Create and Connect to a MySQL Database with Amazon RDS
Introduction
Implementation
Create a MySQL DB instance
In this step, we will use Amazon RDS to create a MySQL DB Instance with db.t2.micro DB instance class, 20 GB of storage, and automated backups enabled with a retention period of one day.
1. Open the AWS Management Console
Open the AWS Management Console in a new browser window, so you can keep this step-by-step guide open. When the console opens, select Database from the left navigation pane and choose RDS to open the Amazon RDS console.

2. Select Region
In the top right corner of the Amazon RDS console, select the Region in which you want to create the DB instance.
Note: AWS Cloud resources are housed in highly available data center facilities in different areas of the world. Each Region contains multiple distinct locations called Availability Zones. You have the ability to choose which Region to host your Amazon RDS activity in.

3. Create database
In the Create database section, choose Create database.

4. Select database engine
You now have options to select your engine. For this tutorial, choose the MySQL icon, leave the default value of edition and engine version, and select the Free Tier template.
Multi-AZ deployment: Note that you will have to pay for Multi-AZ deployment. Using a Multi-AZ deployment will automatically provision and maintain a synchronous standby replica in a different Availability Zone. For more information, see High Availability Deployment.

5. Configure DB instance
You will now configure your DB instance. The list below shows the example settings you can use for this tutorial:
Settings:
DB instance identifier: Type a name for the DB instance that is unique for your account in the Region that you selected. For this tutorial, we will name it rds-mysql-10minTutorial.
Master username: Type a username that you will use to log in to your DB instance. We will use masterUsername in this example.
Master password: Type a password that contains from 8 to 41 printable ASCII characters (excluding /,", and @) for your master user password.
Confirm password: Retype your password

6. Additional DB instance configuration
Instance specifications:
DB instance class: Select db.t2.micro — 1vCPU, 1 GiB RAM. This equates to 1 GB memory and 1 vCPU. To see a list of supported instance classes, see Amazon RDS Pricing.
Storage type: Select General Purpose (SSD). For more information about storage, see Storage for Amazon RDS.
Allocated storage: Select the default of 20 to allocate 20 GB of storage for your database. You can scale up to a maximum of 64 TB with Amazon RDS for MySQL.
Enable storage autoscaling: If your workload is cyclical or unpredictable, you would enable storage autoscaling to enable Amazon RDS to automatically scale up your storage when needed. This option does not apply to this tutorial.
Multi-AZ deployment: Note that you will have to pay for Multi-AZ deployment. Using a Multi-AZ deployment will automatically provision and maintain a synchronous standby replica in a different Availability Zone. For more information, see High Availability Deployment.

7. Configure connectivity
You are now in the Connectivity section where you can provide information that Amazon RDS needs to launch your MySQL DB instance. The following list shows settings for our example DB instance.
Connectivity
Compute resource: Choose Don’t connect to an EC2 compute resource. You can manually set up a connection to a compute resource later.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Select Default VPC. For more information about VPC, see Amazon RDS and Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC).
Additional connectivity configurations
Subnet group: Choose the default subnet group. For more information about subnet groups, see Working with DB Subnet Groups.
Public accessibility: Choose Yes. This will allocate an IP address for your database instance so that you can directly connect to the database from your own device. Note: You will incur charges of $0.005 per hour.
VPC security groups: Select Create new VPC security group. This will create a security group that will allow connection from the IP address of the device that you are currently using to the database created.
Availability Zone: Choose No preference. See Regions and Availability Zones for more details.
RDS Proxy: By using Amazon RDS Proxy, you can allow your applications to pool and share database connections to improve their ability to scale. Leave the RDS Proxy unchecked.
Port: Leave the default value of 3306.

8. Choose authentication option
Amazon RDS supports several ways to authenticate database users. Choose Password authentication from the list of options

9. Verify monitoring
Leave Enable enhanced monitoring unchecked to stay within the Free Tier. Enabling enhanced monitoring will give you metrics in real time for the operating system (OS) that your DB instance runs on. For more information, see Viewing DB Instance Metrics.

10. Set additional configuration options
In the Additional configurations section:
Database options
Database name: Enter a database name that is 1 to 64 alphanumeric characters. If you do not provide a name, Amazon RDS will not automatically create a database on the DB instance you are creating.
DB parameter group: Leave the default value. For more information, see Working with DB Parameter Groups.
Option group: Leave the default value. Amazon RDS uses option groups to enable and configure additional features. For more information, see Working with Option Groups.
Encryption: This option is not available in the Free Tier. For more information, see Encrypting Amazon RDS Resources.
Backup
Backup retention period: You can choose the number of days to retain the backup you take. For this tutorial, set this value to 1 day.
Backup window: Use the default of No preference.
Maintenance
Auto minor version upgrade: Select Enable auto minor version upgrade to receive automatic updates when they become available.
Maintenance Window: Select No preference.
Deletion protection: Turn off Enable deletion protection for this tutorial. When this option is enabled, you're prevented from accidentally deleting the database.
Choose Create Database.

Download a SQL client
Once the database instance creation is complete and the status changes to available, you can connect to a database on the DB instance using any standard SQL client. In this step, we will download MySQL Workbench, which is a popular SQL client.
1. Install MySQL Workbench
Go to the Download MySQL Workbench page to download and install MySQL Workbench. For more information on using MySQL, see the MySQL Documentation.
Note: Remember to run MySQL Workbench from the same device from which you created the DB instance. The security group your database is placed in is configured to allow connection only from the device from which you created the DB instance.

2. Download client
You will be prompted to log in, sign up, or begin your download. You can choose No thanks, just start my download for a quick download.

Connect to the MySQL database
In this step, we will connect to the database you created using MySQL Workbench.
1. Launch MySQL Workbench
Launch the MySQL Workbench application and go to Database > Connect to Database (Ctrl+U) from the menu bar.

2. Specify connection options
A dialog box appears. Enter the following:
Hostname: You can find your hostname on the Amazon RDS console as shown in the screenshot.
Port: The default value should be 3306.
Username: Type in the username you created for the Amazon RDS database. In this tutorial, it is 'masterUsername.'
Password: Choose Store in Vault (or Store in Keychain on MacOS) and enter the password that you used when creating the Amazon RDS database.
Choose OK.

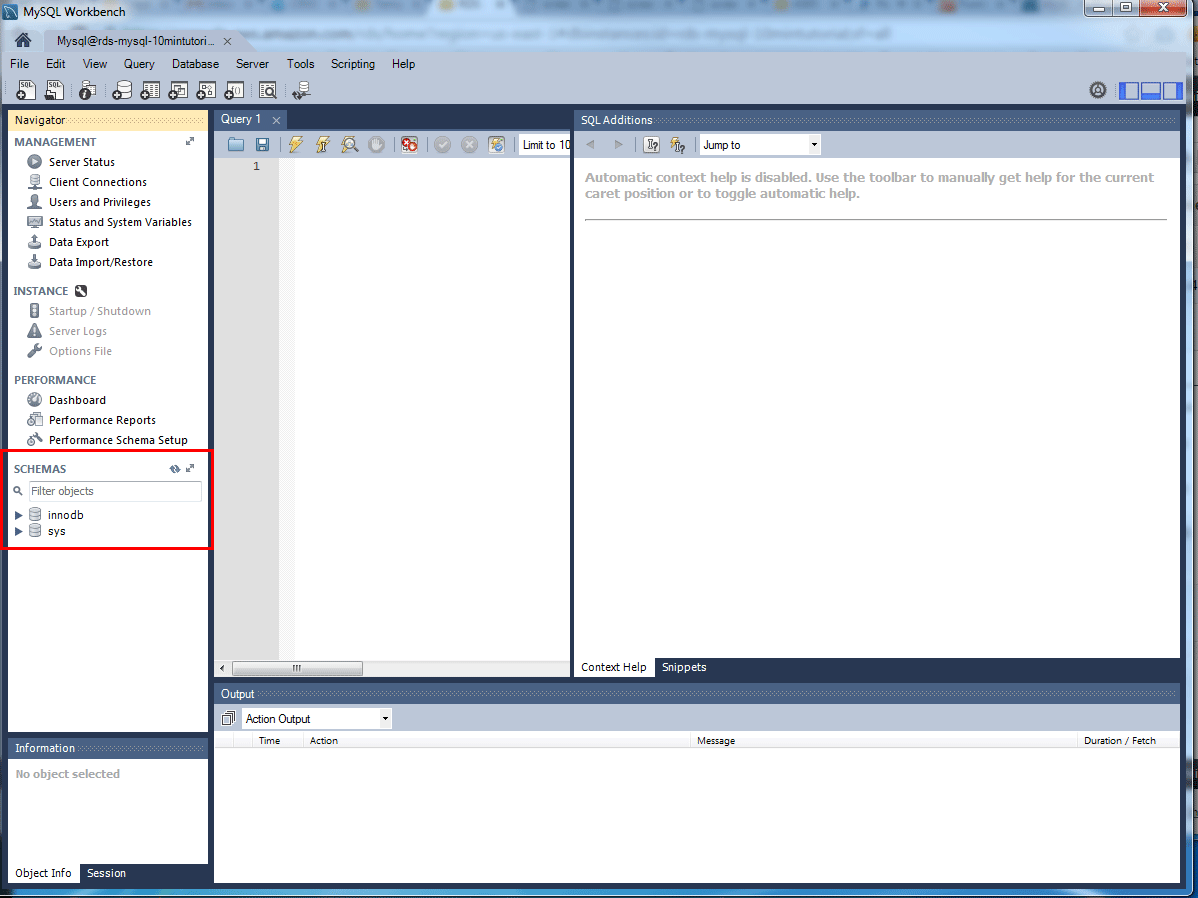
3. Verify database connection
You are now connected to the database! On the MySQL Workbench, you will see various schema objects available in the database. Now you can create tables, insert data, and run queries.
Delete the DB instance
You can easily delete the MySQL DB instance from the Amazon RDS console. It is a best practice to delete instances that you are no longer using so that you don’t keep getting charged for them.
1. Choose the DB instance
Go back to the Amazon RDS console. Select Databases, choose the instance that you want to delete, and then select Delete from the Actions dropdown menu.

2. Confirm instance deletion
You are asked to create a final snapshot and to confirm the deletion. For our example, do not create a final snapshot, acknowledge that you want to delete the instance, and then choose Delete.
Note: Deleting your DB instance may take a few minutes

Congratulations!
You have created, connected to, and deleted a MySQL database instance with Amazon RDS. Amazon RDS makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud. It provides cost-efficient and resizable capacity while managing time-consuming database administration tasks, freeing you up to focus on your applications and business.
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages