Amazon RDS Backup & Restore Using AWS Backup
Introduction
Implementation
1. Open the AWS Backup console
Log in to the AWS Management Console, and open the AWS Backup console.

Configure an on-demand AWS Backup job of an Amazon RDS database
2. Configure the services used with AWS Backup
On the navigation pane on the left side of the AWS Backup console, under My account, choose Settings.
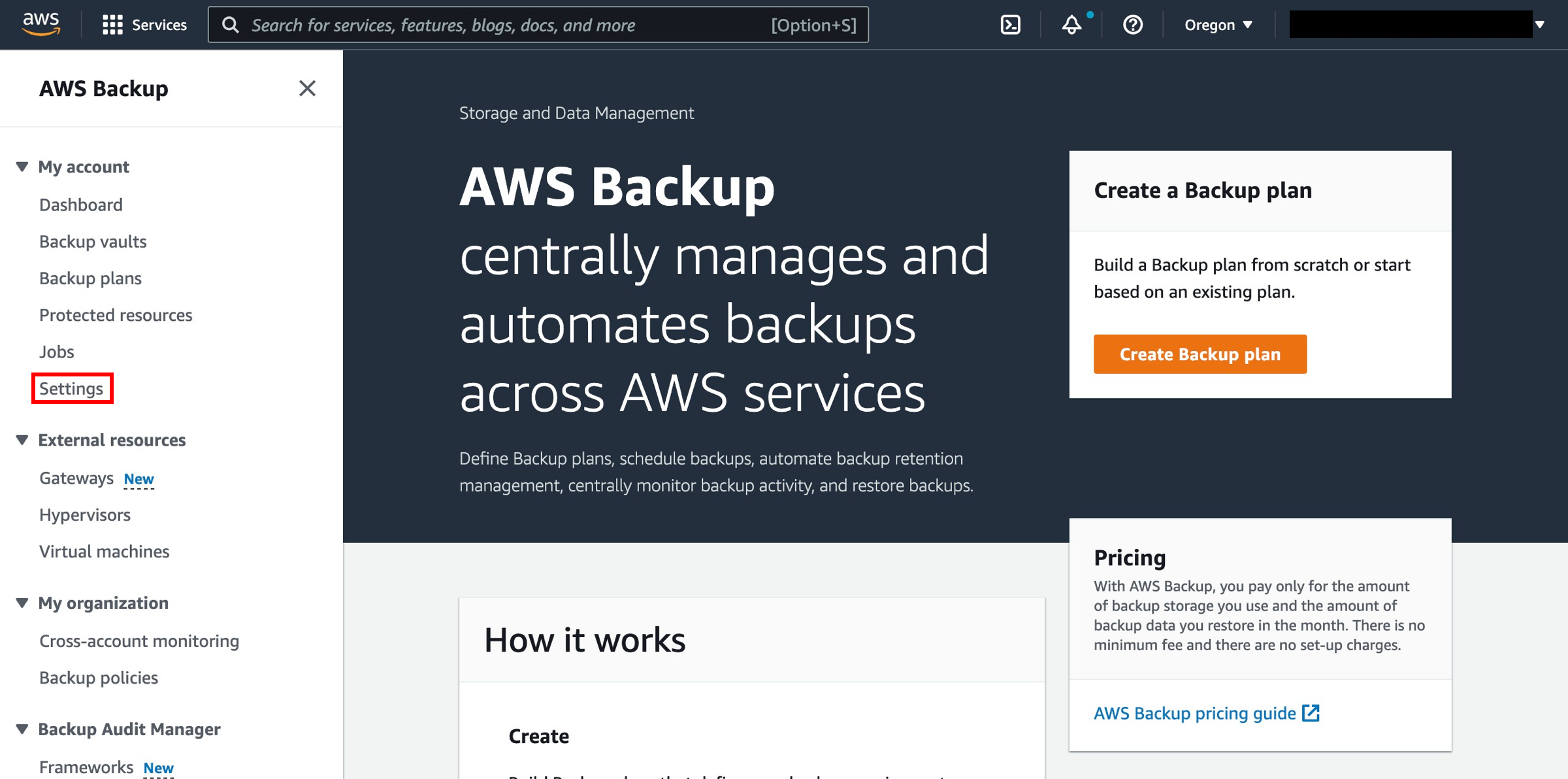
3. Configure resources
On the Service opt-in page, choose Configure resources.

4. Select services for backup
On the Configure resources page, use the toggle switches to enable or disable the services used with AWS Backup. Choose Confirm when your services are configured.
AWS resources that you're backing up should be in the Region you are using for this how-to guide, and resources must all be in the same AWS Region (however, see step 3.2 for information on cross-Region copy). This how-to guide uses the US East (N. Virginia) Region (us-east-1).

5. Create an on-demand backup job of an Amazon RDS database
Back in the AWS Backup console, under My account on the left navigation pane, select Protected resources.

6. Choose Create an on-demand backup
From the dashboard, select the Create on-demand backup button.
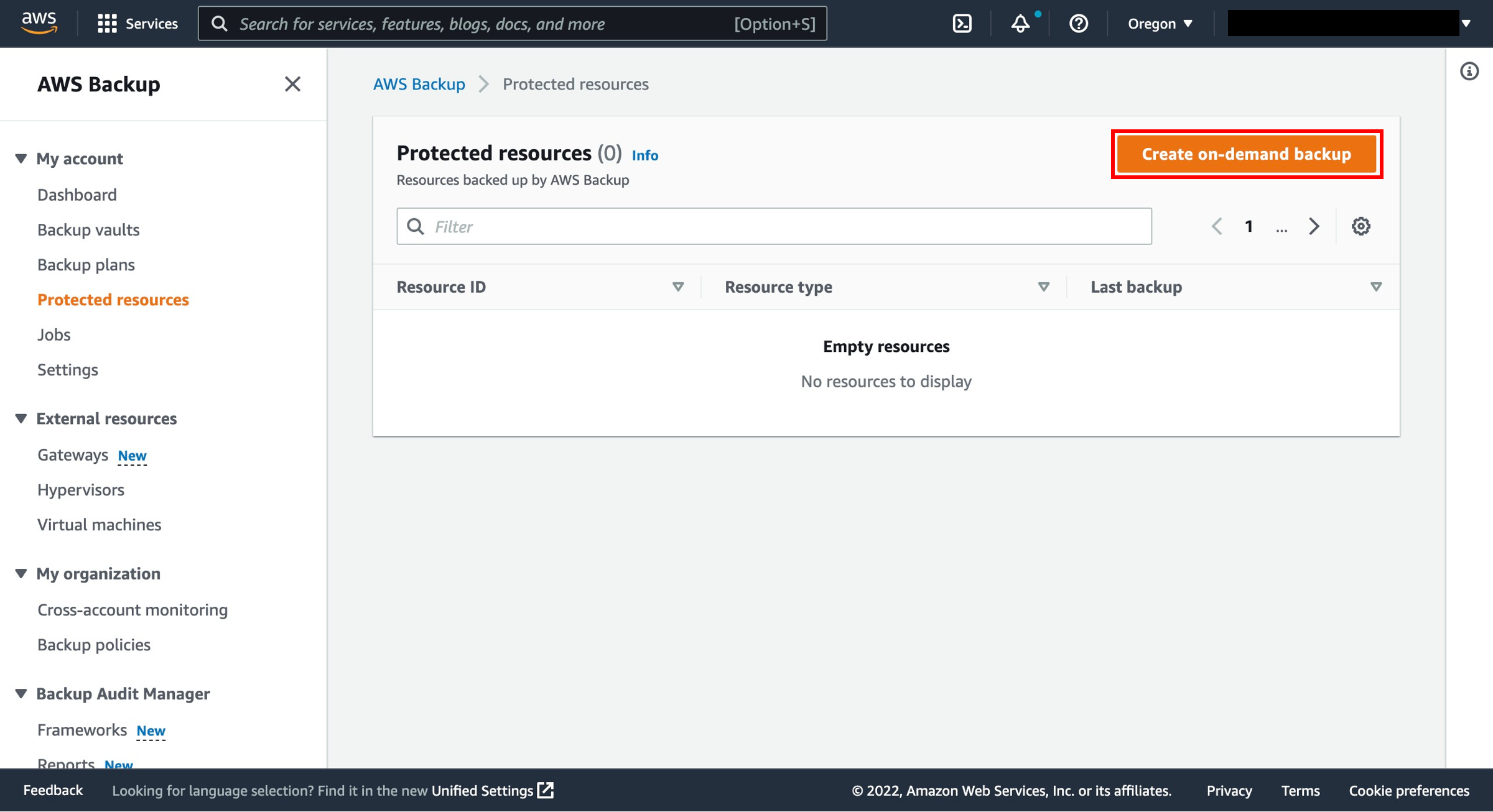
7. Configure on-demand backup settings
On the Create on-demand backup page, choose the following options:
Select the resource type that you want to back up; for example, choose RDS for Amazon RDS.
Choose the database name or ID of the resource that you want to protect; for example, analytics.
Ensure that Create backup now is selected. This initiates your backup job immediately and enables you to see your saved resource sooner on the Protected resources page.
Select the desired retention period. AWS Backup automatically deletes your backups at the end of this period to save storage costs for you.
Choose an existing backup vault. Choosing Create new Backup vault opens a new page to create a vault and then returns you to the Create on-demand backup page when you are finished.
Under IAM role, choose Default role.
Note: If the AWS Backup Default role is not present in your account, then an AWS Backup Default role is created with the correct permissions.
Select the Create on-demand backup button. This takes you to the Jobs page, where you will see a list of jobs.

8. View the backup job details
Choose the Backup job ID for the resource that you chose to back up to see the details of that job.

Configure automatic AWS Backup jobs of an Amazon RDS database
1. Configure the services used with AWS Backup
Back on the left navigation pane in the AWS Backup console, under My account, choose Settings.
2. Configure resources
On the Service opt-in page, choose Configure resources.

3. Select services for backup
On the Configure resources page, use the toggle switches to enable or disable the services used with AWS Backup. Choose Confirm when your services are configured.
AWS resources that you're backing up should be in the Region you are using for this tutorial, and resources must all be in the same AWS Region (however, see step 3.2 for information on cross-Region copy). This tutorial uses the US East (N. Virginia) Region (us-east-1).

4. Configure a backup plan
In the AWS Backup console, select Backup plans on the left navigation pane under My account, and then Create backup plan.

5. Create a new backup plan
AWS Backup provides three ways to get started using the AWS Backup console but for this how-to guide, select Build a new plan:
Start with a template — You can create a new backup plan based on a template provided by AWS Backup. Be aware that backup plans created by AWS Backup are based on backup best practices and common backup policy configurations. When you select an existing backup plan to start from, the configurations from that backup plan are automatically populated for your new backup plan. You can then change any of these configurations according to your backup requirements.
Build a new plan — You can create a new backup plan by specifying each of the backup configuration details, as described in the next section. You can choose from the recommended default configurations.
Define a plan using JSON - You can modify the JSON expression of an existing backup plan or create a new expression.
Backup plan name - You must provide a unique backup plan name. If you try to create a backup plan that is identical to an existing plan, you get an AlreadyExistsException error. For this how-to guide, enter RDS-webapp.

6. Enter a backup rule name
Backup rule name - Backup plans are composed of one or more backup rules. Backup rule names are case sensitive. They must contain from 1 to 63 alphanumeric characters or hyphens. For this how-to guide, enter RDS-Dailies.

7. Create a backup vault
Backup vault - A backup vault is a container to organize your backups in. Backups created by a backup rule are organized in the backup vault that you specify in the backup rule. You can use backup vaults to set the AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) encryption key that is used to encrypt backups in the backup vault and to control access to the backups in the backup vault. You can also add tags to backup vaults to help you organize them. If you don't want to use the default vault, you can create your own.
Create new backup vault - Instead of using the default backup vault that is automatically created for you in the AWS Backup console, you can create specific backup vaults to save and organize groups of backups in the same vault.
i) To create a backup vault, choose Create new Backup vault.
ii) Enter a name for your backup vault. You can name your vault to reflect what you will store in it, or to make it easier to search for the backups you need. For example, you could name it FinancialBackups.
iii) Select an AWS KMS key. You can use either a key that you already created or select the default AWS Backup master key.
iv) Optionally, add tags that will help you search for and identify your backup vault.
v) Select Create Backup vault button.
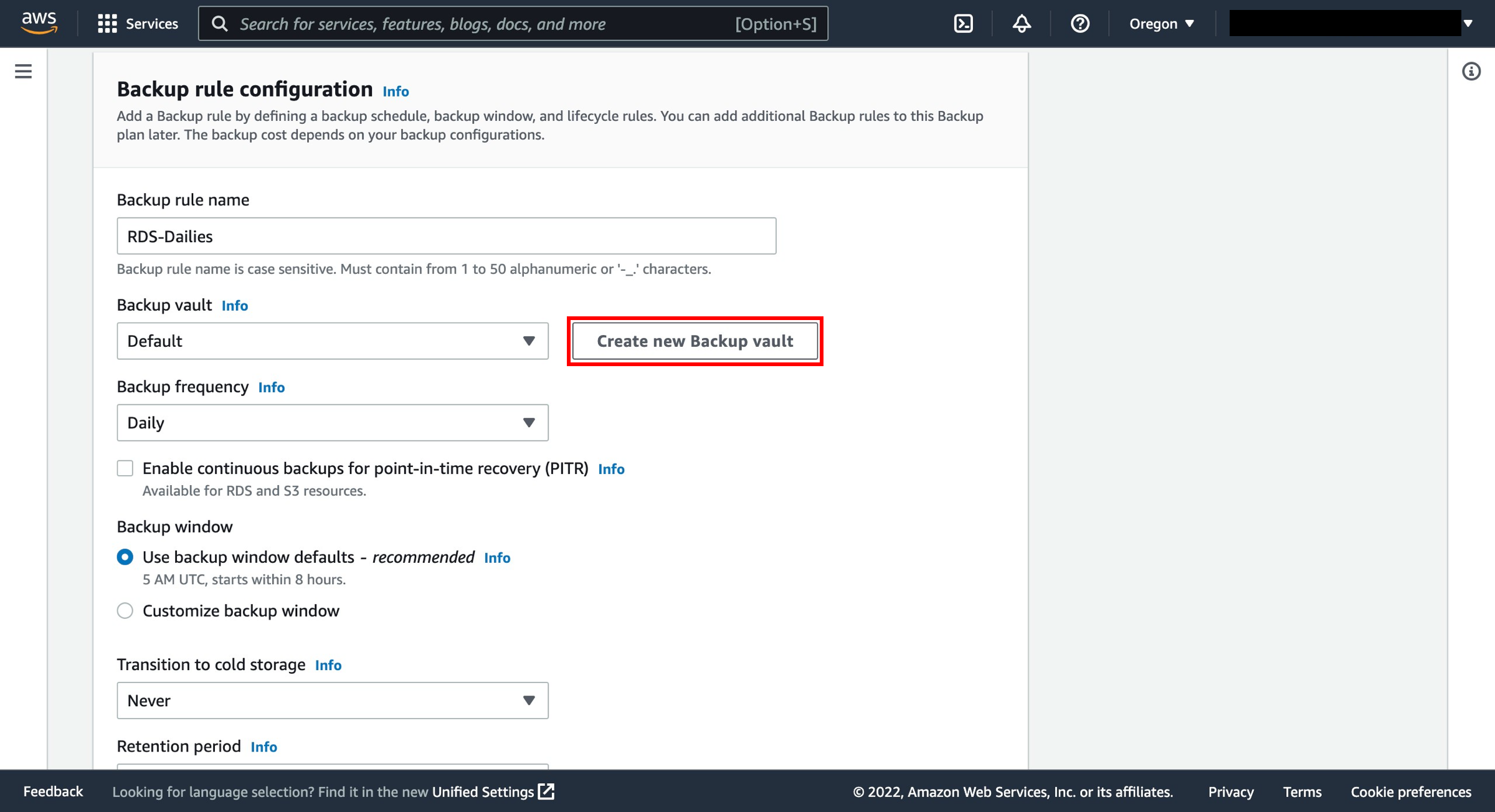
8. Configure the backup vault
Create new backup vault - Instead of using the default backup vault that is automatically created for you in the AWS Backup console, you can create specific backup vaults to save and organize groups of backups in the same vault.
To create a backup vault, choose Create new Backup vault.
Enter a name for your backup vault. You can name your vault to reflect what you will store in it, or to make it easier to search for the backups you need. For example, you could name it FinancialBackups.
Select an AWS KMS key. You can use either a key that you already created or select the default AWS Backup master key.
Optionally, add tags that will help you search for and identify your backup vault.
Select Create Backup vault button.

9. Configure backup schedule
Backup frequency - The backup frequency determines how often a backup is created. You can choose a frequency of every 12 hours, daily, weekly, or monthly. When selecting weekly, you can specify which days of the week you want backups to be taken. When selecting monthly, you can choose a specific day of the month.
Enable continuous backups for point-in-time recovery - With continuous backups, you can perform point-in-time restores (PITR) by choosing when to restore, down to the second. The most time that can elapse between the current state of your workload and your most recent point-in-time restore is 5 minutes. You can store continuous backups for up to 35 days. If you do not enable continuous backups, AWS Backup takes snapshot backups for you.
Backup window - Backup windows consist of the time that the backup window begins and the duration of the window in hours. The default backup window is set to start at 5 AM UTC (Coordinated Universal Time) and lasts 8 hours.

10. Configure retention settings
Transition to cold storage - Currently only Amazon EFS file system backups can be transitioned to cold storage. The cold storage expression is ignored for the backups of Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS), Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS), Amazon Aurora, Amazon DynamoDB, and AWS Storage Gateway.
Retention period - AWS Backup automatically deletes your backups at the end of this period to save storage costs for you. AWS Backup can retain snapshots between 1 day and 100 years (or indefinitely, if you do not enter a retention period), and continuous backups between 1 and 35 days.

11. (Optional) Copy a backup to multiple regions
Copy to destination - As part of your backup plan, you can optionally create a backup copy in another AWS Region. Using AWS Backup, you can copy backups to multiple AWS Regions on-demand, or automatically as part of a scheduled backup plan. Cross-Region Replication (CRR) is particularly valuable if you have business continuity or compliance requirements to store backups a minimum distance away from your production data. When you define a backup copy, you configure the following options:
Copy to destination - The destination Region for the backup copy.
Destination backup vault - The destination backup vault for the copy.
(Advanced Settings) Transition to cold storage
(Advanced Settings) Retention period
Note: Cross-Region Copy incurs additional data transfer costs. You can refer to the AWS Backup pricing page for more information.

12. Create the plan
Tags added to recovery points - The tags that you list here are automatically added to backups when they are created.
Advanced backup settings - Enables application-consistent backups for third-party applications that are running on Amazon EC2 instances. Currently, AWS Backup supports Windows VSS backups. This is only applicable for Windows EC2 Instances running SQL Server or Exchange databases.
Choose Create plan.
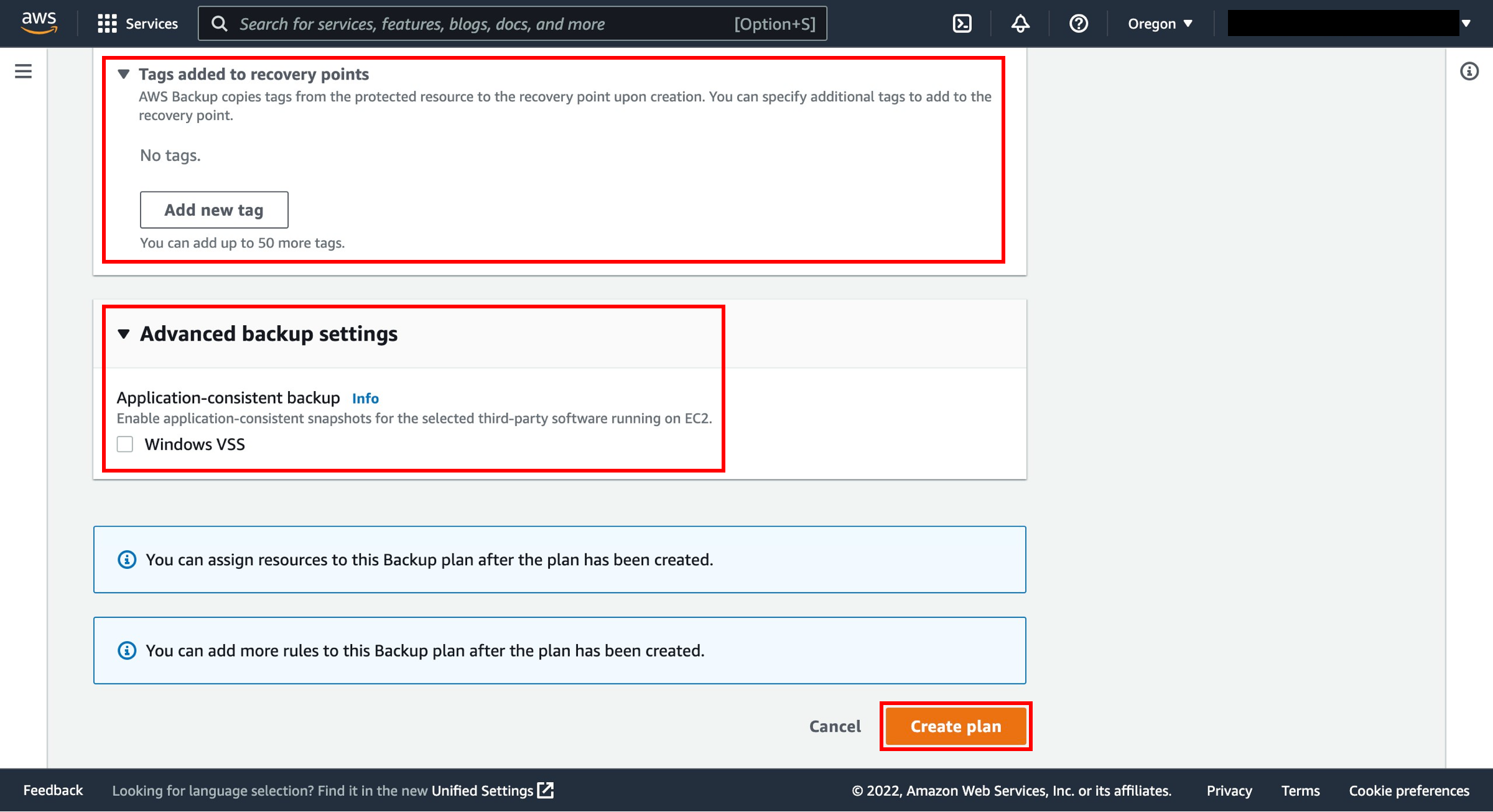
13. Assign resources
When you assign a resource to a backup plan, that resource is backed up automatically according to the backup plan. The backups for that resource are managed according to the backup plan. You can assign resources using tags or resource IDs. Using tags to assign resources is a simple and scalable way to back up multiple resources.
Select the created backup plan, and select the Assign resources button.

14. Enter an assignment name
Resource assignment name - Provide a resource assignment name.
IAM role - When creating a tag-based backup plan, if you choose a role other than Default role, make sure that it has the necessary permissions to back up all tagged resources. AWS Backup tries to process all resources with the selected tags. If it encounters a resource that it doesn't have permission to access, the backup plan fails.

15. Choose a resource selection type
Define resource selection - You can choose to include all resource types or specific resource types.

16. Define resource assignments
For resource ID-based assignment, select Resource type and the name of the resource.
To exclude specific resource IDs, select Resource type and the name of the resource.

17. Assign the resources to the backup plan
For tags-based resource assignment, provide the key-value pair of the Amazon RDS database.
Select Assign resources and the backup plan has the resources assigned to it.

18. View the backup job
Navigate to the AWS Backup console and the backup jobs will be seen under Jobs.
A backup, or recovery point, represents the content of a resource, such as an Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume or Amazon RDS database, at a specified time. Recovery point is a term that refers generally to the different backups in AWS services, such as Amazon EBS snapshots and Amazon RDS backups. In AWS Backup, recovery points are saved in backup vaults, which you can organize according to your business needs. Each recovery point has a unique ID.

Restore of an Amazon RDS database using AWS Backup
1. Select the backup
Navigate to the backup vault that was selected in the backup plan and select the latest completed backup.

2. Restore the RDS instance
To restore the database, click on the recovery point ARN and select Restore.

3. Review restore configuration
The restore of the ARN will bring you to a Restore backup screen that will have Instance specifications and configurations for the Amazon RDS database. Select the DB engine, License Model, and DB instance class.
Multi AZ - Using a Multi-AZ deployment will automatically provision and maintain a synchronous standby replica in a different Availability Zone. Note that you will have to pay for Multi-AZ deployment.
Storage type - Select Provisioned IOPS (SSD).
Provisioned IOPS - The requested number of I/O operations per second that the DB instance can support. Enter 3000.

4. Enter a name for the DB instance
DB Instance Identifier - Type a name for the DB instance that is unique for your account in the Region that you selected. If you're restoring from a DB instance that you deleted after you made the DB snapshot, you can use the name of that DB instance.

5. Configure network and security settings
Select the appropriate network and security settings:
VPC - Select the VPC where the database needs to be restored to.
Subnet group - Select the subnet group in the VPC where the database needs to be restored to.
Public accessibility - You can choose if you need the DB Instances to have a public address or not. If you choose Yes, this will allocate an IP address for your database instance so that you can directly connect to the database from your own device.
Availability zone - Choose No Preference.

6. Select database options
Select the appropriate database options.
Database port - Leave the default value of 3306.
DB parameter group - Leave the default value.
Option Group - Leave the default value. Amazon RDS uses option groups to enable and configure additional features.
IAM DB Authentication Enabled - You can authenticate to your DB instance using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) database authentication. Select Enable IAM DB authentication.

8. Configure encryption
Encryption - This is the master key that will be used to protect the key that is used to encrypt the database volume. You can choose from master keys in your AWS account or enter the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of a key from a different account.

9. Select log types
Log exports - Select the log types to publish to Amazon CloudWatch logs.

10. Configure automatic maintenance
Maintenance - Select Yes if the DB instance should receive automatic engine version upgrades.

11. Choose a restore role
Restore role - Select the Default role or Choose an IAM role.

12. Restore the backup
Select Restore backup.
Your job will then appear under the Jobs section in the Restore jobs tab in the AWS Backup console.
Once the restore job is completed, you can navigate to the Amazon RDS console and use the endpoint to connect to the database.

12. Monitor the restore job
Your job will then appear under the Jobs section in the Restore jobs tab in the AWS Backup console.

12. Find the DB endpoint
Once the restore job is completed, you can navigate to the Amazon RDS console and use the endpoint to connect to the database.

Clean up
In the following steps, you will clean up the resources you created in this how-to guide. It is a best practice to delete instances and resources that you are no longer using so that you are not continually charged for them.
1. Delete the restored database
Open the Amazon RDS console.
In the navigation pane, choose Databases.
Select the restored RDS database, and choose Actions, Delete.

2. Confirm deletion
To confirm deletion, type delete me into the field.
Note: This process can take several seconds to complete.

Additional resources: Working with Amazon RDS and Amazon Aurora
Conclusion
You successfully created an on-demand backup job of an Amazon RDS database! You also used a backup plan to back up Amazon RDS resources. As a great next step, check out recently published AWS Backup blogs to further your AWS Cloud knowledge.
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages
