- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for RFID Store Inventory on AWS
Guidance for RFID Store Inventory on AWS
Overview
How it works
Managing Inventory
This is a logical architecture showing RFID integration of retail store inventory systems using AWS services. It shows the foundational components and flows needed to monitor, maintain, and act on product inventory data.
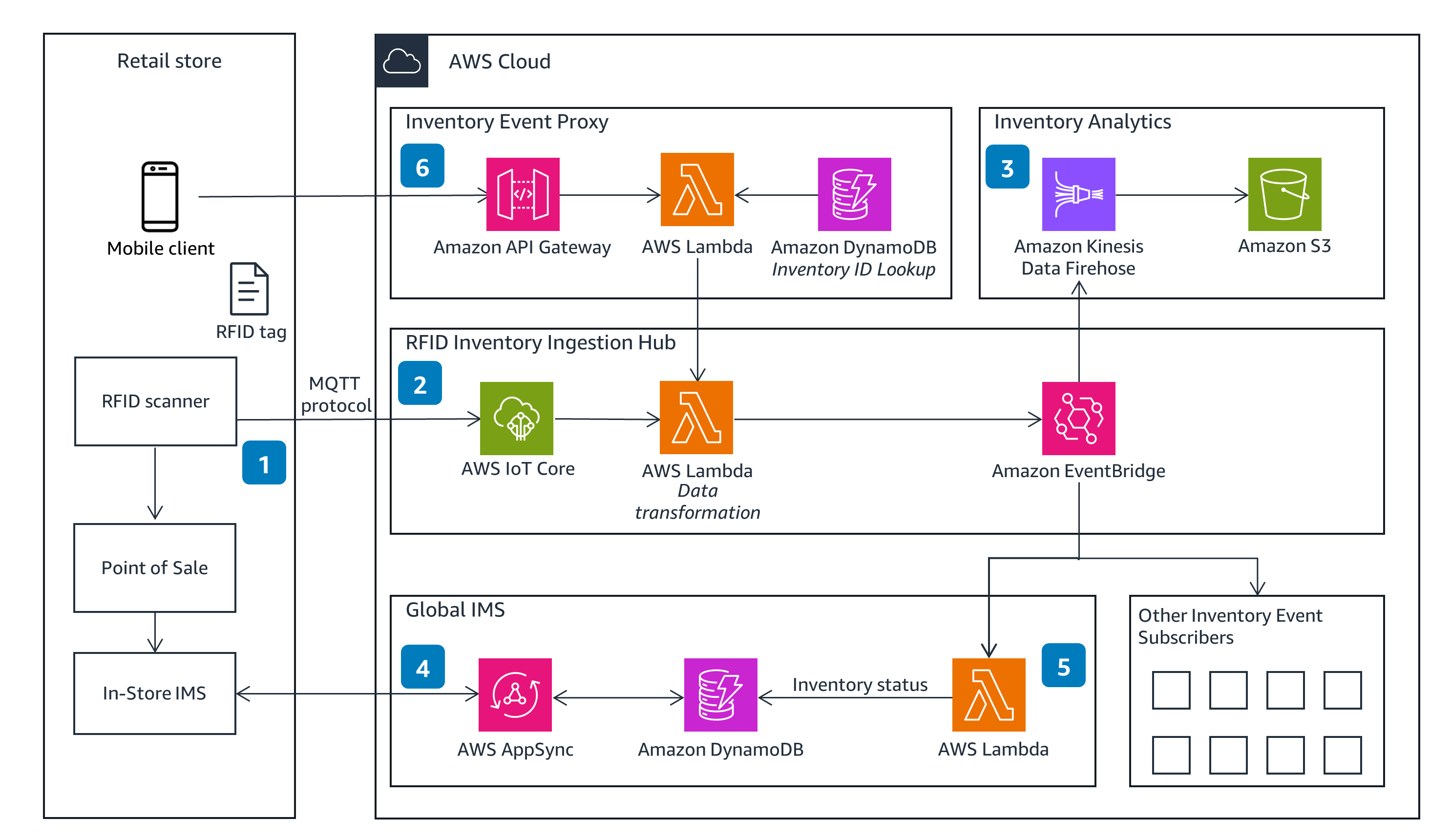
Counting Inventory
This is a logical end-to-end architecture for RFID integration in a retail store that uses AWS services to perform inventory reconciliation.
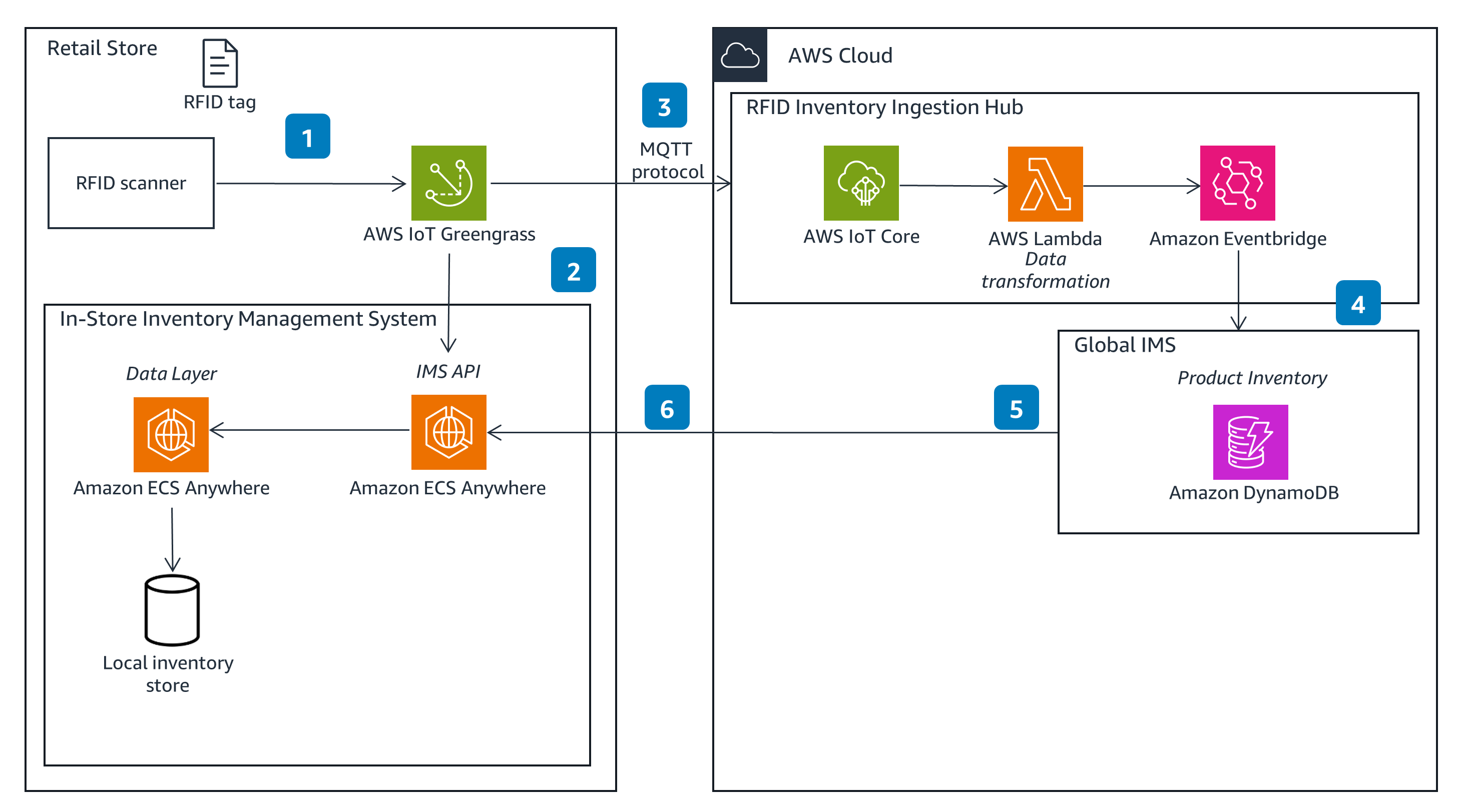
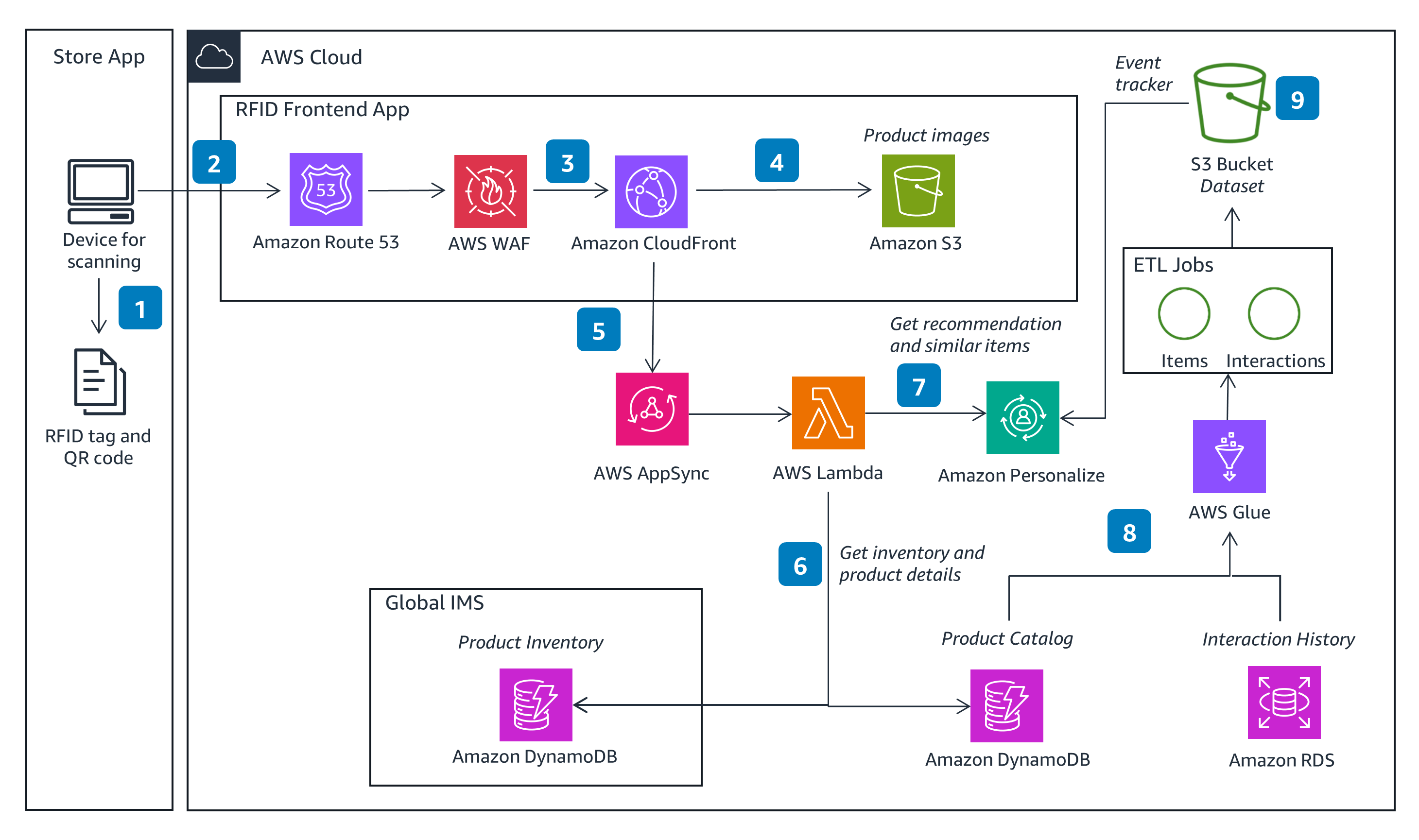
Identifying Inventory
This is a logical end-to-end architecture for RFID integration in a retail store that uses AWS services when product details and recommendations need to be returned to a customer.
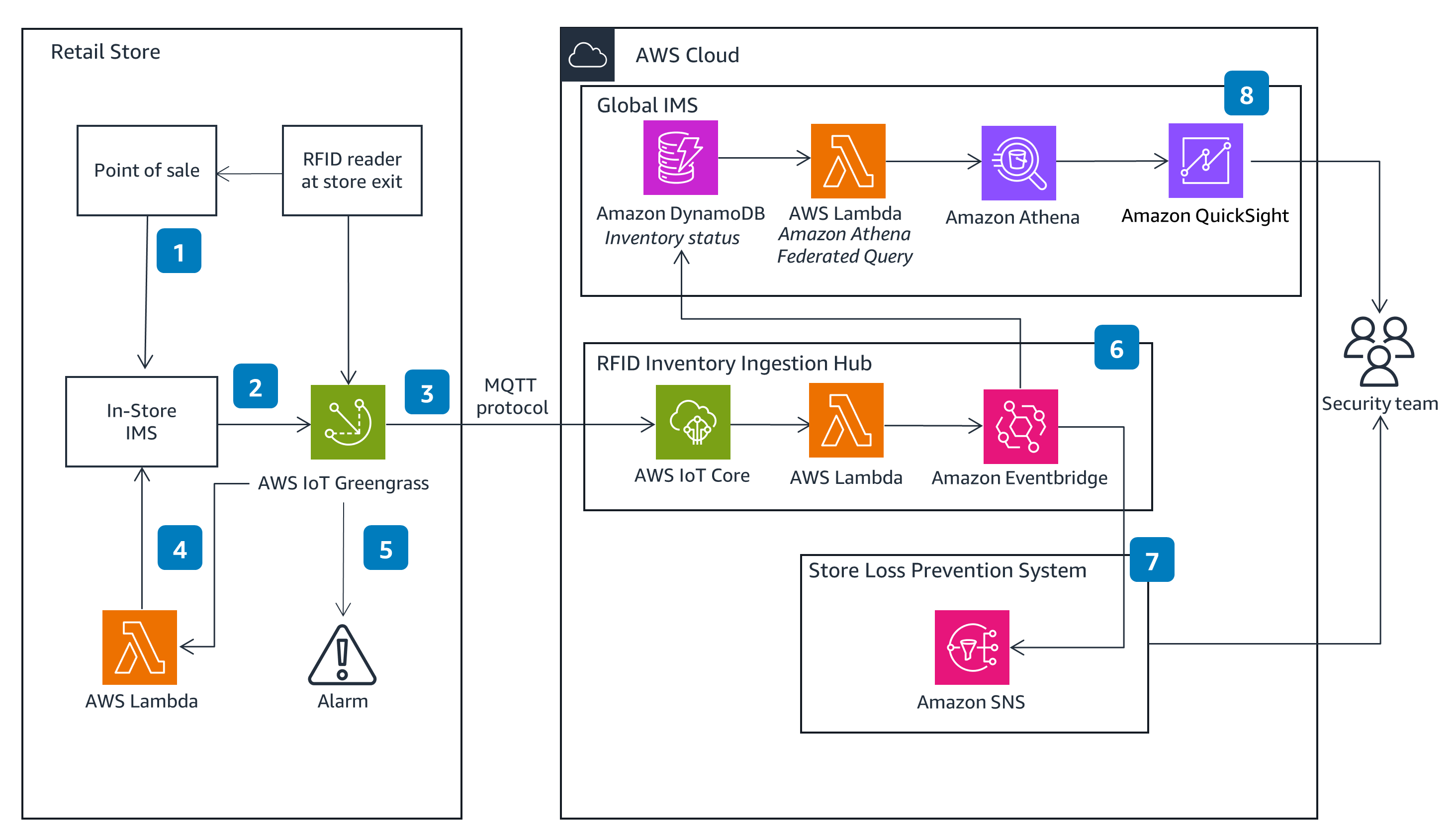
Detecting Shrink
This is a logical end-to-end architecture for RFID integration in a retail store that uses AWS services to prevent and detect asset loss.
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
You can set a workload baseline by using business events collected by RFID scanners or readers, log and metrics from Amazon CloudWatch, and any ancillary or supporting data from other business applications. You can then perform continuous monitoring of these metrics for anomalies or drift (through automation) and set up notifications that alert the right personnel of drift.
You can enable least-privilege access through AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles during interactions between AWS services. All services in this Guidance are patched to help ensure minimal security vulnerabilities.
To maintain reliable connection to the internet for this Guidance, you should implement best practices in your infrastructure, particularly for services such as AWS IoT Greengrass, AWS IoT Core, and API Gateway. These services are highly available and use underlying protocols to ensure delivery and security. AWS IoT Core can provide reliable message delivery using MQTT quality of service. Retail stores can be configured to use AWS IoT Greengrass, allowing for offline IoT processing until connectivity is restored.
This Guidance uses an event-driven architecture based on a publish-subscribe model. This model enables you to incorporate additional services without impacting the architecture’s core functionality. To achieve low latency, you should consider your geographical proximity to users and systems that will interact with this Guidance.
The Guidance uses serverless services, which allows you to pay only for the resources you use. For additional cost savings, you can use provisioned capacity for DynamoDB and S3 Intelligent-Tiering for automatic cost savings.
By processing as much as possible in the cloud, this Guidance keeps hardware requirements to a minimum. In the event that connectivity to AWS is lost, some on-premises hardware is necessary to support operations. Hardware is also required on-premises to interact with the RFID, in-store inventory, and security devices. Services that will require hardware are AWS IoT Greengrass and Amazon ECS Anywhere.
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages