Overview
This Guidance demonstrates how to automate the setup of Amazon CloudWatch dashboards for monitoring and alerting network resources on AWS. It uses AWS tagging and API capabilities to efficiently gather the necessary information to configure the dashboards, including the ability to centralize monitoring across your AWS environment. This automated approach helps you save time and effort in establishing comprehensive network visibility while also making the process more adaptable to changes in your AWS infrastructure.
There are three architecture diagrams: the first illustrates the high-level automation process of deploying CloudWatch dashboards. The second diagram shows detailed information when configuring monitoring. The last diagram shows the flow of events when a CloudWatch alarm is triggered.
How it works
Overview
This architecture diagram illustrates the high-level automation process of deploying Amazon CloudWatch dashboards for network monitoring and alerting. The subsequent slides provide more detailed information on the configuration of monitoring (slide 2) and alerting (slide 3).
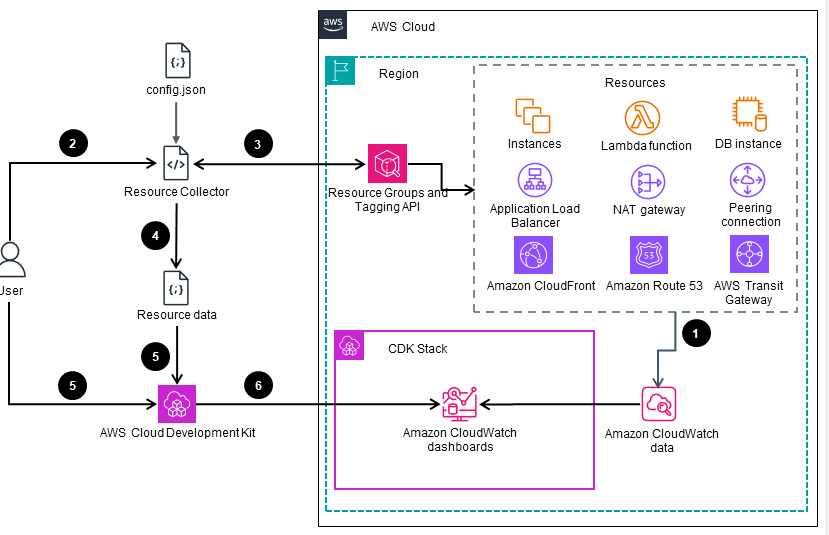
Monitoring
This architecture diagram shows how to generate and deploy the "Event Forwarder Stack," which is required for configuring the AWS accounts where the resources being monitored reside. These are the accounts that need to be configured to forward the CloudWatch alarm events to the central "monitoring" account.
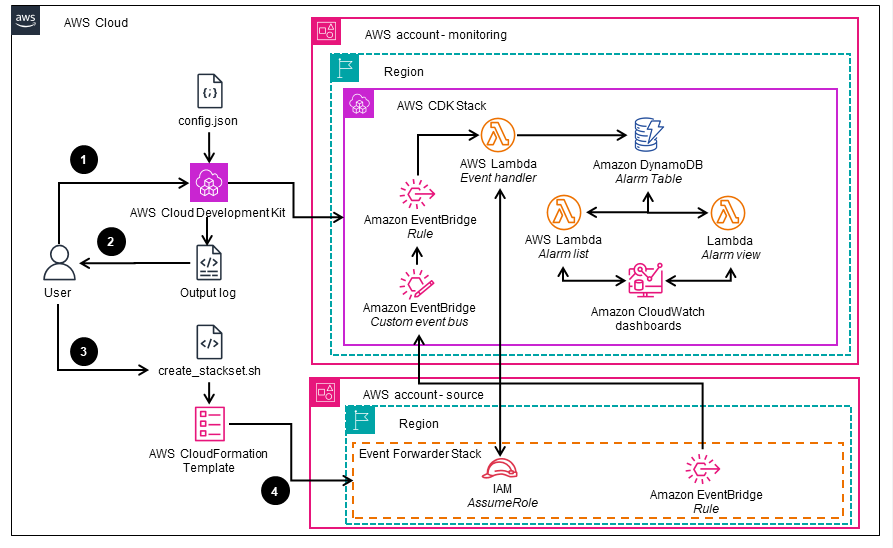
Alerting
This architecture diagram shows the flow of events when a CloudWatch alarm is triggered. The alarm event is forwarded to an Amazon EventBridge event bus and processed by an AWS Lambda function. The ‘view’ and ‘list’ Lambda functions retrieve and render the alarm data in the CloudWatch dashboard.
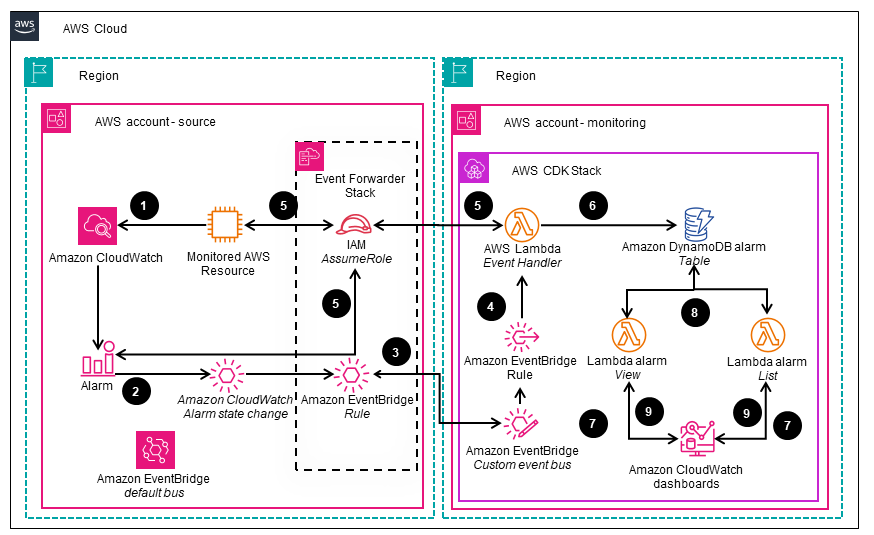
Deploy with confidence
Everything you need to launch this Guidance in your account is right here
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages