Overview
This Guidance demonstrates how to implement event-driven autoscaling for Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) applications using Kubernetes Event-Driven Autoscaler (KEDA). The Guidance shows how to scale deployments based on custom metrics, rather than solely CPU and memory utilization. KEDA integrates with Kubernetes, extending autoscaling capabilities for event-driven workloads. By following this Guidance, you can optimize resource provisioning, improve cost efficiency, and enhance the customer experience for your event-driven applications on Amazon EKS using custom metrics-based autoscaling with KEDA.
How it works
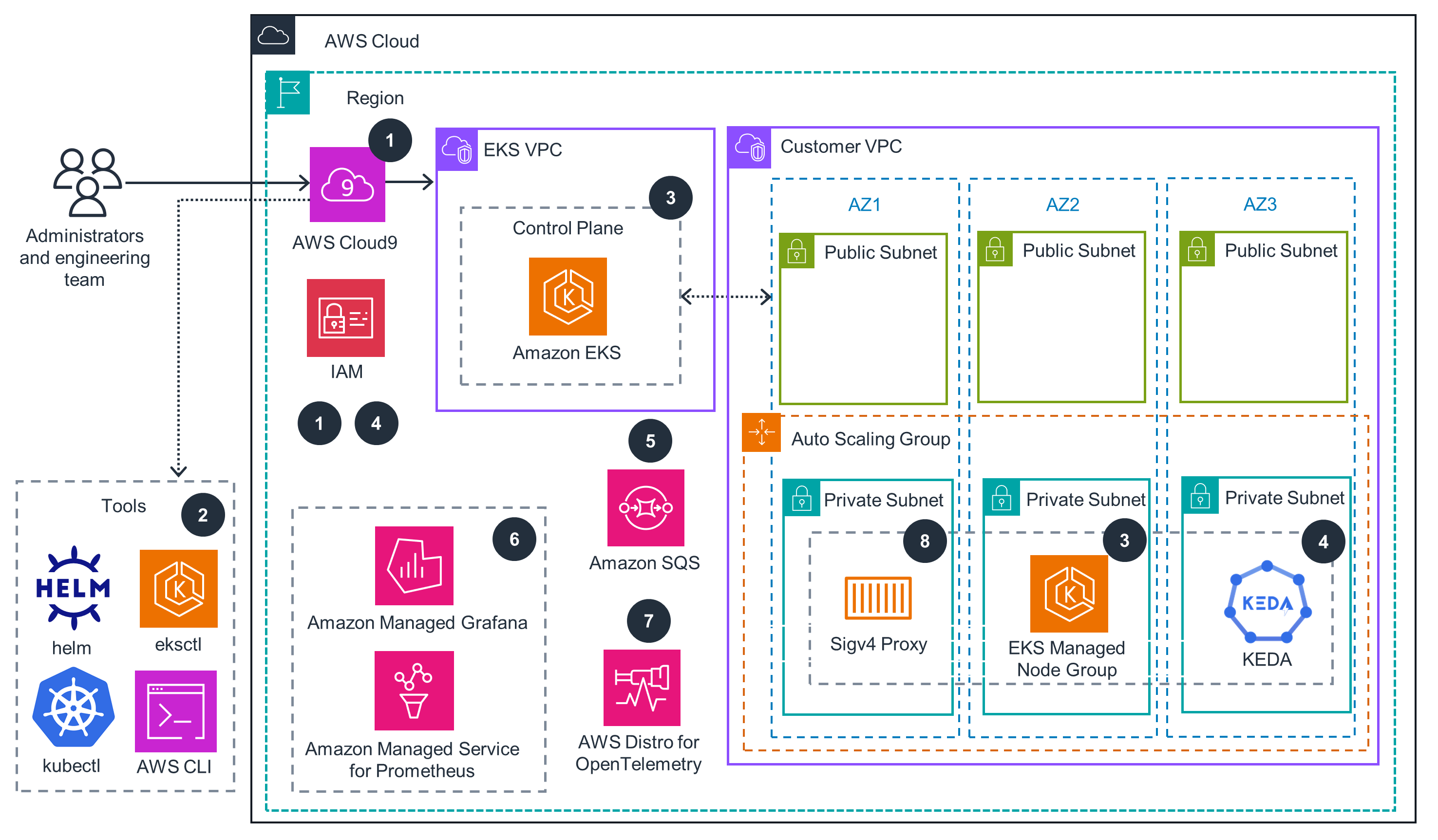
EKS Cluster
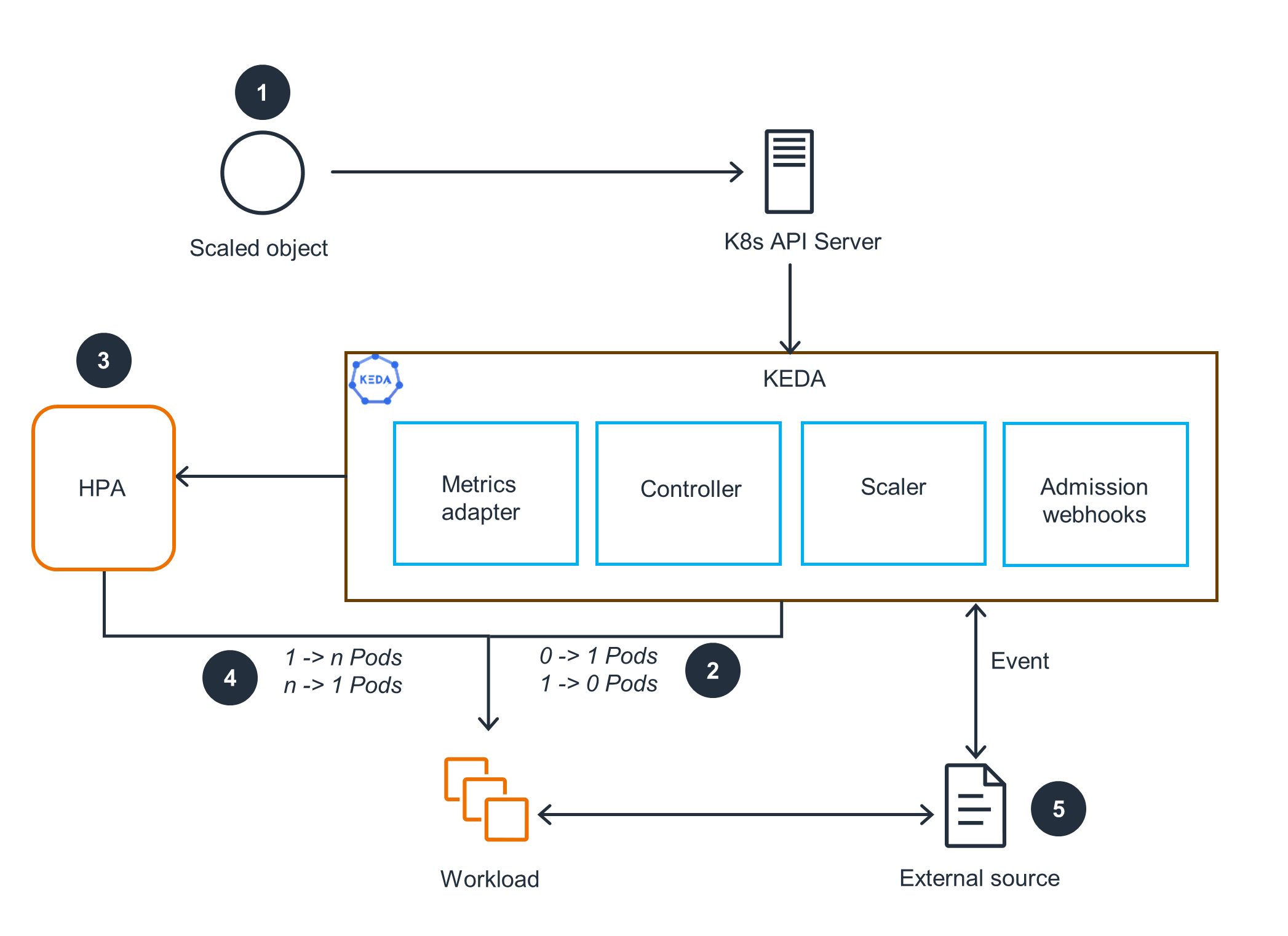
KEDA Overview
This architecture diagram shows an overview of how KEDA, the Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA), and external event sources work together. For KEDA scaling pods, open the next tab.
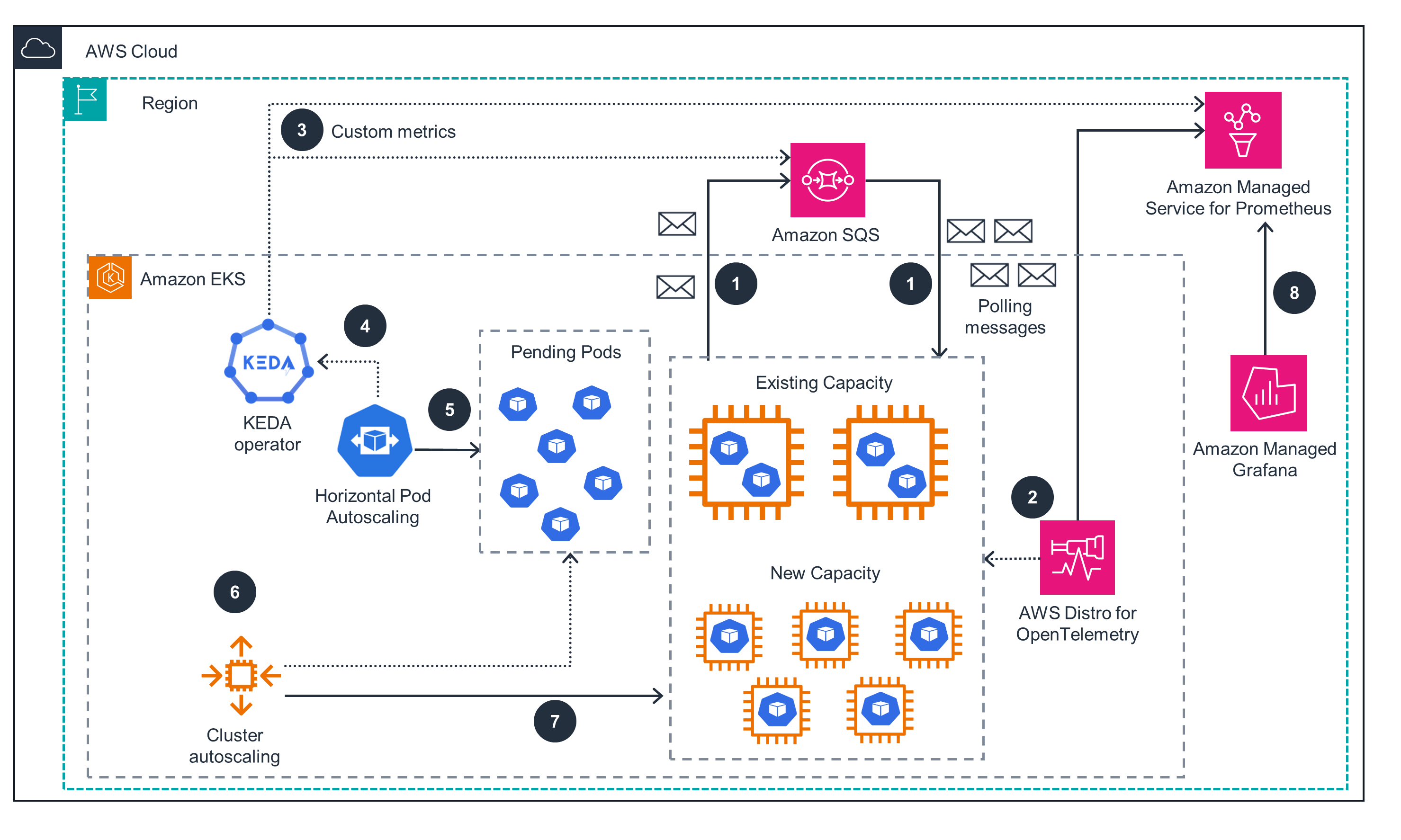
Scaling with KEDA
This architecture diagram shows KEDA scaling deployment pods based on custom metrics sources. For the EKS cluster, open the first tab.
Deploy with confidence
Everything you need to launch this Guidance in your account is right here
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages