- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Event-Driven Media Workflow Automation on AWS
Guidance for Event-Driven Media Workflow Automation on AWS
Overview
How it works
Overview
This diagram gives an overview of how to integrate event-driven third-party partner services and applications into your AWS account. The subsequent tabs show how to integrate this Guidance with various third-party events.
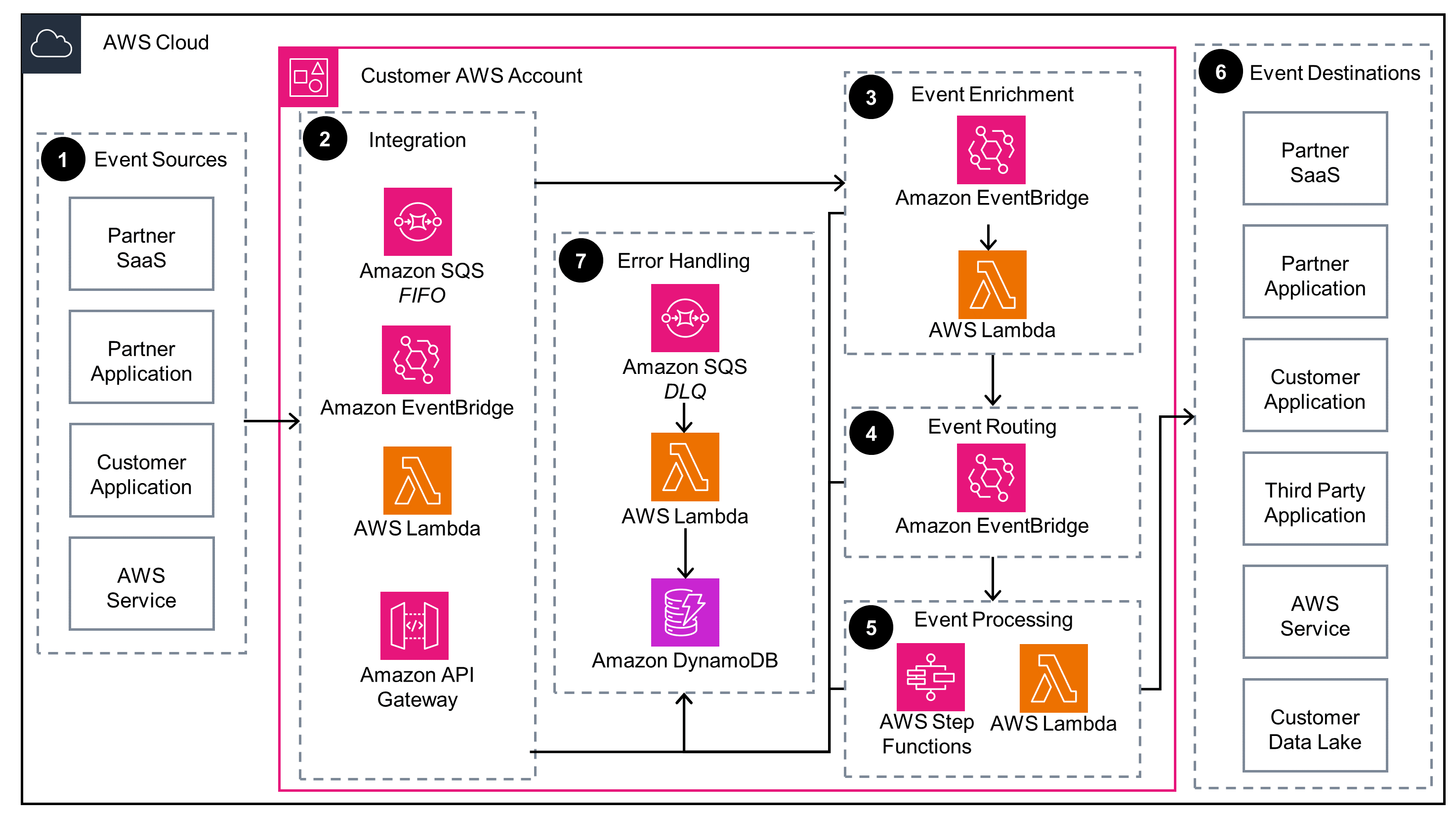
Amazon SNS FIFO event to Amazon SQS FIFO
This diagram shows how to integrate third-party events that are produced from an Amazon EventBridge third-party event source and delivered to an EventBridge Event Bus in your AWS account.
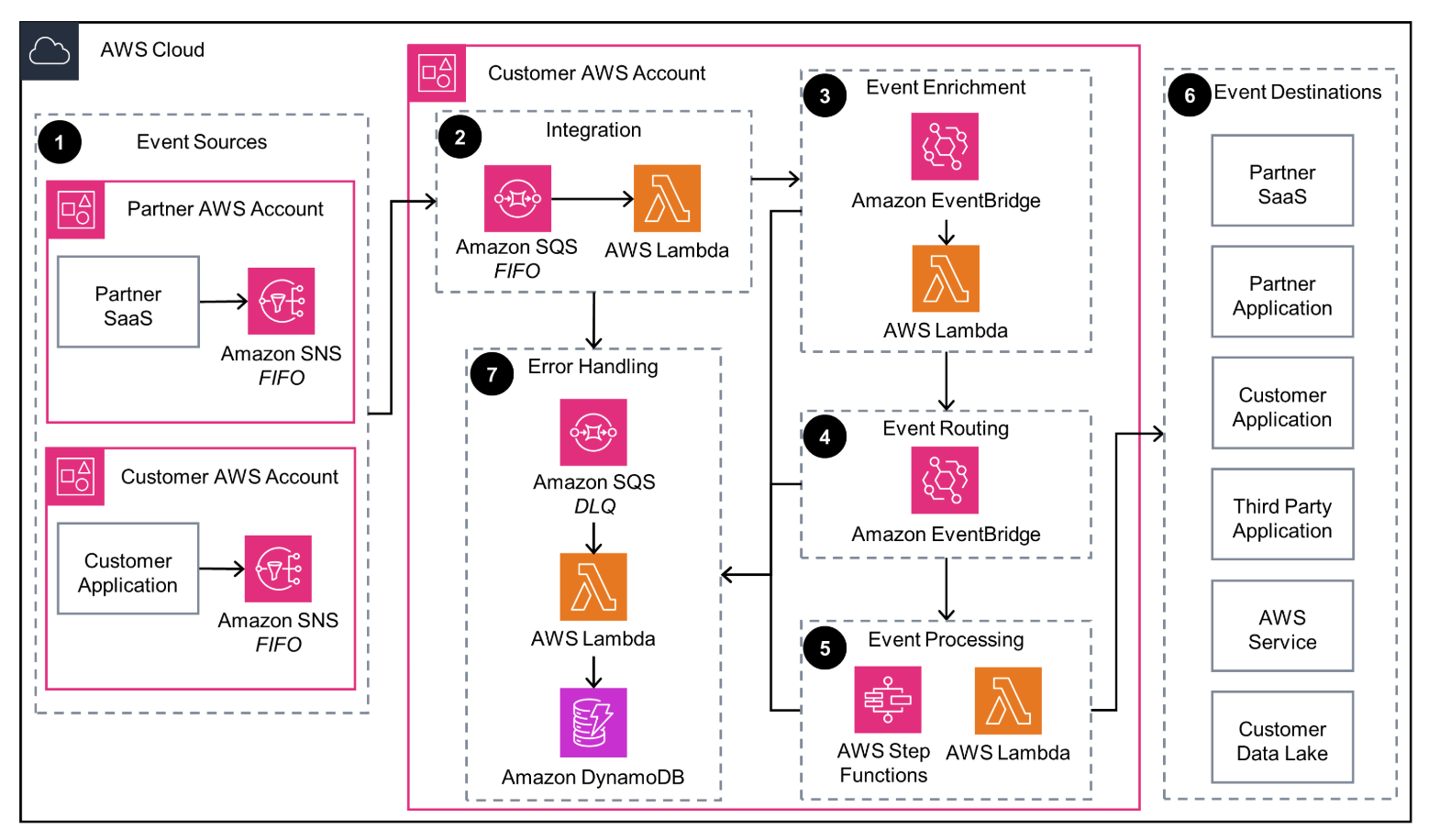
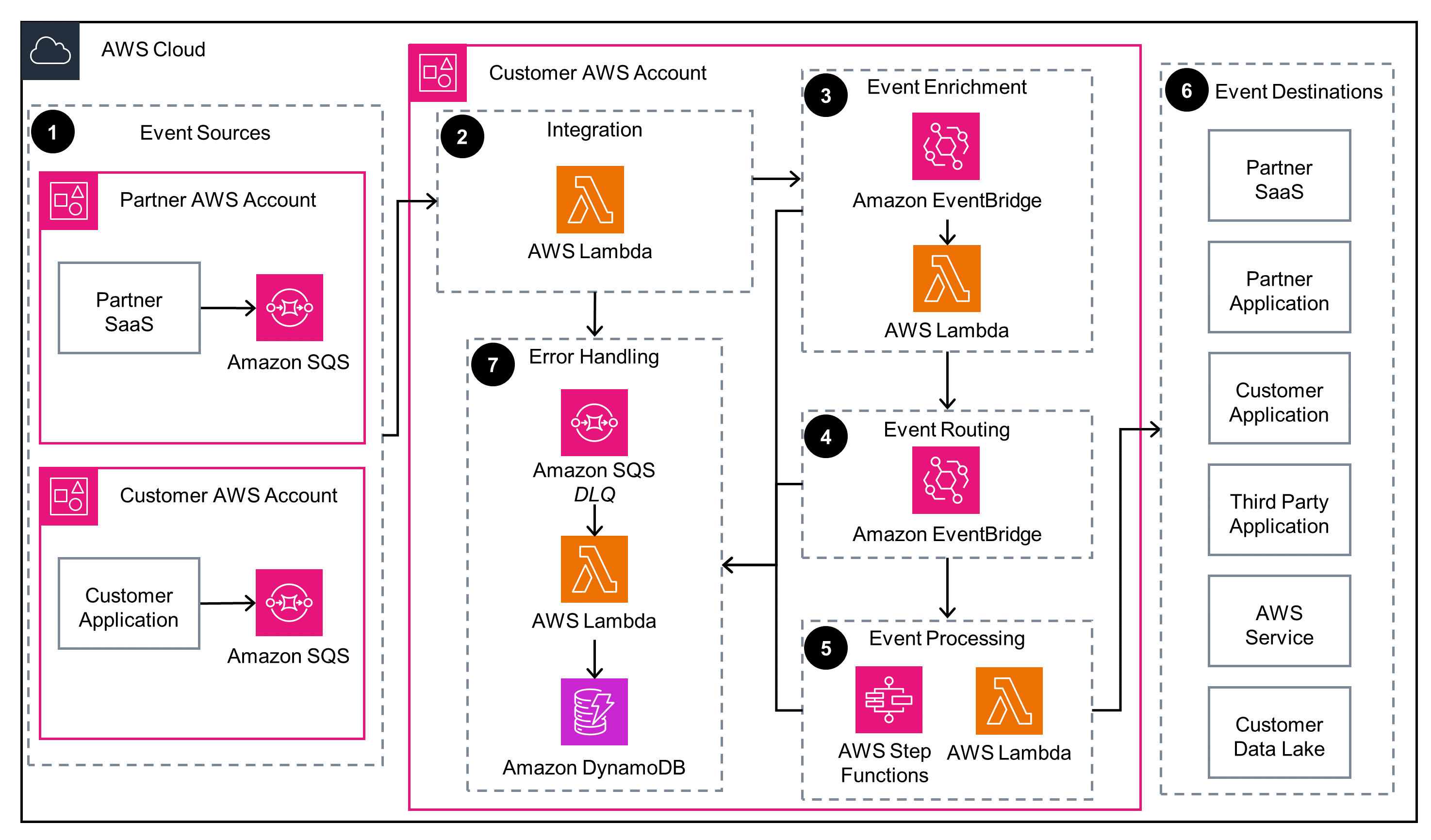
Amazon EventBridge Event Bus SaaS Integration
This diagram shows how to integrate third-party events that are produced from an Amazon EventBridge third-party event source and delivered to an EventBridge Event Bus in your AWS account.
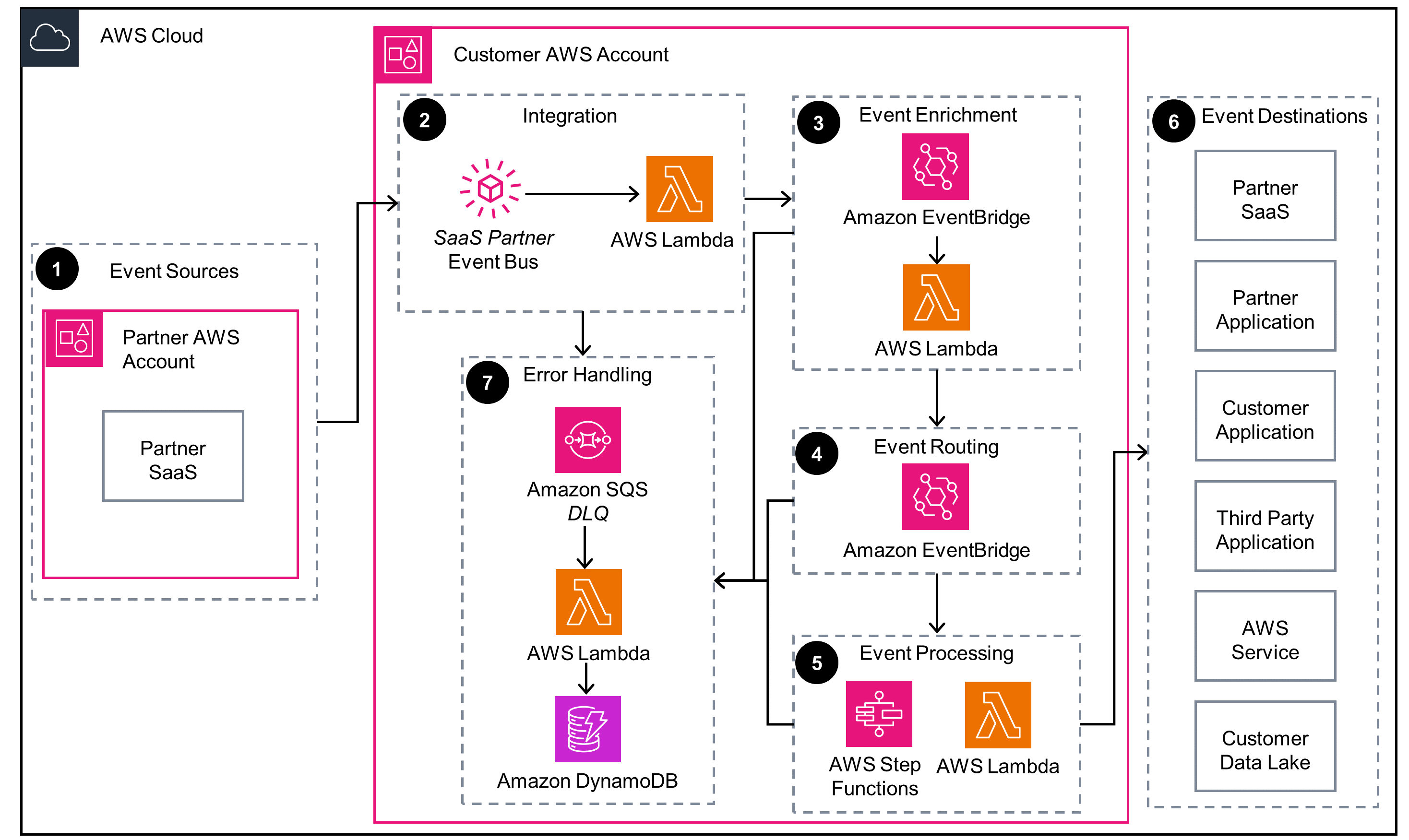
How it works (continued)
Amazon EventBridge Custom Event Bus Integration
This diagram shows how to integrate partner events that are produced from a partner’s Software as a Service (SaaS) or your application. The events are delivered to an Amazon EventBridge custom event bus in your AWS account.
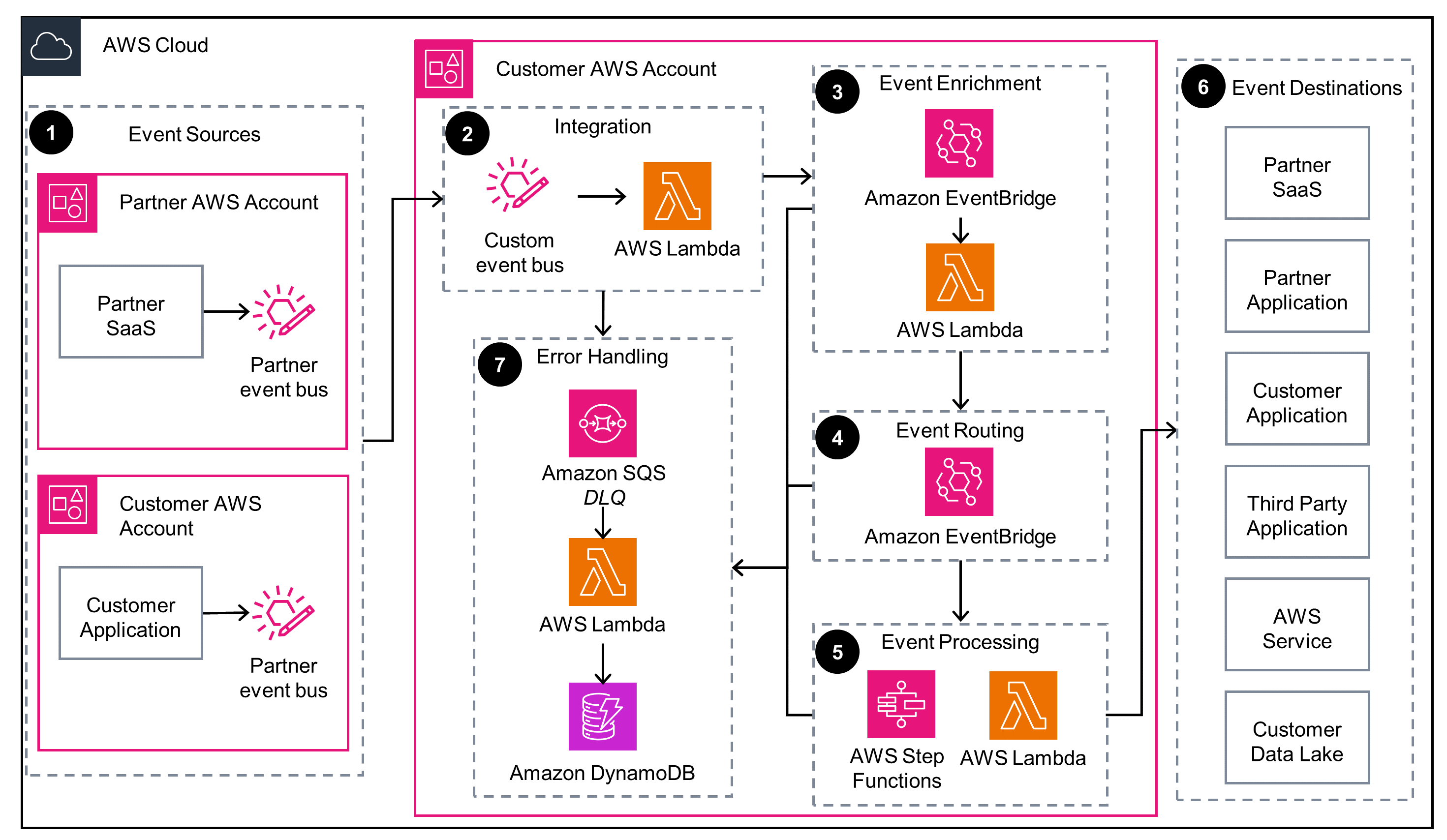
Amazon SQS to AWS Lambda Integration
This diagram shows how to integrate partner events that are produced by an Amazon SQS queue with an AWS Lambda function in your AWS account.
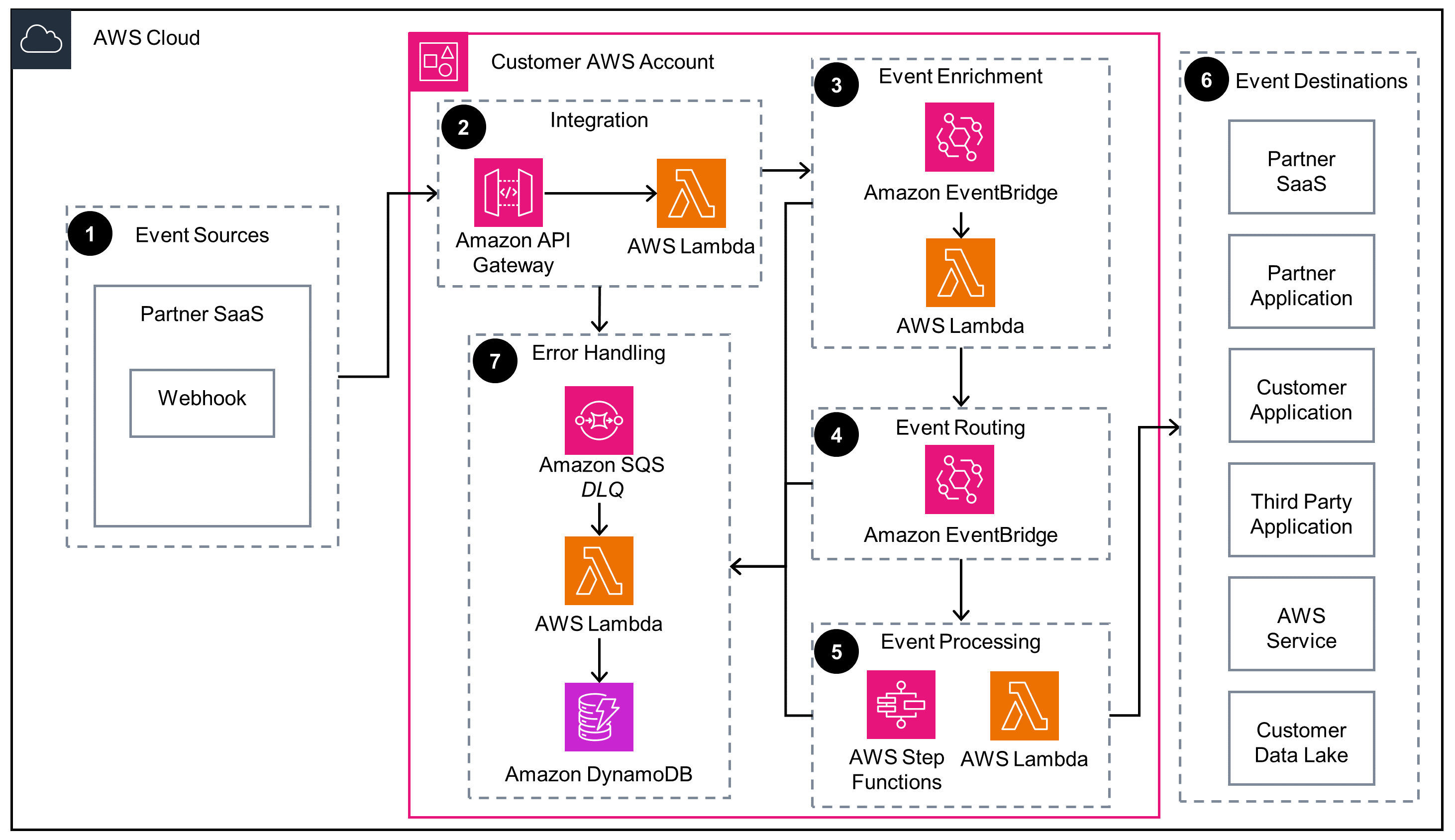
Partner Webhook Integration
This diagram shows how to integrate partner events produced by a partner webhook with an Amazon API Gateway endpoint.
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
This Guidance uses services managed by AWS like Amazon SQS , Lambda , API Gateway , EventBridge , Step Functions , and DynamoDB to enhance operational excellence. These services operate at the Regional level, utilizing multiple Availability Zones for high availability and fault tolerance. Built-in error handling and dead-letter queues provide visibility into failures, enabling timely detection and mitigation. The serverless nature of these services simplifies operations and reduces operational overhead.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), Lambda , API Gateway , Amazon SQS , and DynamoDB contribute to a secure architecture. IAM enables granular access control and least-privilege access to resources. API Gateway authorizes inbound API requests, while Amazon SQS queue policies manage queue access. DynamoDB encrypts data at rest using keys managed by AWS.
EventBridge automatically retries failed event deliveries and sends unprocessed events to a dead-letter queue. Lambda functions can be configured to send failed events to an Amazon SQS dead-letter queue for further analysis and processing. This fault tolerance and error handling ensure reliable event processing and prevent data loss.
The event-driven microservices architecture, built with serverless services like Lambda , Amazon SQS , and EventBridge , automatically scales based on demand, ensuring optimal resource utilization. Furthermore, DynamoDB allows for decoupled storage, scaling throughput and capacity independently to meet performance requirements.
This Guidance optimizes costs through the effective use of AWS services that follow a pay-as-you-go pricing model, charging only for the resources consumed during event processing. For example, the serverless nature of Lambda enables right-sizing compute resources to match workload demands, preventing over-provisioning. Amazon SQS and Amazon SNS minimize data transfer costs by efficiently routing and delivering events. DynamoDB offers cost-effective storage and granular capacity provisioning, allowing independent scaling of throughput and storage based on requirements.
EventBridge , Lambda , API Gateway , Amazon SQS , and Amazon SNS contribute to sustainability by minimizing inactive resource usage. These serverless services are active only when processing events, reducing energy consumption and your infrastructure footprint. The event-driven microservices architecture with Lambda further optimizes resource utilization by running only the necessary code, minimizing the overall environmental impact.
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages