- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Scheduling Batch Jobs for AWS Mainframe Modernization
Guidance for Scheduling Batch Jobs for AWS Mainframe Modernization
Overview
This Guidance demonstrates how to build a simple scheduler for batch jobs migrated to AWS Mainframe Modernization using AWS services such as Amazon EventBridge scheduler and AWS Step Functions. Batch processing is an important component of enterprise applications running on mainframe, and as these batch processes are migrated from mainframe to AWS, they require similar integration between batch processing and scheduling functions. This scheduler pattern can be used for both re-platform migrations, with Common Business Oriented Language (COBOL) or PL1 applications, and re-factor migrations, with the COBOL/PL1 code converted to Java.
This Guidance includes two architectures to show how Amazon EventBridge initiates the AWS Step Functions workflow for a single batch job and an orchestration with multiple batch jobs.
How it works
Single run
This architecture shows the AWS Step Functions workflow for BatchJobExecution for a single batch job.

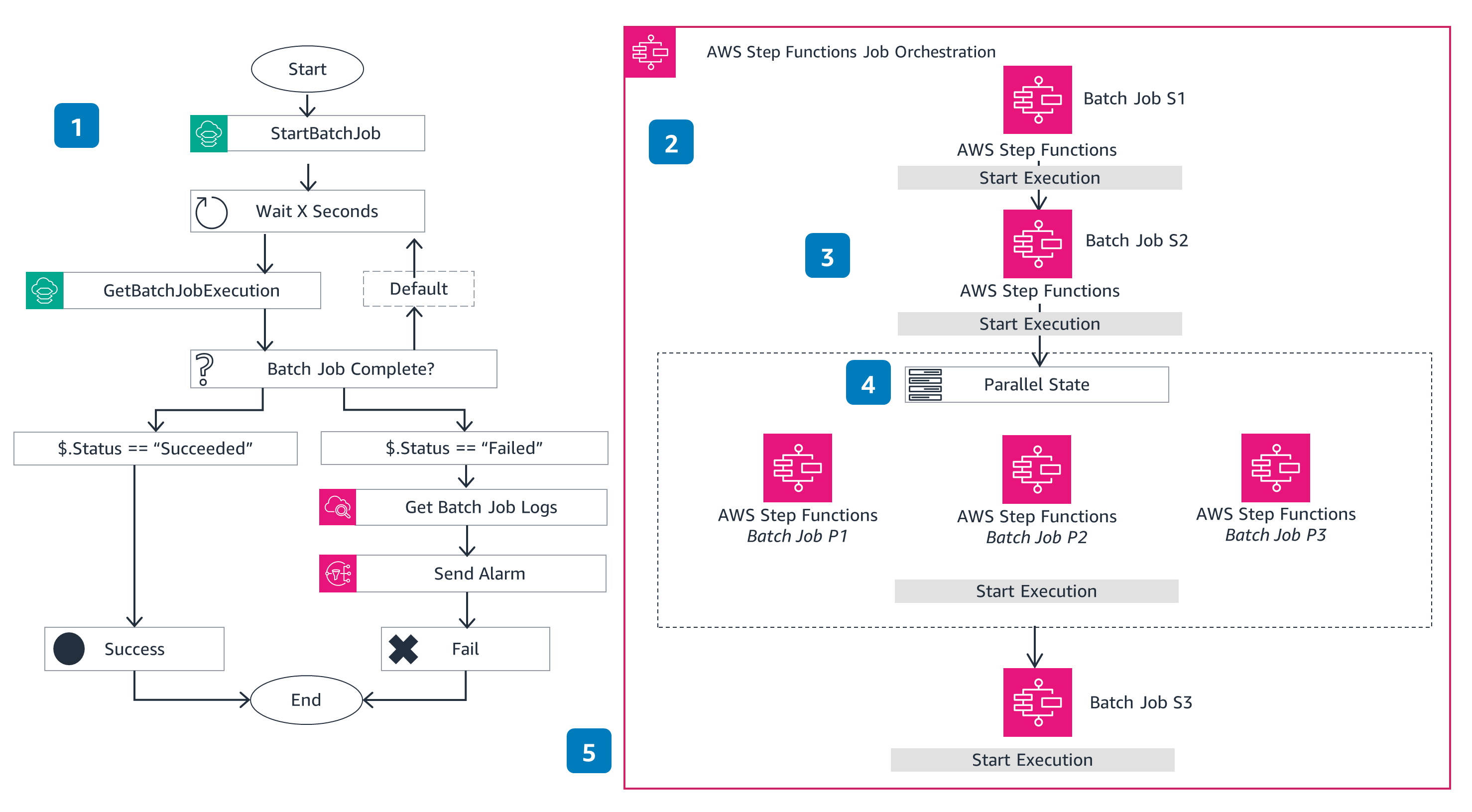
Batch run
This architecture shows the AWS Step Functions workflow for JobOrchestration for multiple batch jobs.
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
EventBridge and Step Functions integrate with CloudWatch alarms. In case of an AWS Mainframe Modernization batch job failure or any other type of failure, Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) can send alerts to the user.
IAM policies manage user access, providing minimum permissions for users to create new schedules or modify existing schedules. The IAM execution role controls service access for services that invoke a batch job on AWS Mainframe Modernization.
Step Functions comes with retry and catch mechanisms, which allow you to implement automated retries of a particular batch job.
Scheduling batch job flows is mostly pre-defined. This Guidance is built on serverless technologies such as EventBridge and Step Functions, so there is no need to provision new hardware or software to set up additional jobs. You can schedule new jobs can by defining additional Step Functions and setting up triggers from EventBridge.
Step Functions cost is based on the number of state transitions only. Because Step Functions is serverless, costs will be based on usage instead scheduler instances that are continuously running. There is no separate cost for hardware or software. Additionally, AWS Free Tier offers 4,000 Step Functions state transitions.
EventBridge scheduler invokes Step Functions only when it is scheduled to run. Further, the underlying hardware and software component are only provisioned when Step Functions is invoked. This helps you keep resource utilization to a minimum.
Implementation Resources
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages