Overview
This Guidance demonstrates how to architect a resilient, multi-Region application using AWS services, such as Amazon DynamoDB global tables. It illustrates best practices for detecting and responding to Region-scoped outages, providing high availability and minimizing downtime for mission-critical applications. This Guidance helps you achieve application resiliency by dynamically routing traffic away from affected Regions and leveraging global data replication.
How it works
Primary
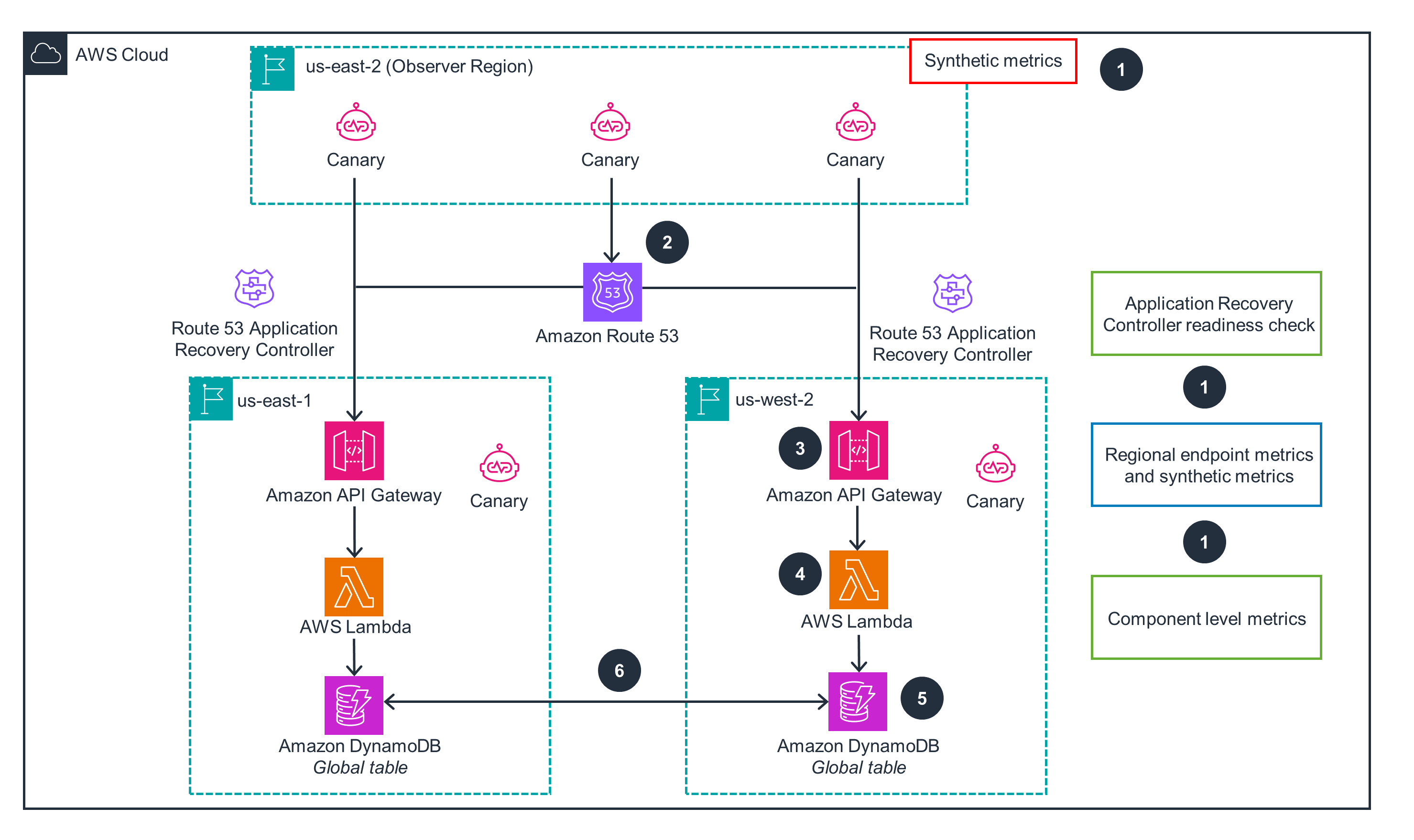
This architecture diagram shows how to set up and build a resilient, multi-Region application. For cross-Region failover and failback, open the other tab.
Cross-Region Failover and Failback
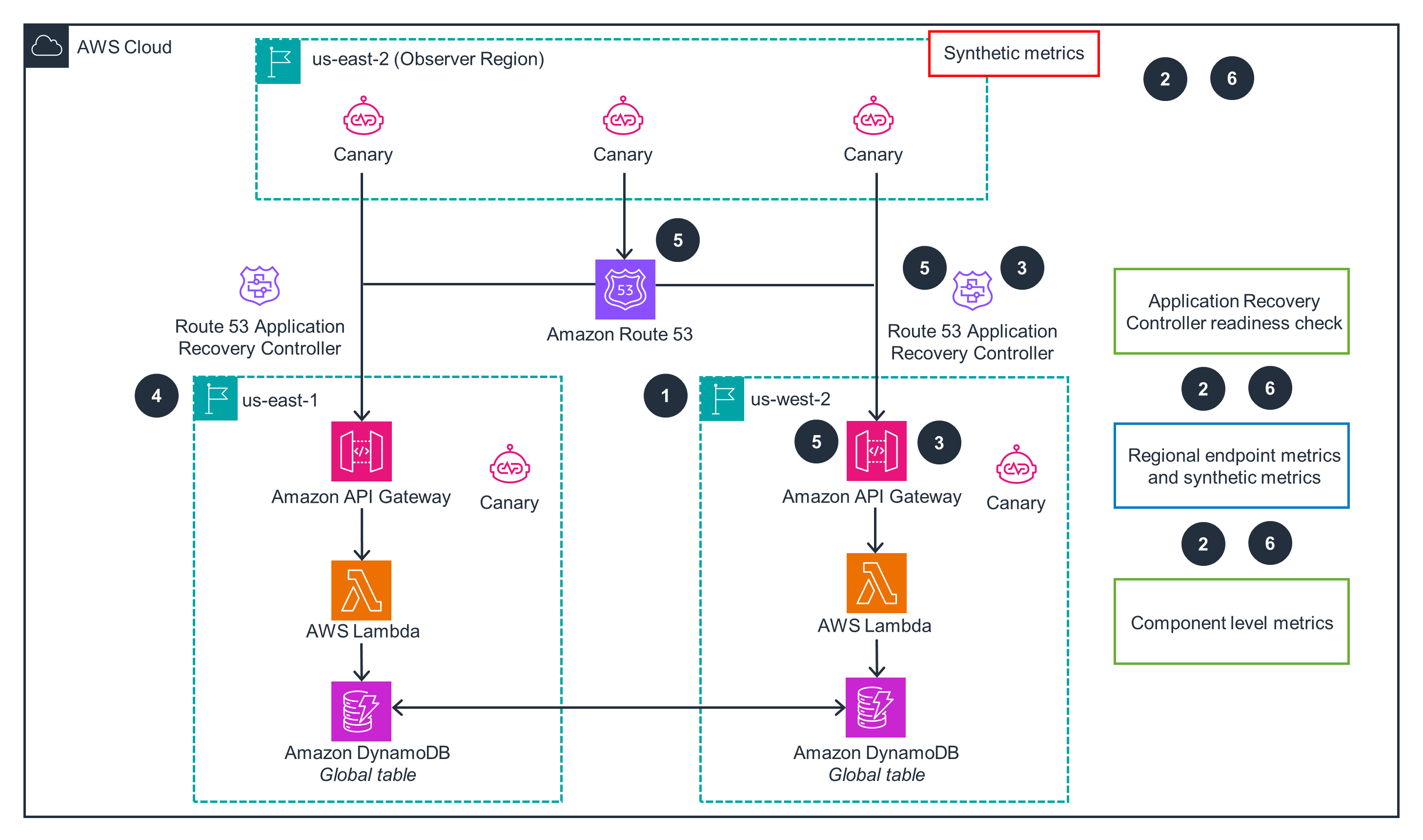
This architecture diagram shows how to perform cross-Region failover and failback in the event of an outage. For setup of the primary Region, open the other tab.
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
Deploy with confidence
Ready to deploy? Review the sample code on GitHub for detailed deployment instructions to deploy as-is or customize to fit your needs.
Related Content
Blog
Build resilient applications with Amazon DynamoDB global tables: Part 4
This blog post discusses the operational concerns for a multi-Region deployment, including observability, deployment pipelines, and runbooks.
Disclaimer
The sample code; software libraries; command line tools; proofs of concept; templates; or other related technology (including any of the foregoing that are provided by our personnel) is provided to you as AWS Content under the AWS Customer Agreement, or the relevant written agreement between you and AWS (whichever applies). You should not use this AWS Content in your production accounts, or on production or other critical data. You are responsible for testing, securing, and optimizing the AWS Content, such as sample code, as appropriate for production grade use based on your specific quality control practices and standards. Deploying AWS Content may incur AWS charges for creating or using AWS chargeable resources, such as running Amazon EC2 instances or using Amazon S3 storage.
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages