- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Aerospace Technician’s Assistant on AWS
Guidance for Aerospace Technician’s Assistant on AWS
Overview
This Guidance demonstrates how aerospace technicians can use a generative artificial intelligence (generative AI)-powered 'assistant' to answer natural language technical questions using custom document libraries for authoritative answers. With airplane assembly and repair manuals often comprising thousands of pages, it is time-consuming for technicians to search these physical documents manually. Using optical character recognition (OCR), scanned documents can be converted into searchable text and then integrated with the AI assistant to enable natural language queries. Technicians can quickly search by keywords or receive answers to spoken questions, enhancing efficiency while maintaining quality and safety in assembly and troubleshooting processes.
How it works
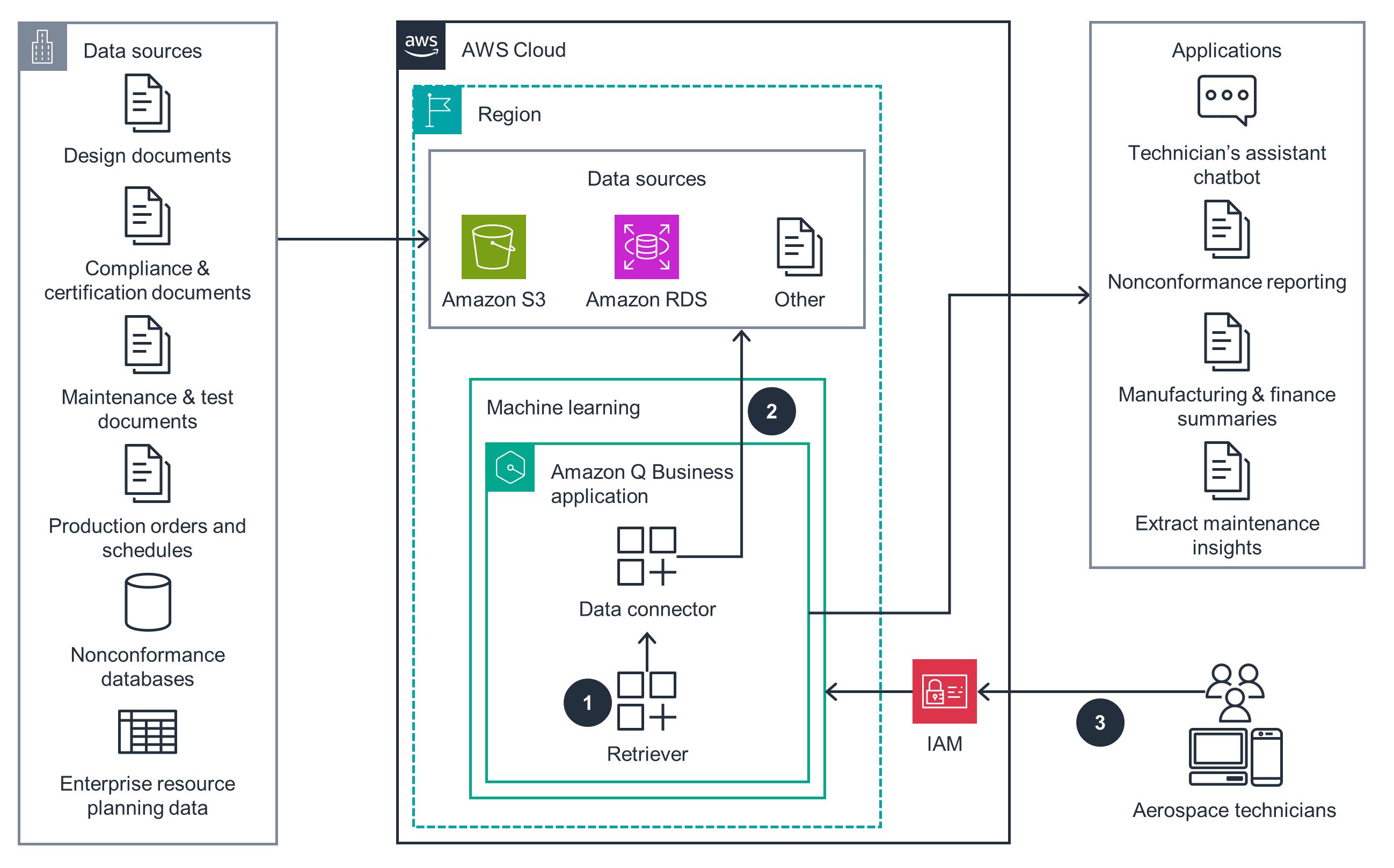
Amazon Q
This architecture diagram shows how to use Amazon Q to enable natural language searching of paper documents.
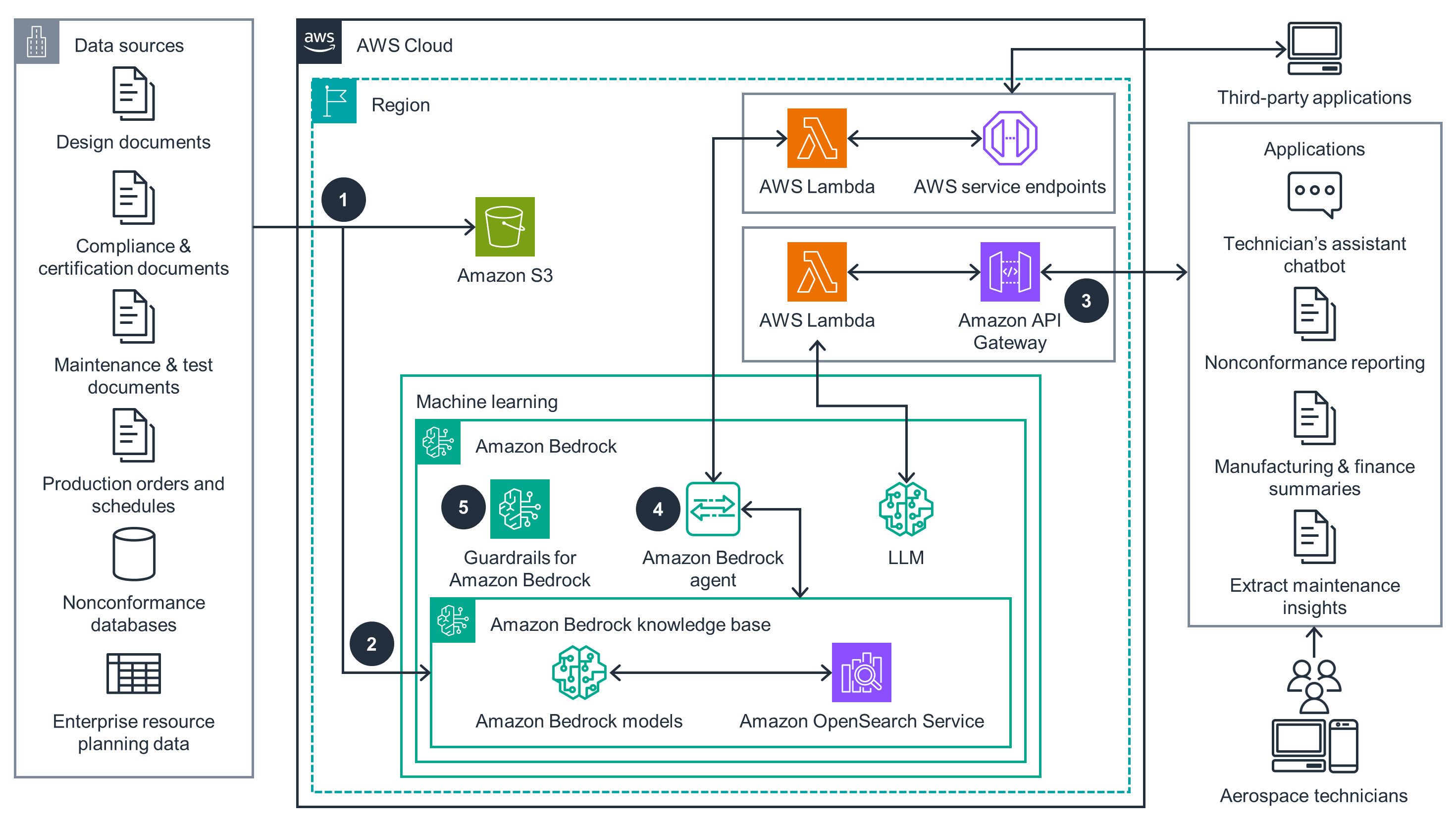
Amazon Bedrock
This architecture diagram shows how to use Amazon Bedrock to enable natural language searching of paper documents.
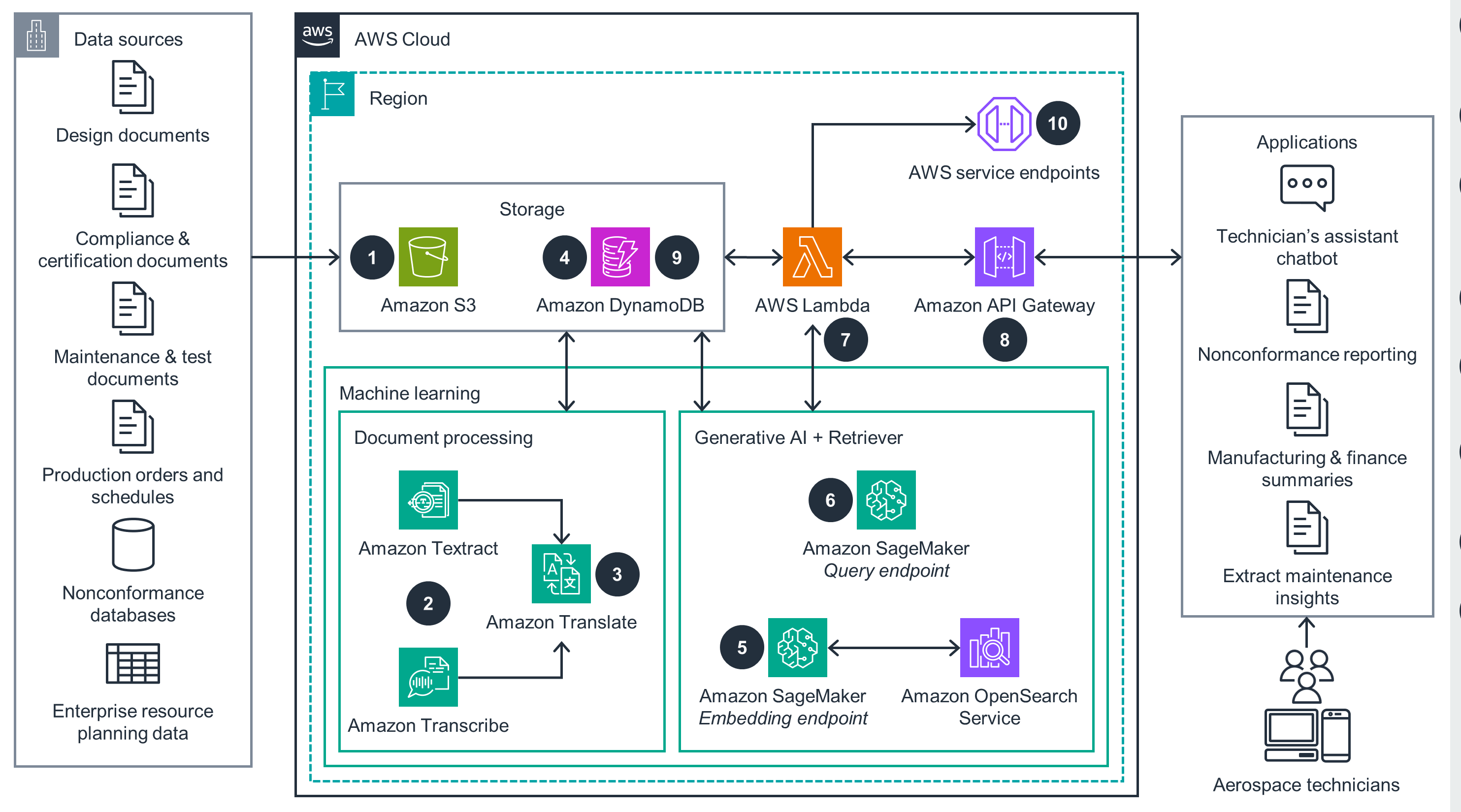
Amazon SageMaker
This architecture diagram shows how to use Amazon SageMaker to enable natural language searching of paper documents.
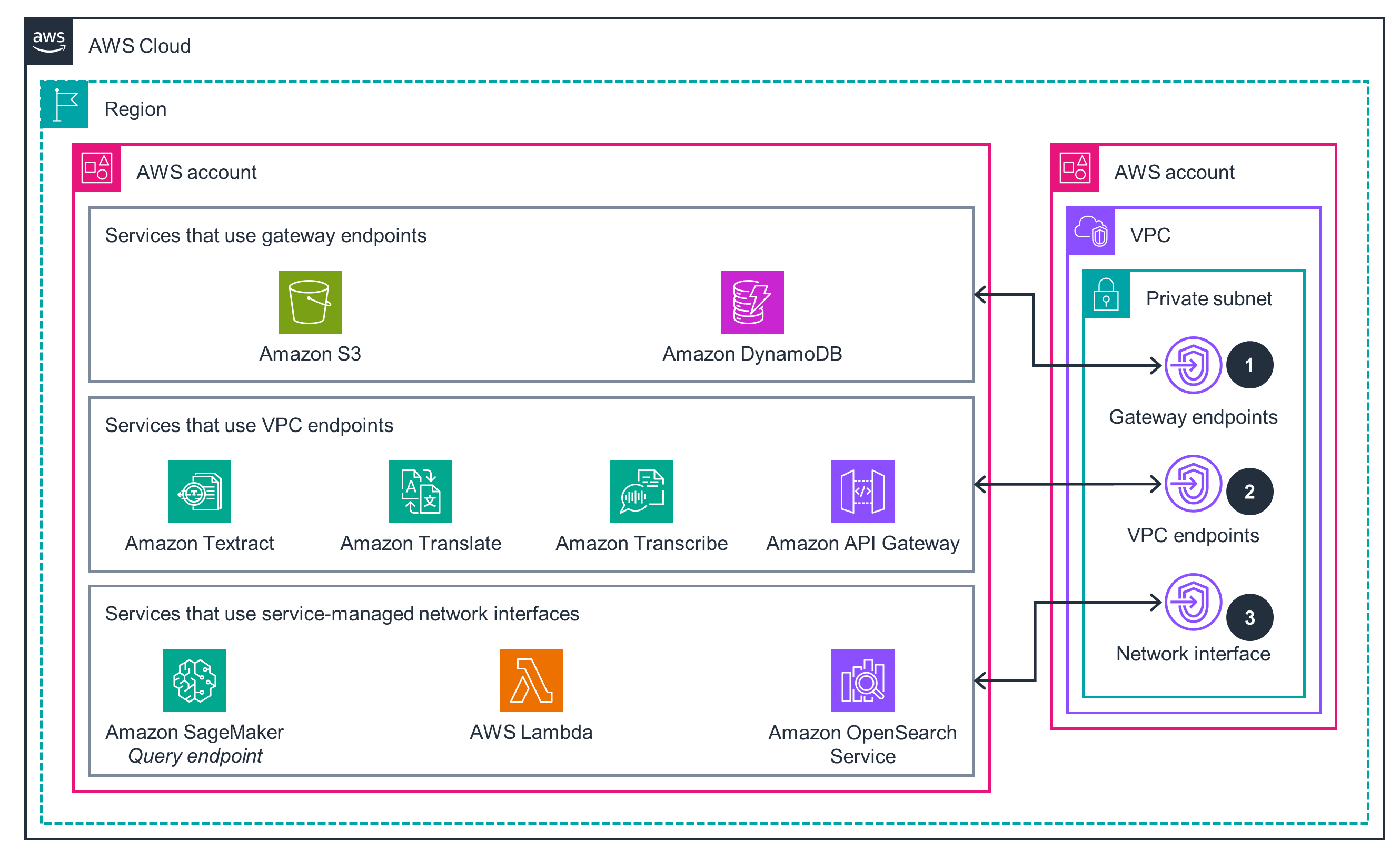
VPC Networking
This architecture diagram shows how to enable VPC networking for services used in generative AI solutions.
Get Started
Try out this Guidance
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
Lambda, API Gateway, and DynamoDB generate Amazon CloudWatch log files that track operational steps for ingesting new documents into the knowledge base. CloudWatch also tracks interactions for web-based user chat sessions, constructing prompts, and invoking generative AI models. Logging at every stage of the processing pipeline is essential for identifying errors and maintaining the availability and performance of the chatbot, and you can use these log files (as well as other integrated tools, like AWS X-Ray) to trace implementation errors to resolve problems. DynamoDB tables also track individual user chat history and the state of document ingestion. You can use these tables (along with point-in-time recovery) to re-create an error state. This Guidance provides a direct mechanism for user feedback on each technical response generated so that it can regularly tune the model and provide strategies for meeting your business objectives.
Amazon VPC provides a virtual network that logically isolates all its resources, and only authorized users and services have access to the resources in this Guidance. This Guidance deploys Lambda, OpenSearch Service, and SageMaker to a VPC and uses VPC endpoints so that these services can securely communicate with functions managed by AWS (like API Gateway) without traversing the public internet. SageMaker, Amazon Bedrock, and Amazon Q Business store LLM chat history; the associated data stay in your private account and never feed into public LLM repositories. Guardrails for Amazon Bedrock also prevent the LLM from displaying any unauthorized or inappropriate content.
Amazon S3 lets you store technical knowledge base documents with extremely high durability. DynamoDB provides native backup, restoration, and point-in-time recovery so that you can quickly restore operations in the event of a disruption. All these services are fully managed by AWS for high reliability and availability; for example, DynamoDB automatically creates three replicas of all tables in separate Availability Zones.
Amazon Bedrock, Amazon Q, Lambda, and DynamoDB are all fully managed services, so you don’t need to select instance types or manage scaling. Additionally, they are all serverless, so they automatically scale capacity to match demand. These services host the LLM, implement workflows through agents, manage the knowledge base, and store the document metadata and chat history. Additionally, Lambda enables a high degree of concurrency, so the technician’s assistant can support a large number of simultaneous users.
By using Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering, you can tailor your document storage retention policies. For example, you can automatically move infrequently accessed documents to lower-cost tiers like Amazon S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval. DynamoDB supports a time-to-live (TTL) feature that automatically deletes old entries (such as expired chat histories) from your table so that they don’t consume write bandwidth. By using these services and features, you can minimize the recurring costs of storage for your knowledge base. All the computational services use a pay-as-you-go model, and that cost directly scales with your usage of the technician’s assistant chatbot; as a result, you can save by not overprovisioning capacity.
Amazon S3, DynamoDB, Amazon Q, Amazon Bedrock, and Lambda are fully managed services that automatically scale their allocation of resources based on demand. Additionally, Amazon S3 supports S3 Intelligent-Tiering policies, and DynamoDB supports a TTL feature. You can use these options to automatically delete unused data (such as documents or session histories) to minimize your storage, subsequently lowering your carbon footprint. Additionally, this Guidance scales computational resources based on demand, helping you avoid energy waste.
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages