- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Trusted Secure Enclaves on AWS
Guidance for Trusted Secure Enclaves on AWS
Protect and isolate your highly sensitive workloads with a secure enclave
Overview
How it works
Overview
This architecture diagram shows how to configure comprehensive, multi-account workloads with unique security and compliance requirements.
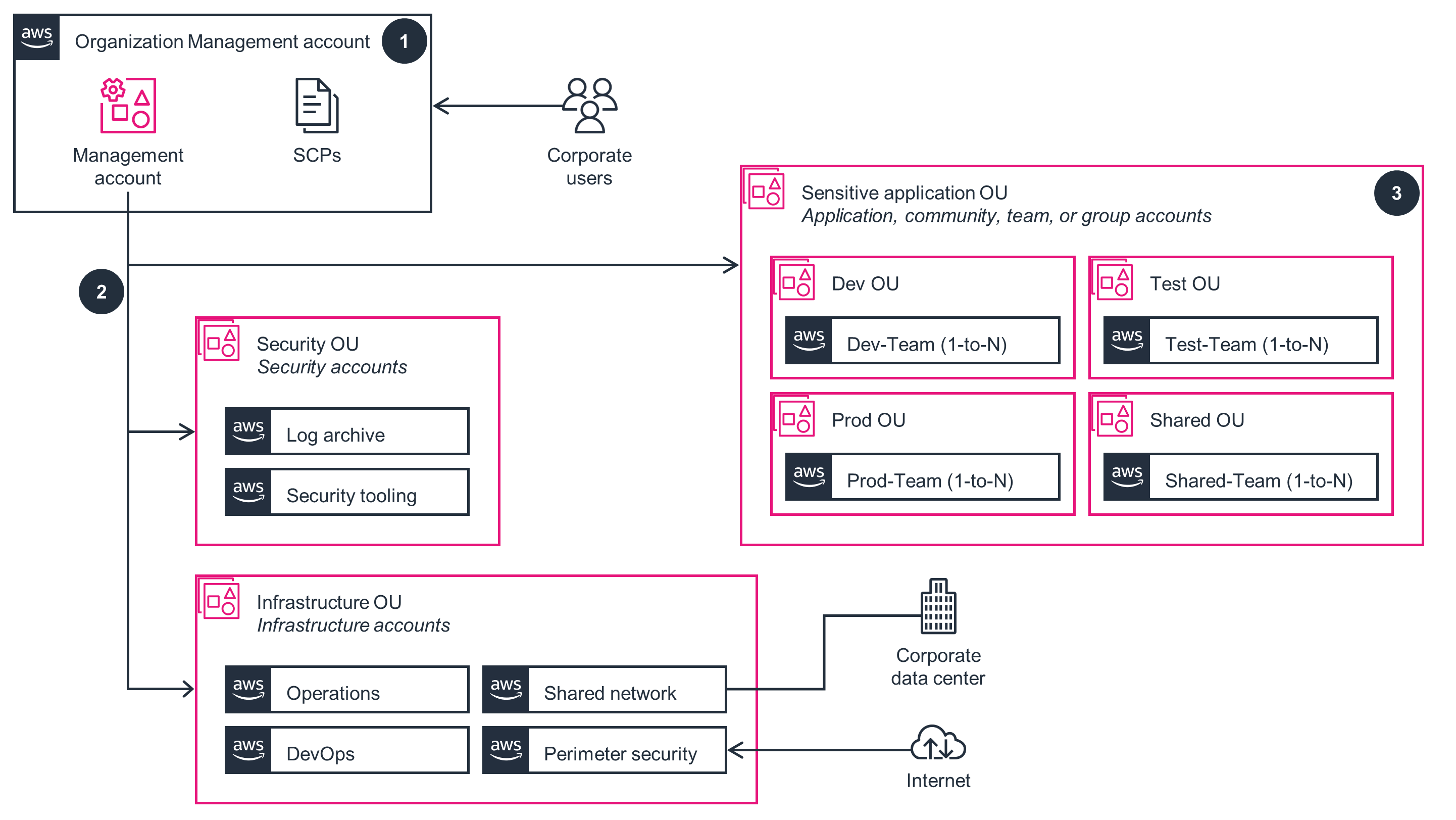
Organization Management Account
This architecture diagram shows how an organization can group multiple accounts, all controlled by a single customer entity. Follow the steps in this architecture diagram to deploy the Organization Management Account part of this Guidance.
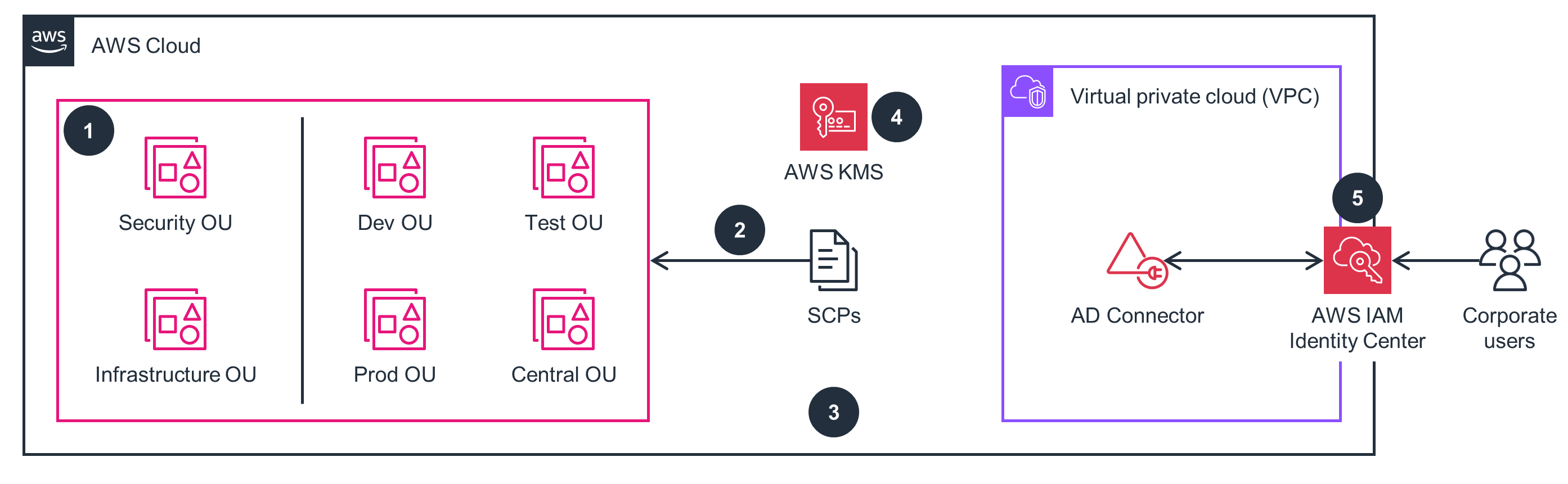
Security Accounts
This architecture diagram shows how to centrally configure a comprehensive log collection across AWS services and accounts. Follow the steps in this architecture diagram to deploy the Security Accounts part of this Guidance.

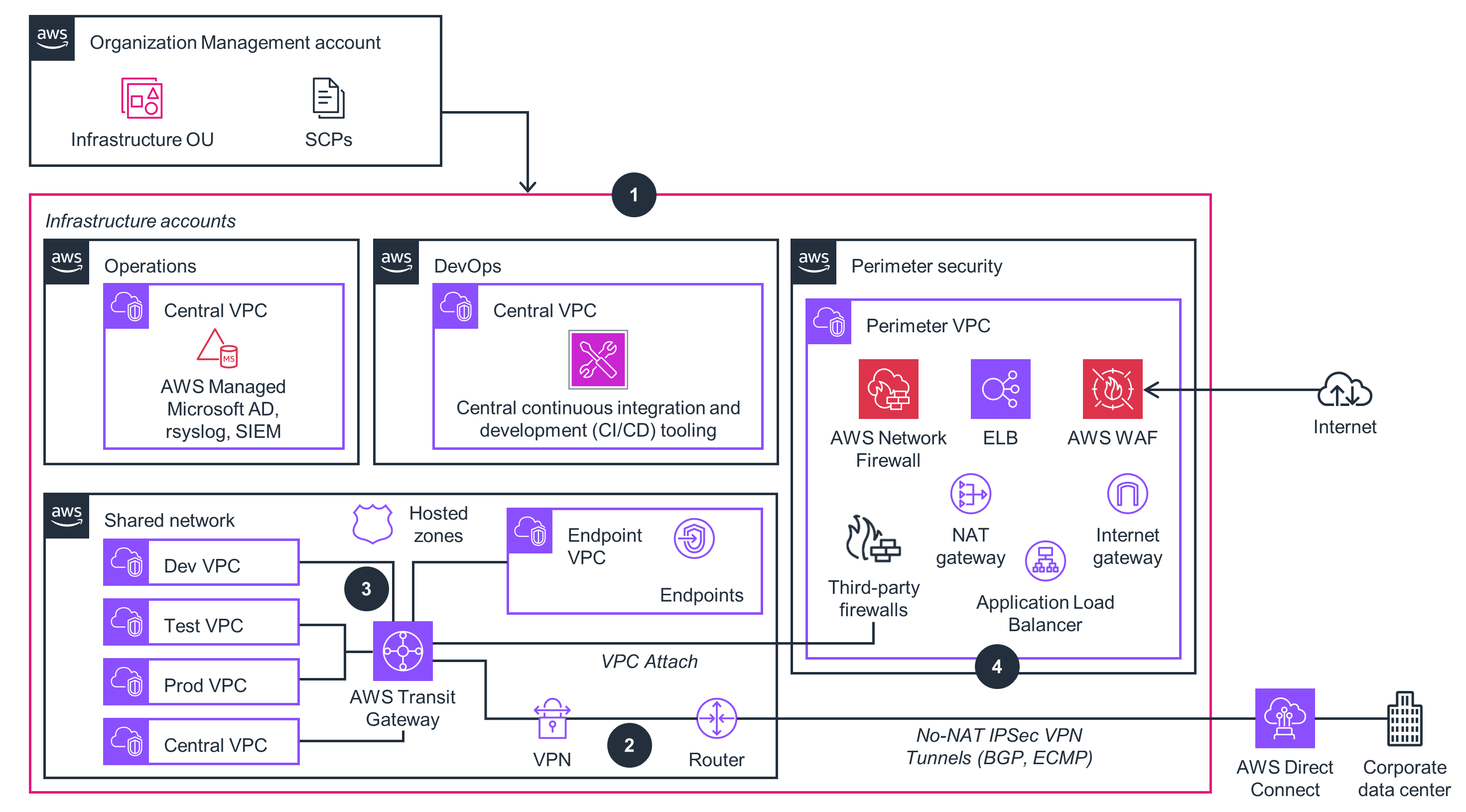
Infrastructure Accounts
This architecture diagram shows how a centralized, isolated networking environment is built with Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs). Follow the steps in this architecture diagram to deploy the Infrastructure Accounts part of this Guidance.
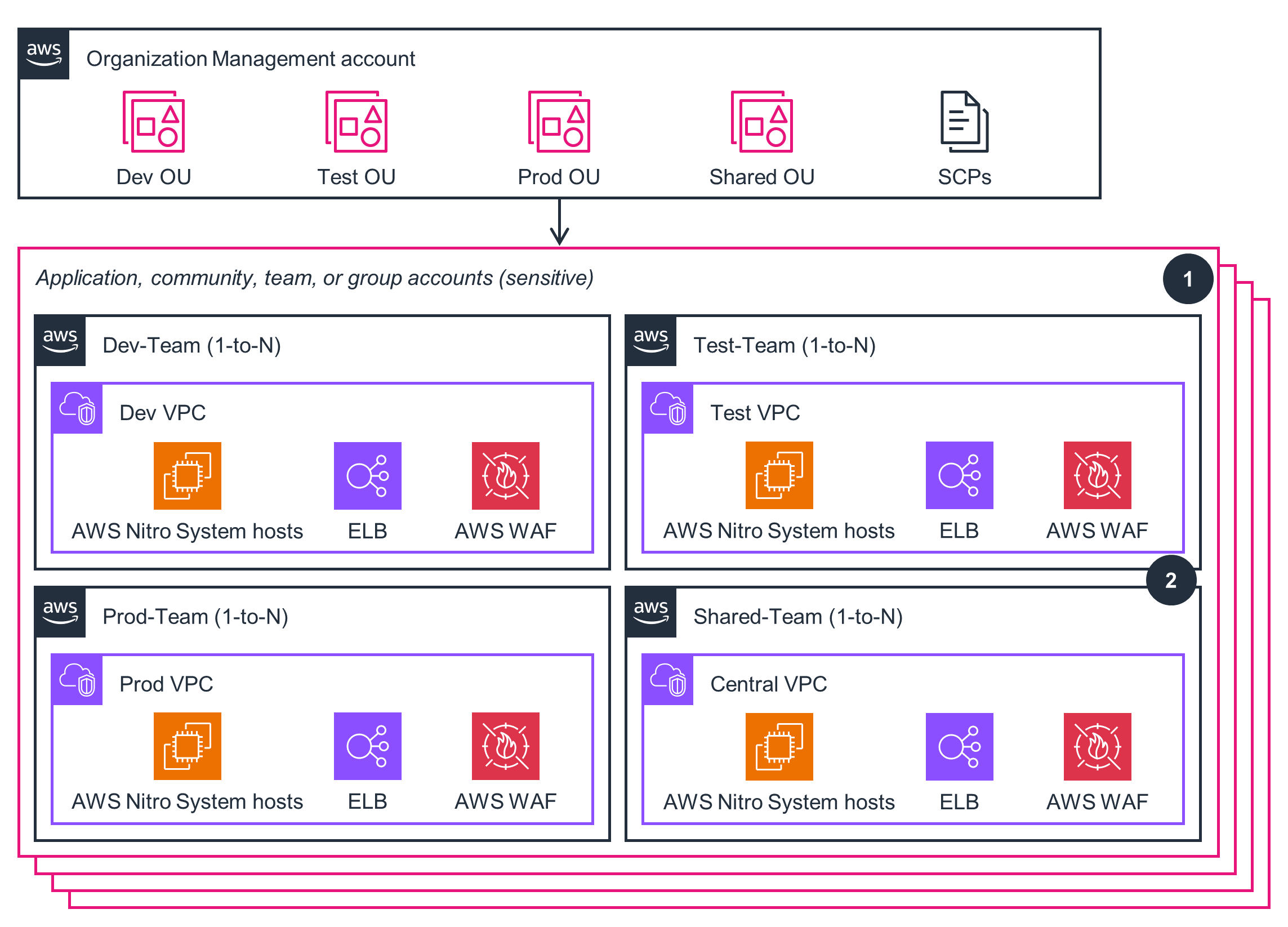
Application, Community, Team, or Group Accounts (Sensitive)
This architecture diagram shows how to configure segmentation and separation between workloads belonging to different stages of the software development lifecycle, or between different IT administrative roles. Follow the steps in this architecture diagram to deploy the Application, Community, Team, or Group Accounts part of this Guidance.
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
This Guidance uses Organizations with AWS CloudFormation stacks and configurations to create a secure foundation for your AWS environment. This provides an infrastructure-as-code (IaC) solution that accelerates your implementation of technical security controls. Config rules remediate any configuration deltas that have been determined to negatively impact the prescribed architecture. You can use the AWS global commercial infrastructure for sensitive classified workloads and automate secure systems to deliver missions faster while continually improving your processes and procedures.
This Guidance uses Organizations to facilitate the deployment of organizational guardrails, such as API logging with CloudTrail. This Guidance also provides preventative controls using prescriptive AWS SCPs as a guardrail mechanism, principally used to deny specific or entire categories of APIs within your environment (to make sure that workloads are deployed only in prescribed Regions) or deny access to specific AWS services. CloudTrail and CloudWatch logs support a prescribed comprehensive log collection and centralization across AWS services and accounts. AWS security capabilities and the multitude of security-relevant services are configured in a defined pattern that helps you meet some of the strictest security requirements in the world.
This Guidance uses multiple Availability Zones (AZs), so the loss of one AZ does not impact application availability. You can use CloudFormation to automate the provisioning and updating of your infrastructure in a safe and controlled manner. This Guidance also provides prebuilt rules for evaluating AWS resource configurations and configuration changes within your environment, or you can create custom rules in AWS Lambda to define best practices and guidelines. You can automate the ability to scale your environment to meet demand and mitigate disruptions such as misconfigurations or transient network issues.
This Guidance simplifies cloud infrastructure management by using Transit Gateway, which serves as a central hub that connects multiple VPCs through a single gateway, making it easier to scale and maintain the network architecture. This simplifies your network architecture and facilitates efficient traffic routing between different AWS accounts within your organization.
This Guidance provides the ability to avoid or remove unneeded costs or the use of suboptimal resources. Organizations provides centralization and consolidated billing, facilitating the strong separation of resource use and cost optimization. This Guidance prescribes moving AWS public API endpoints into your private VPC address space, using centralized endpoints for cost efficiency. Additionally, you can use AWS Cost and Usage Reports(AWS CUR) to track your AWS usage and estimate charges.
This Guidance helps you reduce the carbon footprint associated with managing workloads within your own datacenters. The AWS global infrastructure offers supporting infrastructure (such as power, cooling, and networking), a higher utilization rate, and faster technology refreshes than traditional data centers. Additionally, the segmentation and separation of workloads helps you reduce unnecessary data movement, and Amazon S3 offers storage tiers and the ability to automatically move data to efficient storage tiers.
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages