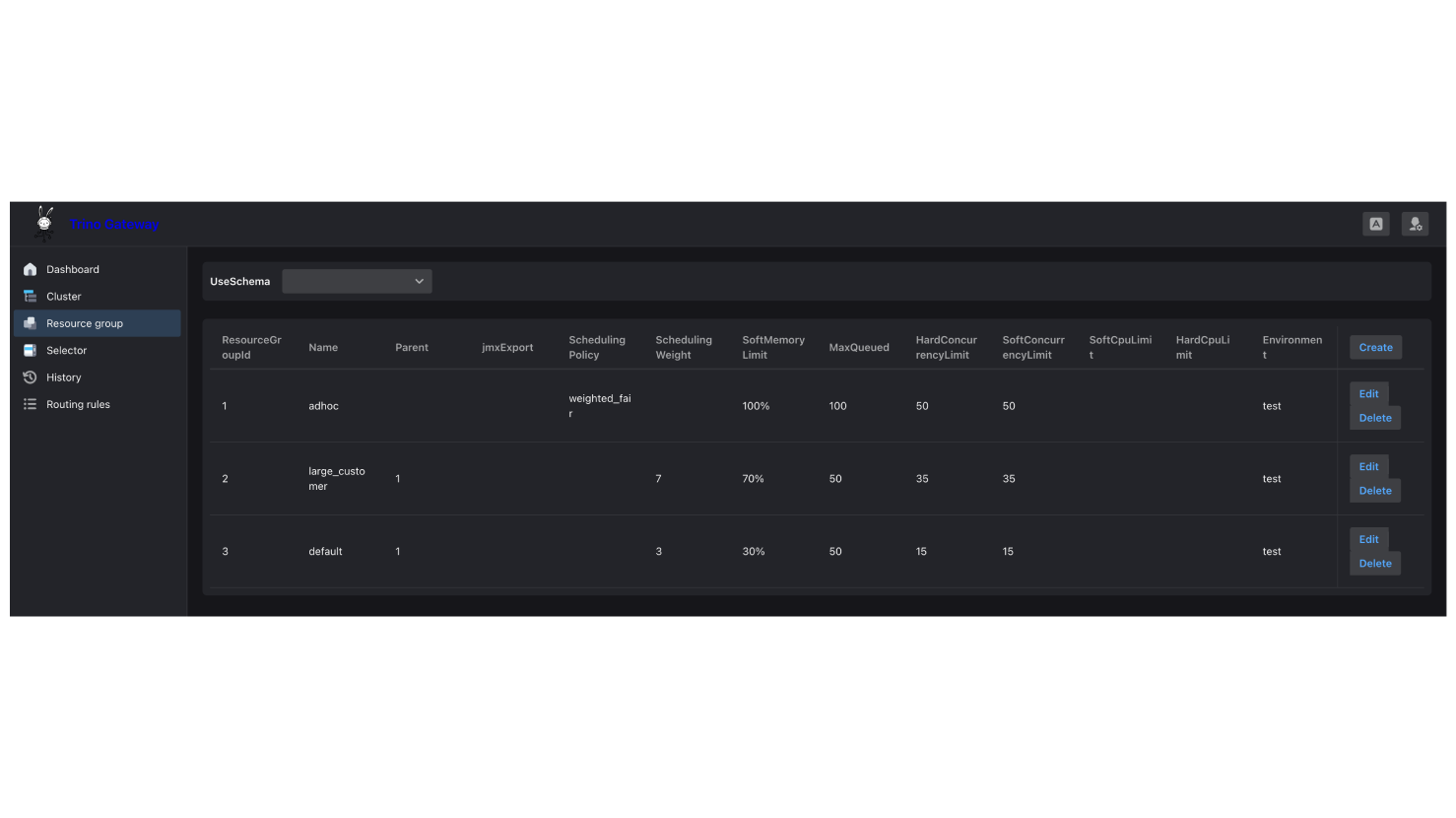
1. 點擊Resource group。設定父群組adhoc,分得100% memory, 100 MaxQueued, 50 concurrent queries 。
2. 設定子群組large_customer,分得70% memory, 50 MaxQueued, 35 concurrent queries, weight=7
設定子群組default,分得30% memory, 50 MaxQueued, 15 concurrent queries, weight=3
或使用API新增或修改,例如:
|
#新增large_customer resource group curl -X POST http://{trino_gw_alb_fqdn}/trino/resourcegroup/create \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "name": "large_customer", "softMemoryLimit": "70%", "maxQueued": 50, "softConcurrencyLimit": 35, "hardConcurrencyLimit": 35, "schedulingPolicy": null, "schedulingWeight": 7, "jmxExport": null, "softCpuLimit": null, "hardCpuLimit": null, "parent": 1, "environment": "test" }' |
|
#修改parent resource group curl -X POST http://{trino_gw_alb_fqdn}/trino/resourcegroup/update \ -d '{ "resourceGroupId": 1, "name": "adhoc", "softMemoryLimit": "100%", "maxQueued": 100, "softConcurrencyLimit": 50, "hardConcurrencyLimit": 50, "schedulingPolicy": "weighted_fair", "schedulingWeight": null, "jmxExport": null, "softCpuLimit": null, "hardCpuLimit": null, "parent": null, "environment": "test" }' |
父群組(Parent Group)可以設定資源比重,分給掛在底下的子群組(Subgroups),本身不能實際執行查詢。資源群組的設定包含了一個 environment = test欄位,它會去對應 Trino node.properties 設定檔中的 node.environment 數值。透過這個機制,即使你有多個不同的 Trino 集群(例如 Test 與 Prod),也能將它們的資源群組設定存放在同一個Trino Gateway的資料庫中統一管理,系統會自動根據環境標籤載入對應的配置。
本範例中,父群組設定了排程策略(schedulingPolicy)決定了排隊中的查詢(Queued Queries)該如何被選中執行,以及子群組(Sub-groups)何時有資格啟動查詢。排程策略共有以下 4 種可選值:
- fair (預設值)
- weighted_fair
- weighted
- query_priority
當策略設定為 weighted_fair 時,相比於單純依照 schedulingWeight 比例進行選擇的 weighted 策略,更能有效防止*飢餓(Starvation)*的情況發生。
目前的設定表示有一個父群組 adhoc,採用 weighted_fair 策略,底下有兩個子群組:
adhoc (parent, schedulingPolicy=weighted_fair)
├── large_customer (權重=7, 佔比 70%) ← 當前有 14 個查詢正在執行
└── default (權重=3, 佔比 30%) ← 當前有 3 個查詢正在執行
系統將計算相對使用率來判斷誰比較忙,是否超出預期份額
- 總共運行:14+3=17
- large_customer 所佔份額: 14 / 17 = 82.4%,預期份額 70%
- default 所佔份額: 3 / 17 = 17.6%,預期份額 30%
由於 default 群組的計算結果較低代表它目前比較空閒。因此,Trino Coordinator 下一步會優先調度 default 群組中的排隊查詢(Queued Queries)來執行。
選擇器配置操作步驟:
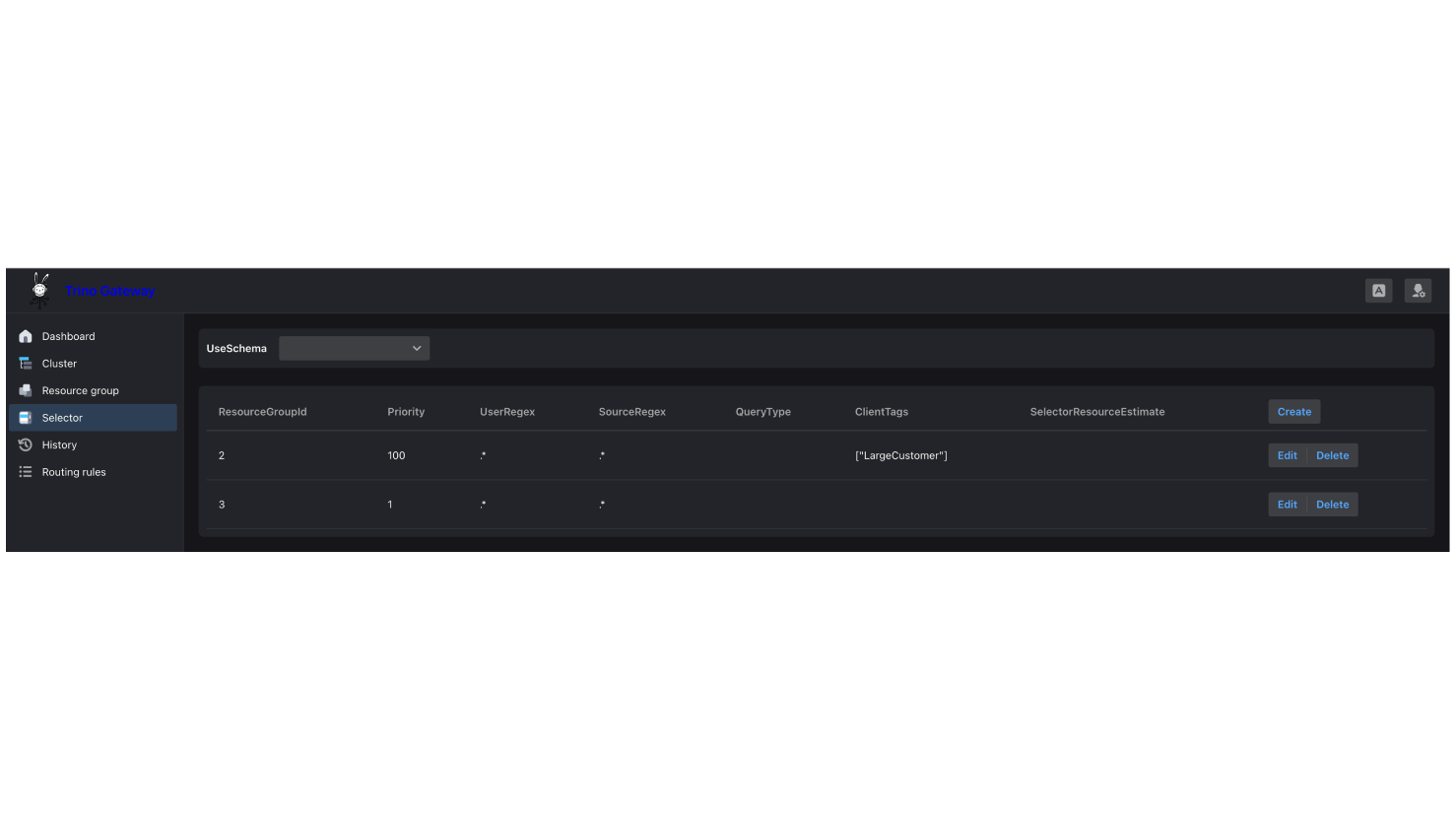
1.點擊 Selector,加入以下兩個 Selectors:1) 當 Header 為 LargeCustomer 的查詢轉導到 Resource Group Id: 2 (large_customer),2) 其他則 Fallback 到 Resource Group Id: 3 (default)
|
curl -X POST http://{trino_gw_alb_fqdn}/trino/selector/create \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "priority": 100, "userRegex": ".*", "sourceRegex": ".*", "queryType": null, "clientTags": "[\"LargeCustomer\"]", "selectorResourceEstimate": null, "resourceGroupId": 2 }' |
|
curl -X POST http://{trino_gw_alb_fqdn}/trino/selector/create \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "priority": 1, "userRegex": ".*", "sourceRegex": ".*", "queryType": null, "clientTags": null, "selectorResourceEstimate": null, "resourceGroupId": 3 }'
|
一個查詢只能被 Coordinator 分配到一個資源群組。系統會根據選擇器的優先級. (Priority)從高到低檢查,並由第一個符合條件的選擇器執行(不同於上述的自定義路由規則),完成了資源群組和選擇器的配置後,下一小節將設定 Trino A 的資源群組數據庫到Trino Gateway 的 Postgres,並重啟 Trino A的Coordinator。
後端 Trino A 集群操作步驟:
1. 為了讓 Trino A 取得集中化資源群組數據庫的設定,需要更新 Coordinator 的 resource-group.properties 如下:
resource-groups.configuration-manager=db
resource-groups.config-db-url=jdbc:postgresql://{postgres_fqdn}:5432/gateway
resource-groups.config-db-user={your_user}
resource-groups.config-db-password={your_password}
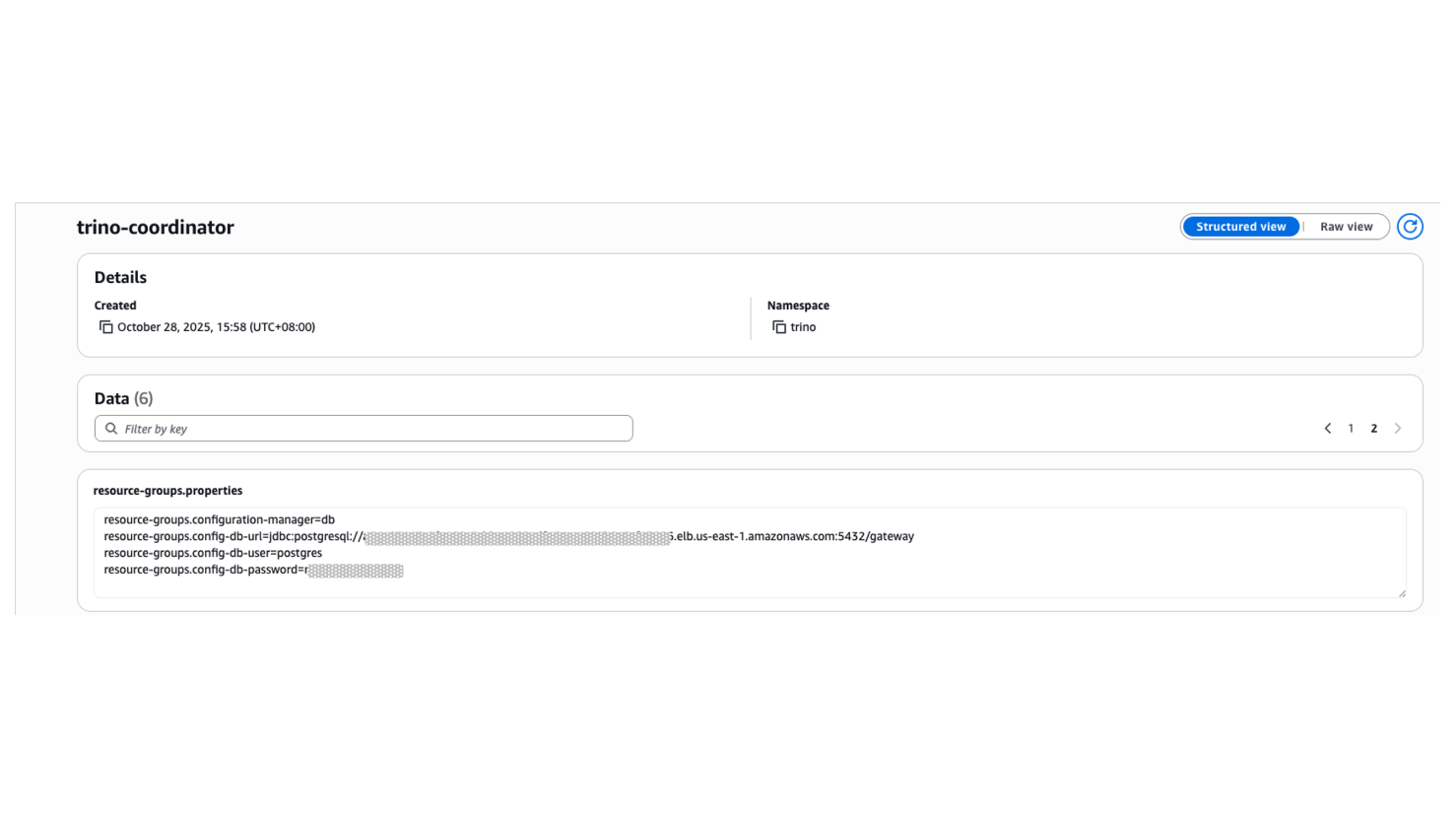
2.重啟 Trino A Coordinator
驗證資源群組和選擇器的路由
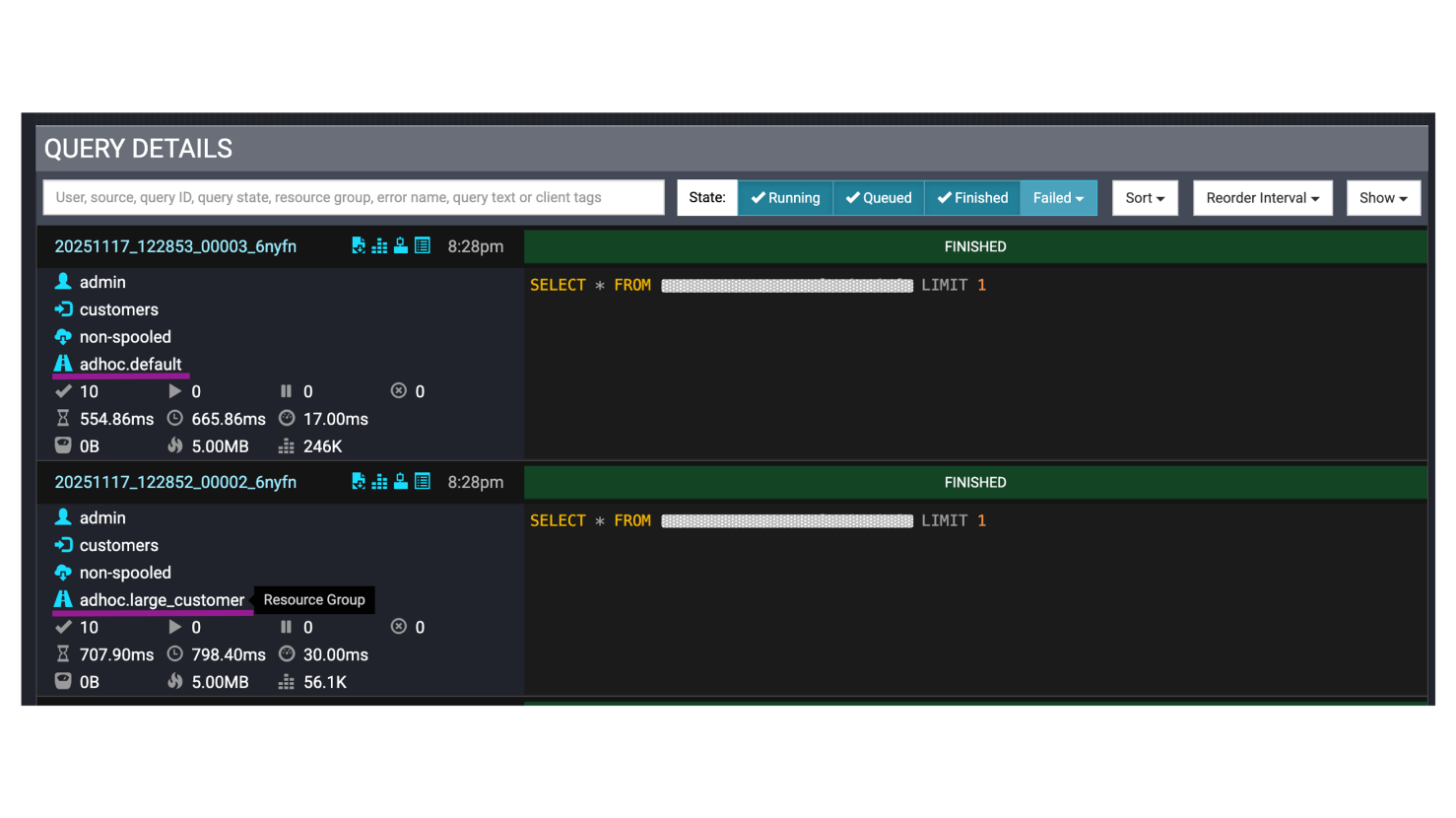
全部開啟接下來我們要驗證大客戶和其他人下的查詢確實分開到不同資源群組。執行以下指令來發送兩個請求,一個帶有'X-Trino-Client-Tags': 'LargeCustomer' 期待以large_customer執行,另一個則是不指定,期待由default執行。
|
> python client/http_client.py --resource-group-test |
|
http_client.py snippet: |
|
if __name__ == "__main__": import argparse parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Trino Gateway Client') parser.add_argument('--resource-group-test', action='store_true', help='Test resource group configuration') args = parser.parse_args()
if args.resource_group_test: simple_resource_group_test()
def simple_resource_group_test(): """ Test Resource Group configuration Send two queries to verify resource group selector: 1. With LargeCustomer tag → large_customer group 2. Without tag → default group """ gateway_host = os.getenv('TRINO_GATEWAY_HOST', 'your_gw_host') gateway_port = int(os.getenv('TRINO_GATEWAY_PORT', 'your_port')) catalog = os.getenv('TRINO_CATALOG', 'your_catalog') schema = os.getenv('TRINO_SCHEMA', 'your_db') user = os.getenv('TRINO_USER', 'admin') query = "SELECT * FROM xxxx_table LIMIT 1" … … # Test 1: Query with LargeCustomer tag (should go to large_customer group) print("\n[Test 1] Query with LargeCustomer tag") print("-" * 80) try: conn = trino.dbapi.connect( host=gateway_host, port=gateway_port, user=user, source='customers', catalog=catalog, schema=schema, http_scheme='http', extra_credential=extra_credential, http_headers={ 'X-Trino-Client-Tags': 'LargeCustomer' }, )
cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(query) rows = cursor.fetchall() cursor.close() conn.close()
except Exception as e: print(f"\n✗ Error: {e}") print(f"Error type: {type(e).__name__}")
time.sleep(3) # Test 2: Query without tags (should go to default group) print("\n[Test 2] Query without client tags") print("-" * 80) try: conn = trino.dbapi.connect( host=gateway_host, port=gateway_port, user=user, source='customers', catalog=catalog, schema=schema, http_scheme='http', extra_credential=extra_credential, # No http_headers - no client tags )
cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(query) rows = cursor.fetchall() cursor.close() conn.close()
except Exception as e: print(f"\n✗ Error: {e}") print(f"Error type: {type(e).__name__}") |
登入Trino A的UI,確認兩個不同的查詢,一個正確使用large_customer的資源群組,另一個則正確使用default。
總結
全部開啟透過本文的實戰演練,我們從零開始搭建了一套基於 Trino Gateway 的高可用 Trino 集群架構。從最初的後端集群註冊,到動態路由規則的配置,再到精細化的資源群組管理,每一步都展示了 Trino Gateway 如何解決 Trino 原生架構中可能發生單點故障的痛點,並為企業級應用提供了靈活且可靠的查詢分流機制。
無論你是想要為不同等級的客戶劃分專屬資源,或是希望在不同任務的查詢之間實現資源隔離,Trino Gateway 的路由規則與資源群組機制都能為你提供彈性的解決方案。搭配 weighted_fair 等智能調度策略,還能有效避免查詢飢餓問題,確保系統資源得到公平且高效的利用。
希望這篇文章能幫助你順利踏上 Trino Gateway 的實戰之路。如果你正在構建或優化自己的Trino數據平台,不妨將 Trino Gateway 納入你的技術棧中體驗他帶來的穩定性與靈活性。
作者資訊
Joey Wu, Solutions Architect, AWS
Joey Wu (吳家宜) 任職於台灣 AWS 的解決方案架構師,具備十年以上軟體經驗。主攻後端開發也曾擔任測試 、SRE 及資料分析師的角色,涉獵多有實屬雜兵。喜歡探索技術背後的原理並解決客戶問題。近年來致力於大數據平台及生成式 AI 應用,協助企業客戶探索新的使用情境及方向。
