- Industry›
- AWS for Media & Entertainment›
- IBC 2025 Demo Showcase
Create: Revolutionize content creation, distribution, and operational efficiency
Experience the evolution of broadcast production with AWS's cloud-based solutions featuring AI-enhanced live production, streamlined media exchange, advanced audio capabilities, and automated news workflows.
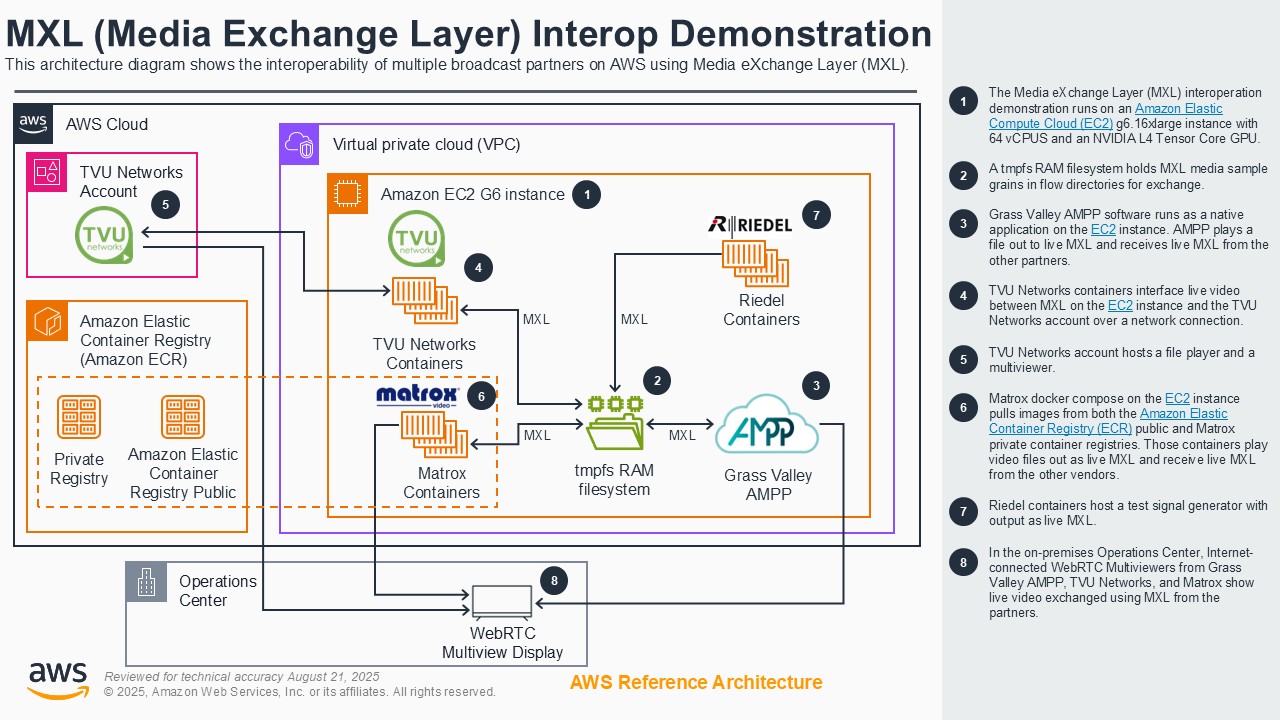
MXL (Media Exchange Layer) interoperation
Broadcasters seek customizable and dynamic live video workflows with cost-effective scalability and enhanced operational efficiency, security, and reliability. For the highest tiers of live content, they want to combine the best tools for the job with uncompressed quality and ultra-low latency. The Media Exchange Layer (MXL) is an open-source framework that enables real-time exchange of uncompressed video, audio, and metadata between professional media software media functions, as part of the EBU's Dynamic Media Facility (DMF) reference architecture. This demonstration shows how multiple broadcast software AWS Partners, including Grass Valley, Matrox, TVU Networks, and Riedel can exchange media using MXL on Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) G6 instances with NVIDIA L4 Tensor Core GPUs, highlighting how complex live broadcast workflows can be transitioned to cloud-native solutions. The demo also shows how Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) can securely store, manage, and deploy container instances for software media functions.
Architecture diagram
Demo partners
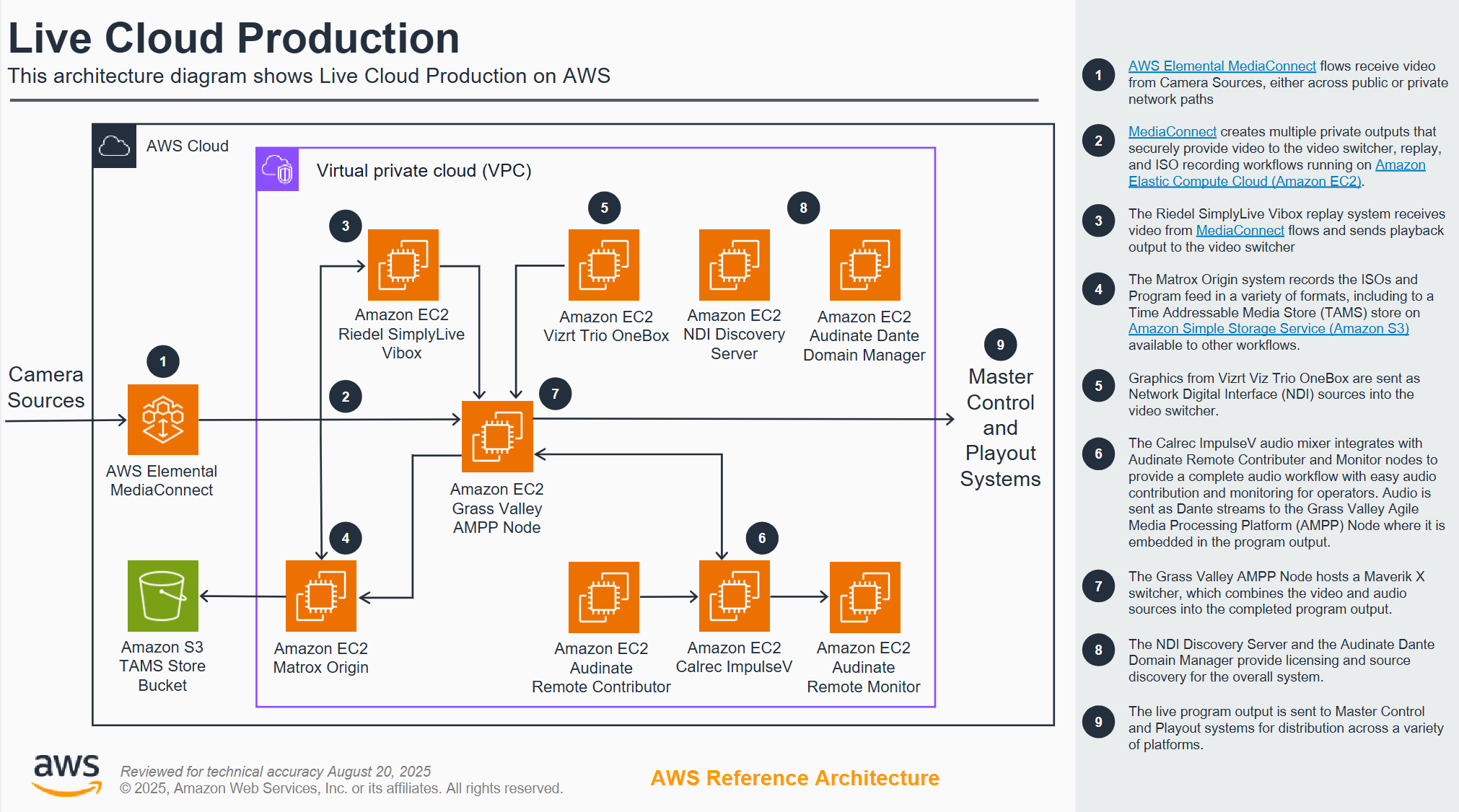
Live cloud production
Broadcasters interested in deploying live cloud production (LCP) workloads for full-time production use require automated, scalable and reliable deployment solutions, on which they can base ongoing observability and monitoring requirements. This demonstration highlights a robust and future-ready broadcast workflow built entirely on AWS, utilizing solutions from proven broadcast technology partners with decades of industry experience. The demo integrates advanced vision mixing, centralized graphics control, broadcast-grade audio, and reliable replay systems—all working together to deliver a seamless live production environment. Featuring real-world sports footage, the demonstration showcases mature, production-proven workflows that emphasize interoperability, distributed production, and operational resilience. This setup illustrates how established industry leaders are leveraging AWS to provide scalable, sustainable, and highly reliable live production solutions that meet the evolving demands of modern broadcasting
Architecture diagram
Demo partners
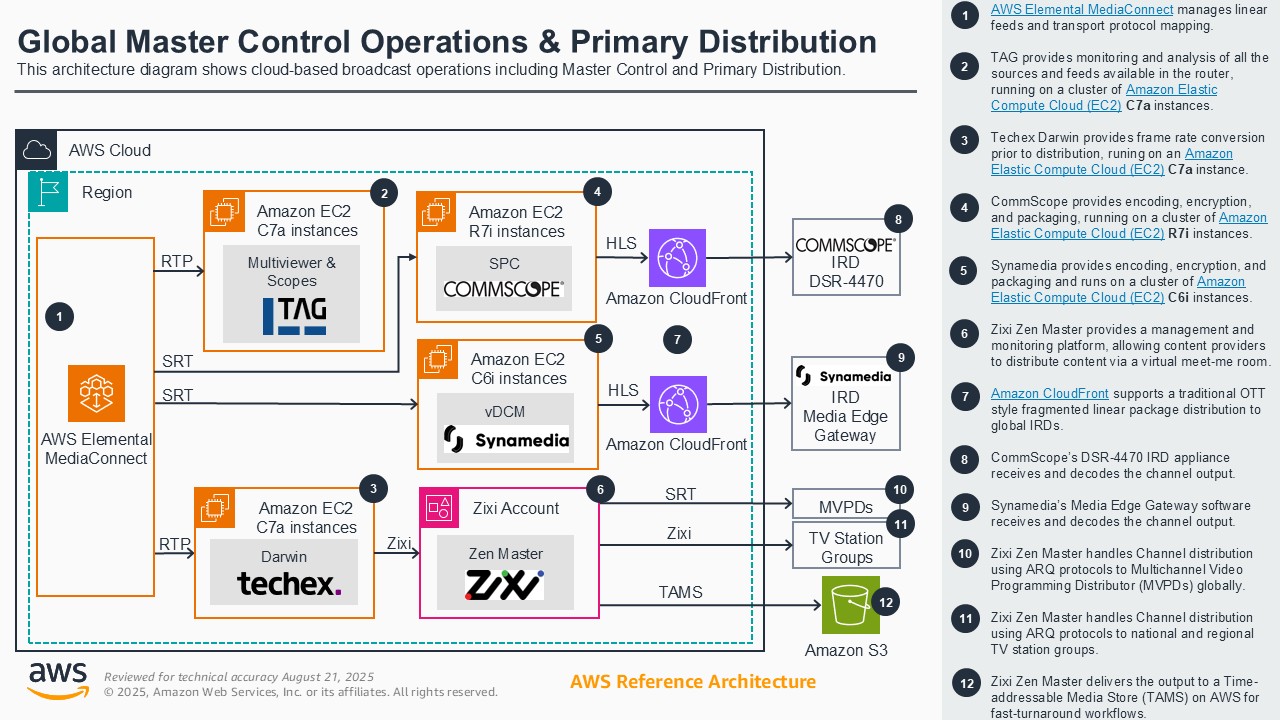
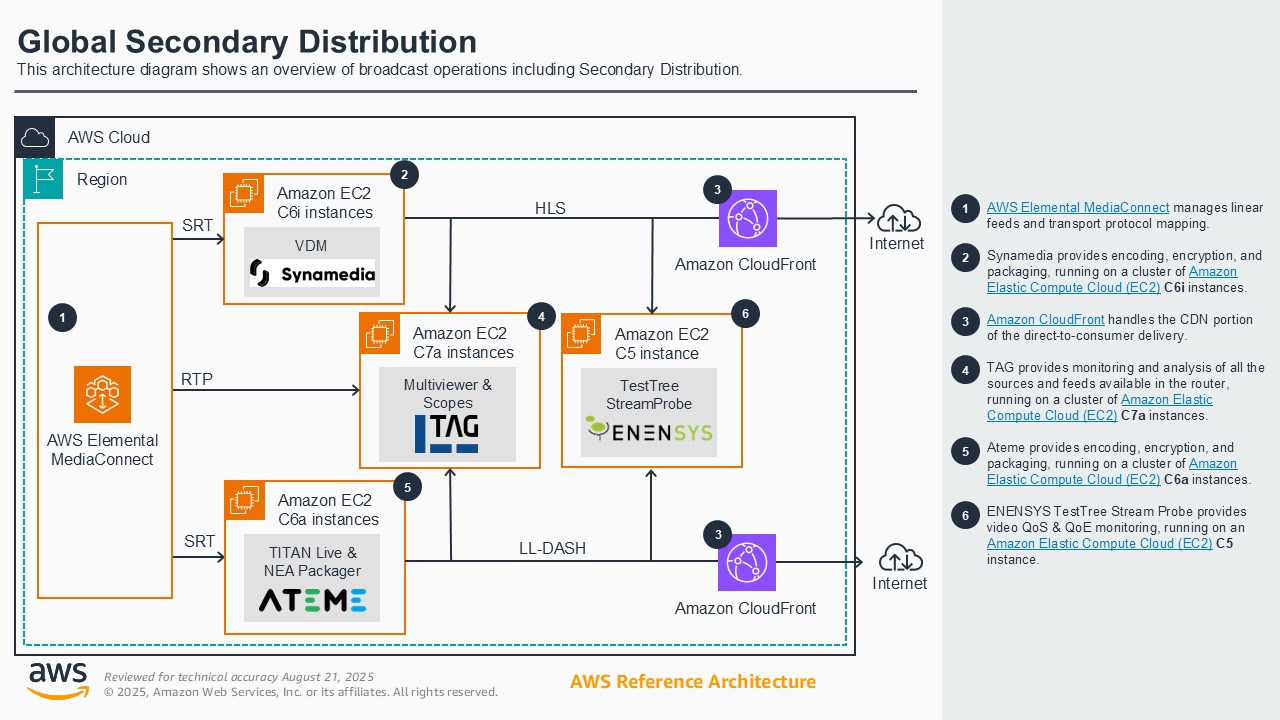
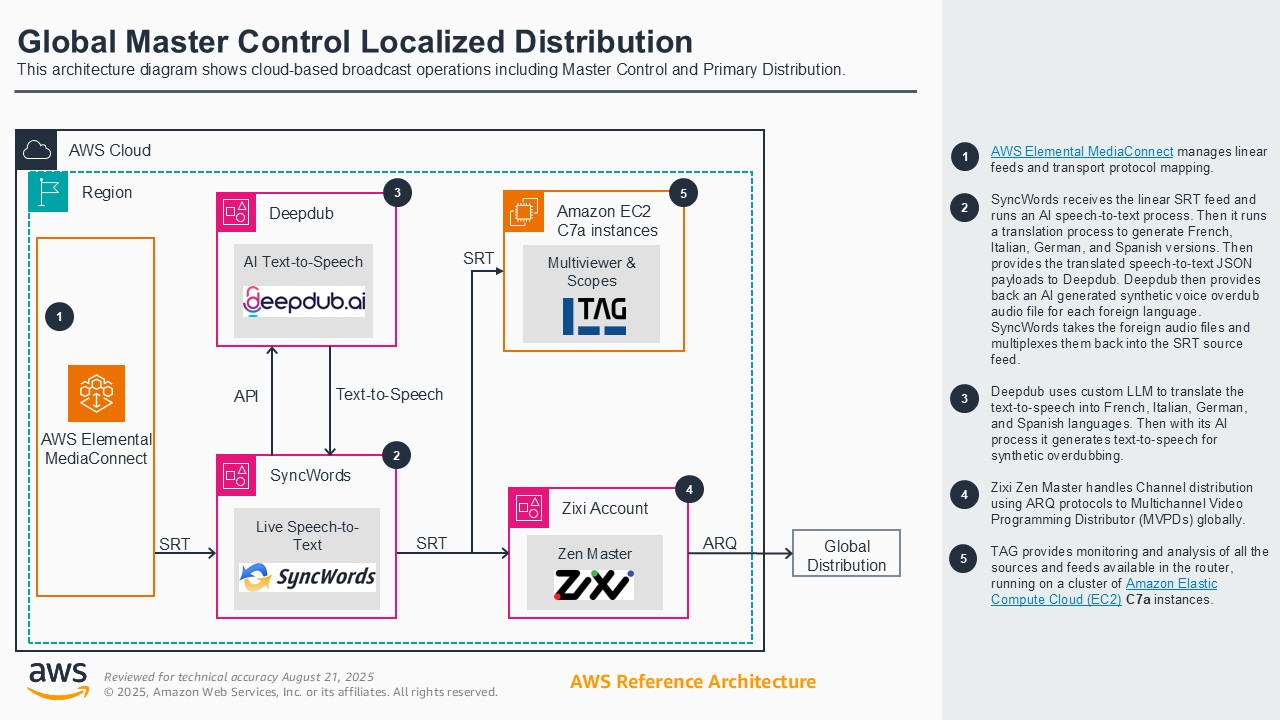
MCR Global contribution and distribution
Broadcasters historically have had to rely on costly, inflexible satellite and on-premises ecosystems for linear broadcast distribution. This demonstration shows how broadcasters can leverage AWS's global infrastructure, AWS Elemental Media Services, and AWS Partner software solutions to securely ingest, process, route, and distribute linear content worldwide with unmatched speed, reliability, quality, and operational control. Attendees will learn how running and operating master control, primary, and secondary distribution workflows in AWS can improve scalability, cost-efficiency, and agility, providing a clear advantage over traditional satellite models and ISP provider dependencies. This enables broadcasters to innovate and adapt in a rapidly changing media landscape while reaching more distributors and consumers globally.
Architecture diagram
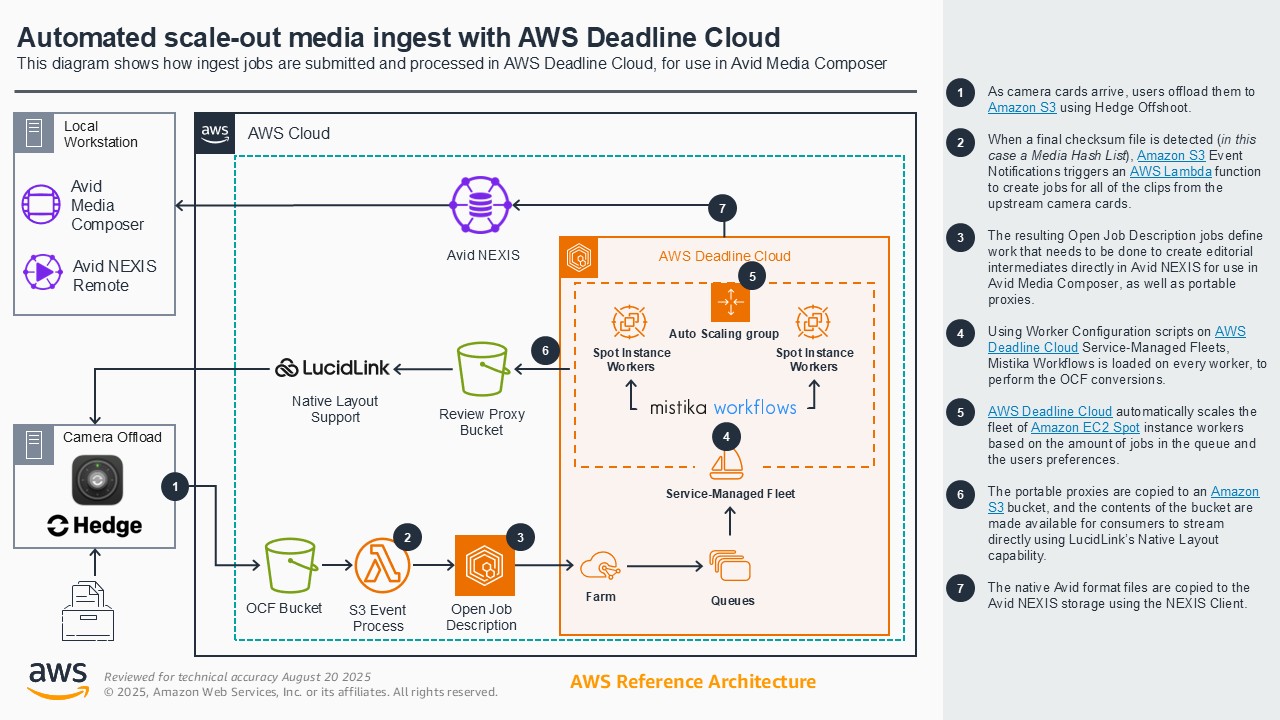
Automated ingest
During production, media companies face a common challenge when a variety of video formats are generated by different camera systems. Traditionally, preparing this footage for post-production requires a series of complicated and time-consuming manual steps to organize, transcode, and ingest the media before it becomes available to the editorial team. Automated media ingestion on AWS enables creative teams to streamline their post-production workflows through a fully automated transcoding pipeline. When media assets land in Amazon S3, AWS services automatically trigger Deadline managed render nodes running SGO Mistika. These nodes access the source media directly from S3 through LucidLink Native Layout feature, process the content, and generate OP-Atom MXF files that are written directly to AVID NEXIS storage using the NEXIS Client for Linux. The automated approach shown in this demo eliminates manual operations, reduces operational overhead, and ensures media is readily available in the required format for editorial teams.
Architecture diagram
Demo partners
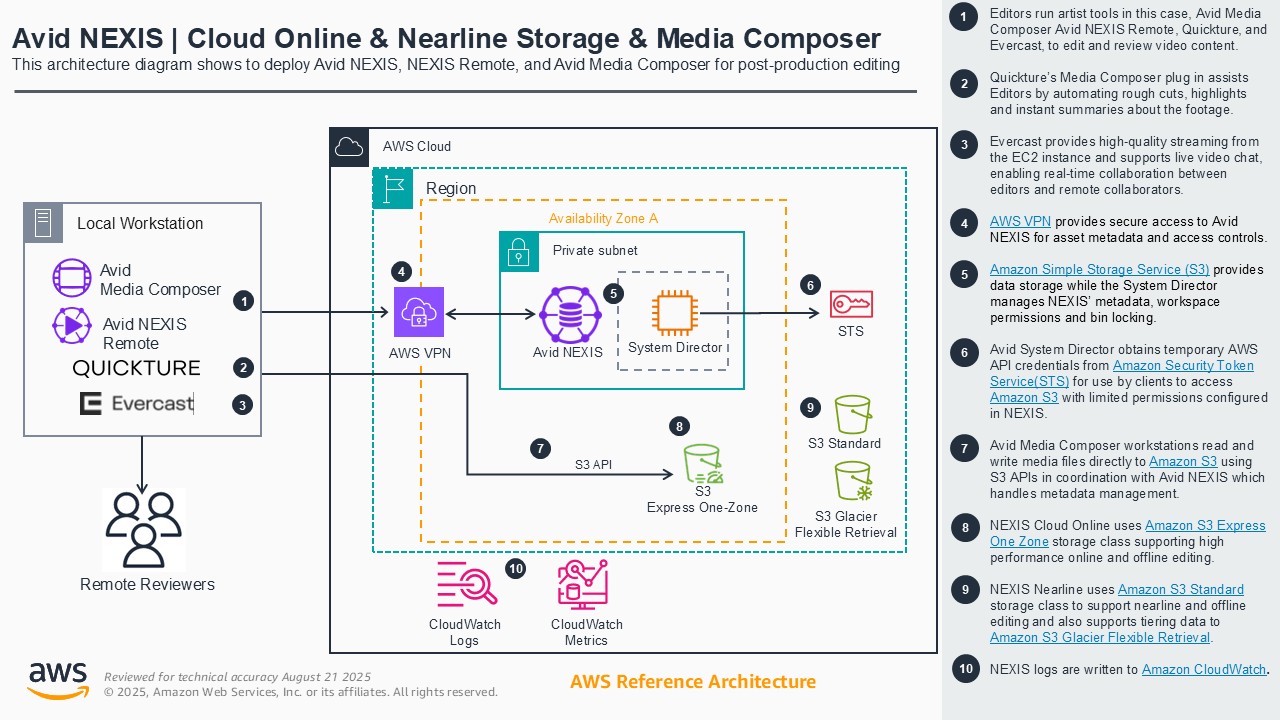
Avid on AWS
Media production companies have traditionally been constrained by fixed facility locations, complex on-premises infrastructure, and the need to co-locate creative talent. Transform your media production with Avid on AWS, where global teams seamlessly collaborate using familiar Avid tools like Media Composer and NEXIS storage. Deploy production studios instantly worldwide, freeing your artists to work from anywhere. Hybrid workflows are now possible through Avid Nexis Remote, allowing customers to leverage their existing workstations while scaling with cloud-based virtual workstations as needed - all while keeping media centrally secured in the AWS Cloud. Accelerate the editing process through AI-powered tools such as Quickture that automate the creation of rough-cuts. Experience real-time collaboration with color-accurate 4K streaming through Evercast, enabling producers and editors to work together effectively even when geographically separated.
Architecture diagram
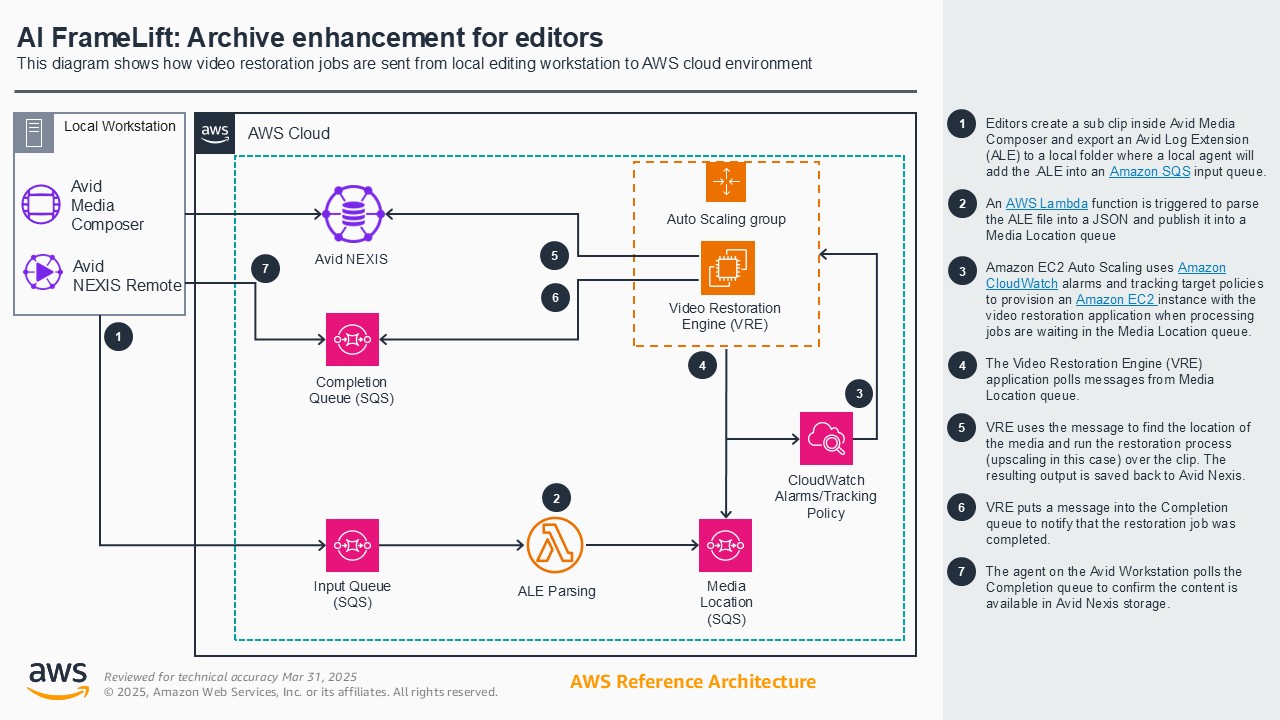
AI FrameLift: Archive enhancement for editors
Media companies often are unable to maximize the value of their vast libraries of historical footage due to the original capture resolution being lower than that expected by modern audiences. Instead of costly bulk upscaling, this demo shows how editors can rapidly apply super resolution to bring low resolution content to up to 2K for just the segments they need, when they need it - directly from their familiar editing environment. Whether working on-premises or in the cloud, teams can leverage AWS's powerful GPU-accelerated instances to run AI models that upscale selected clips or individual frames without interrupting their creative flow. This targeted approach accelerates production timelines, letting you bring compelling historical content to audiences faster and more economically.
Architecture diagram
Demo partners
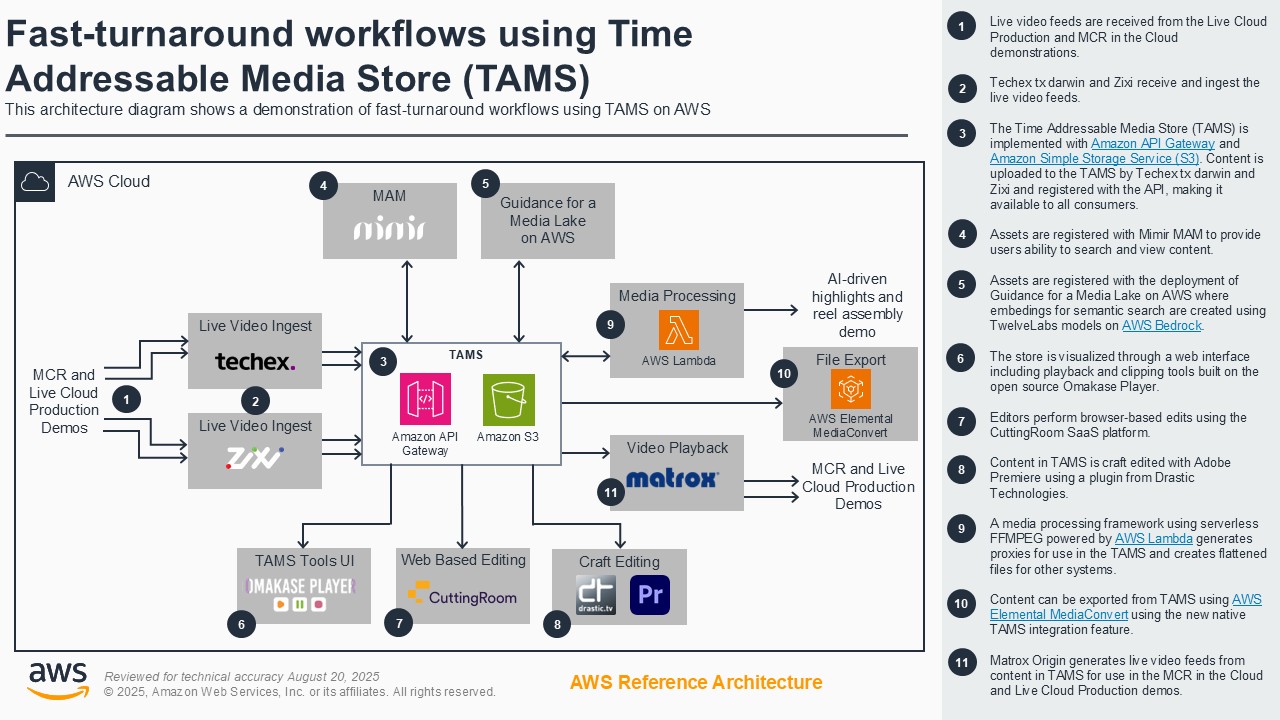
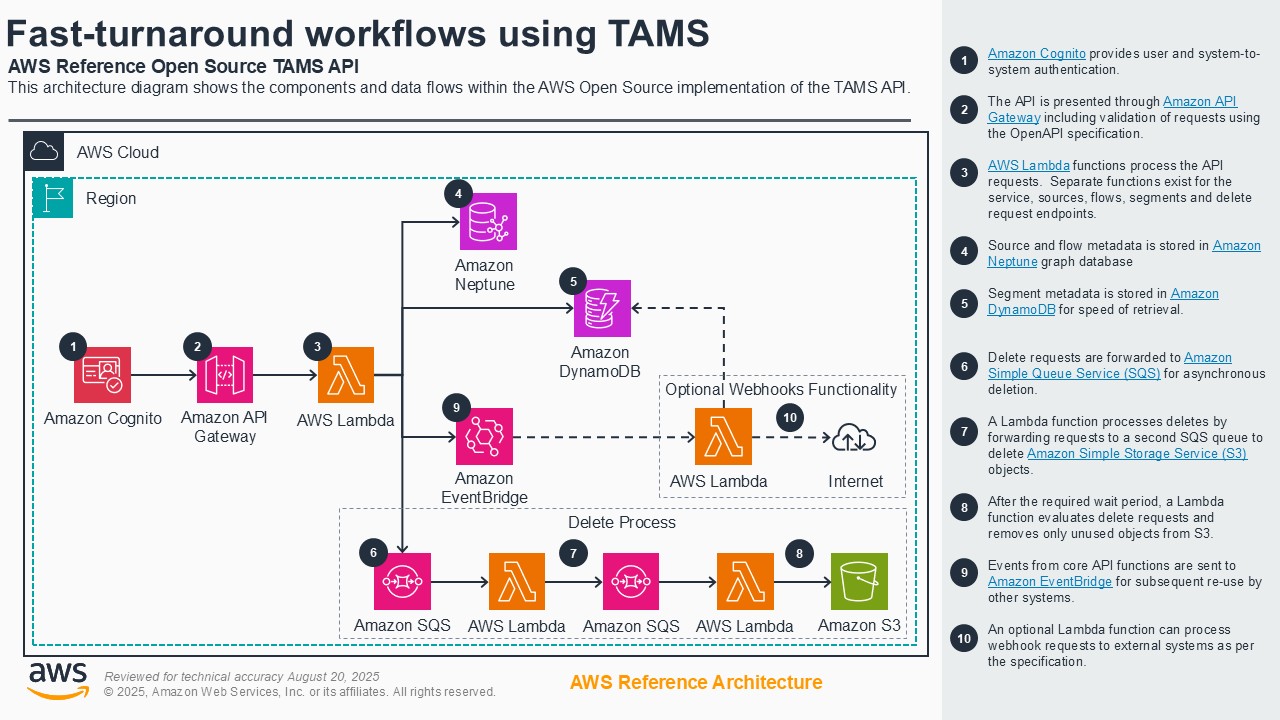
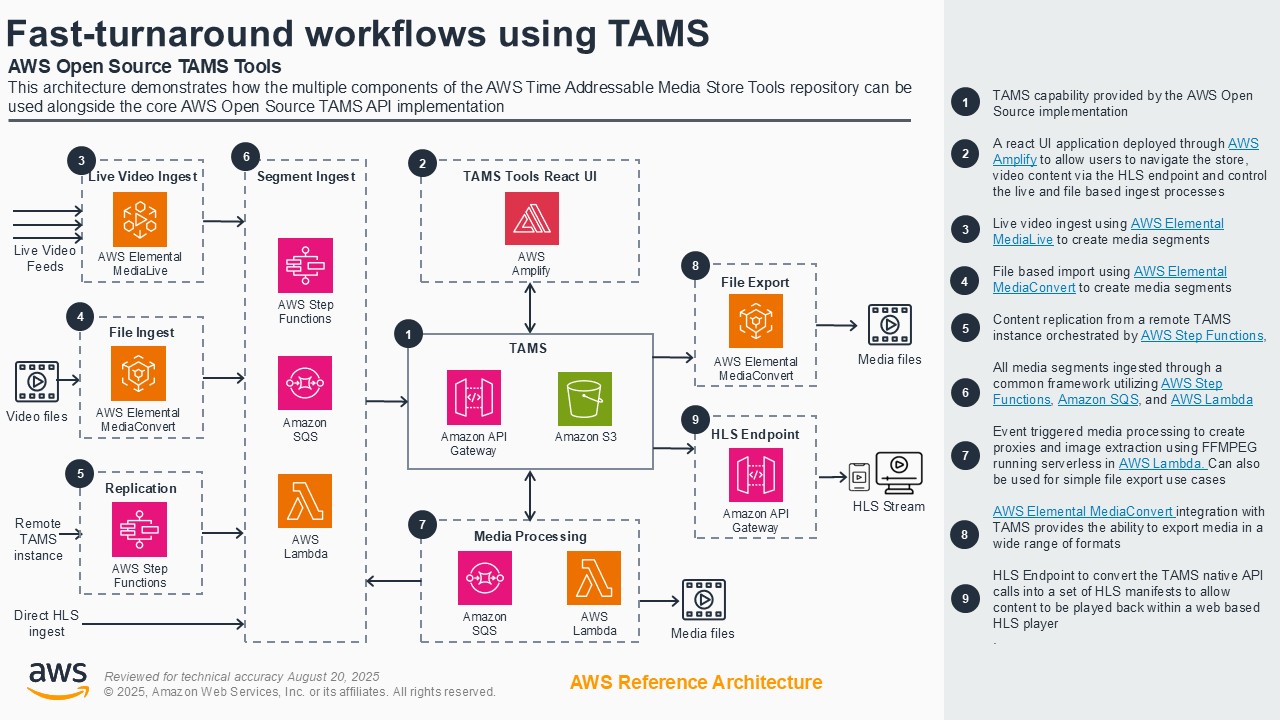
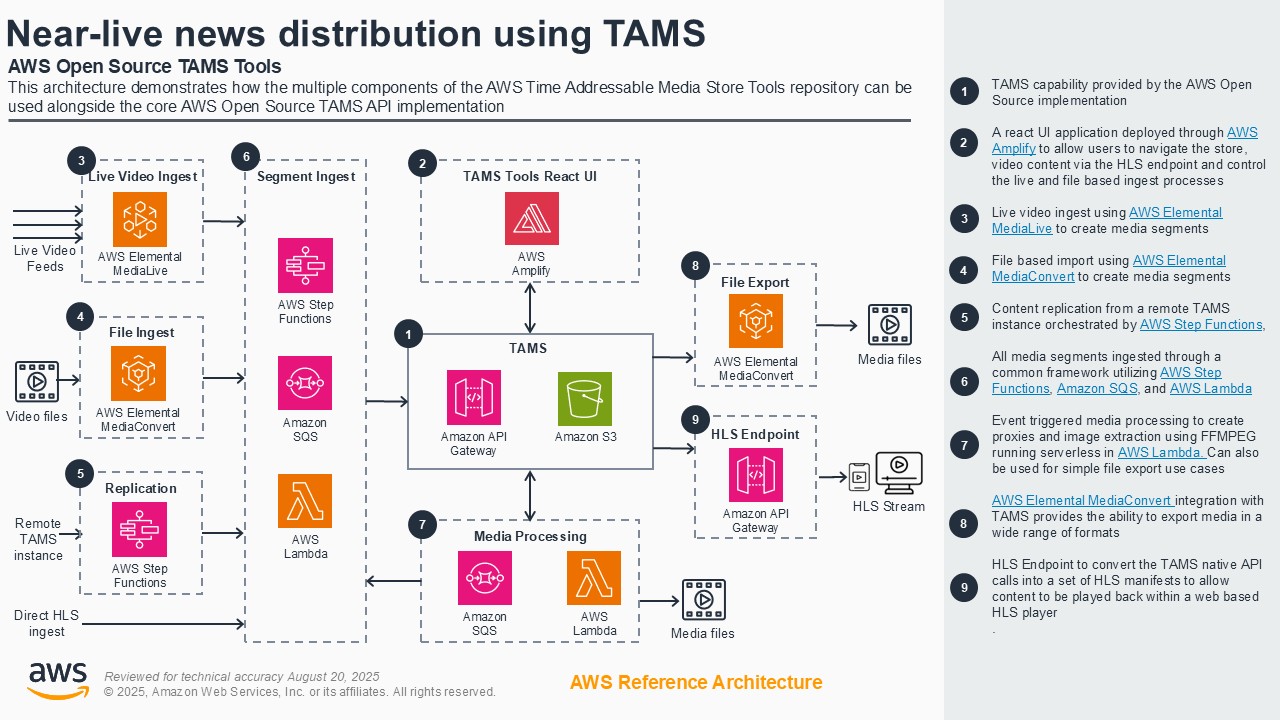
Fast-turnaround workflows using TAMS
Fast-turnaround workflows for news, sports, and live entertainment face challenges of vendor lock-in and inflexible or costly solutions. Customers can address these challenges by using the open-source Time-addressable Media Store (TAMS) API on AWS to ingest live feeds into a scalable timeline of media elements. The TAMS API provides a common means to access time-addressed media for multiple production workflow tools. This eliminates redundant data duplication and enables efficient workflows across platforms and teams. This demo shows an end-to-end cloud-native workflow using TAMS on AWS, including ingest, content manipulation in browser-based and virtual workstation-based editors, export for social media, AI analysis of segments, and playout to a live production gallery.
Architecture diagram
Demo partners
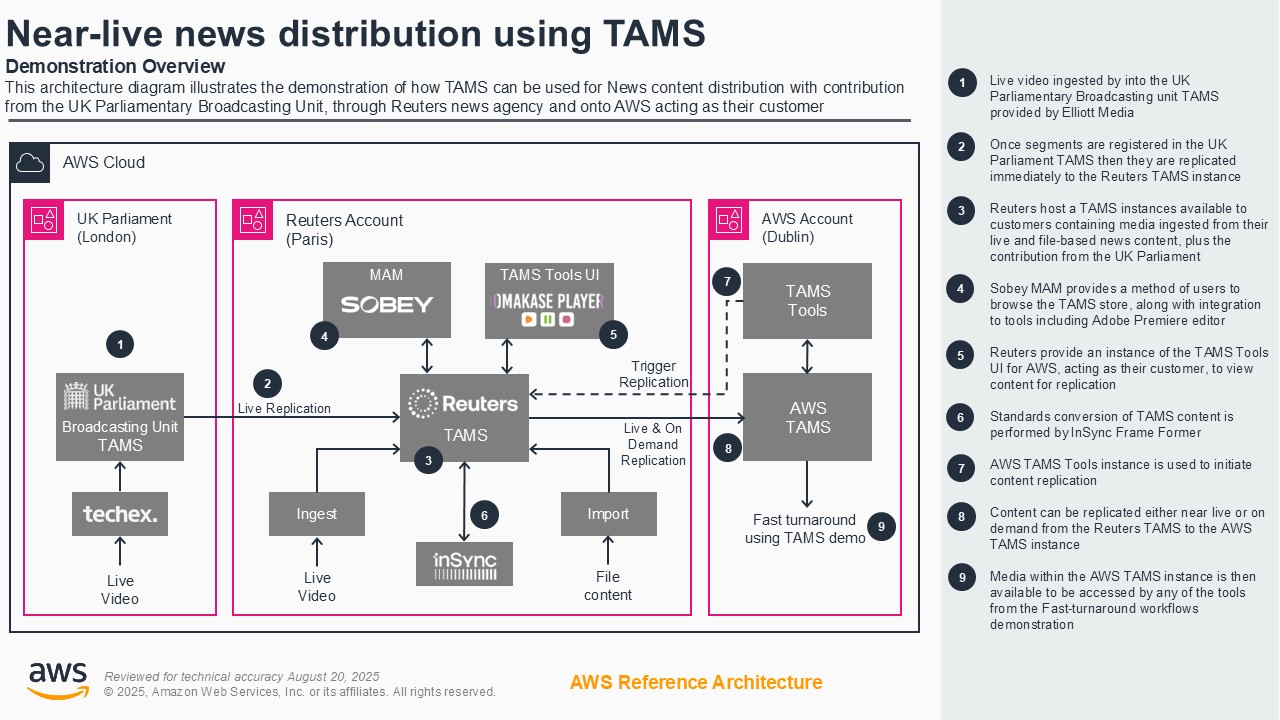
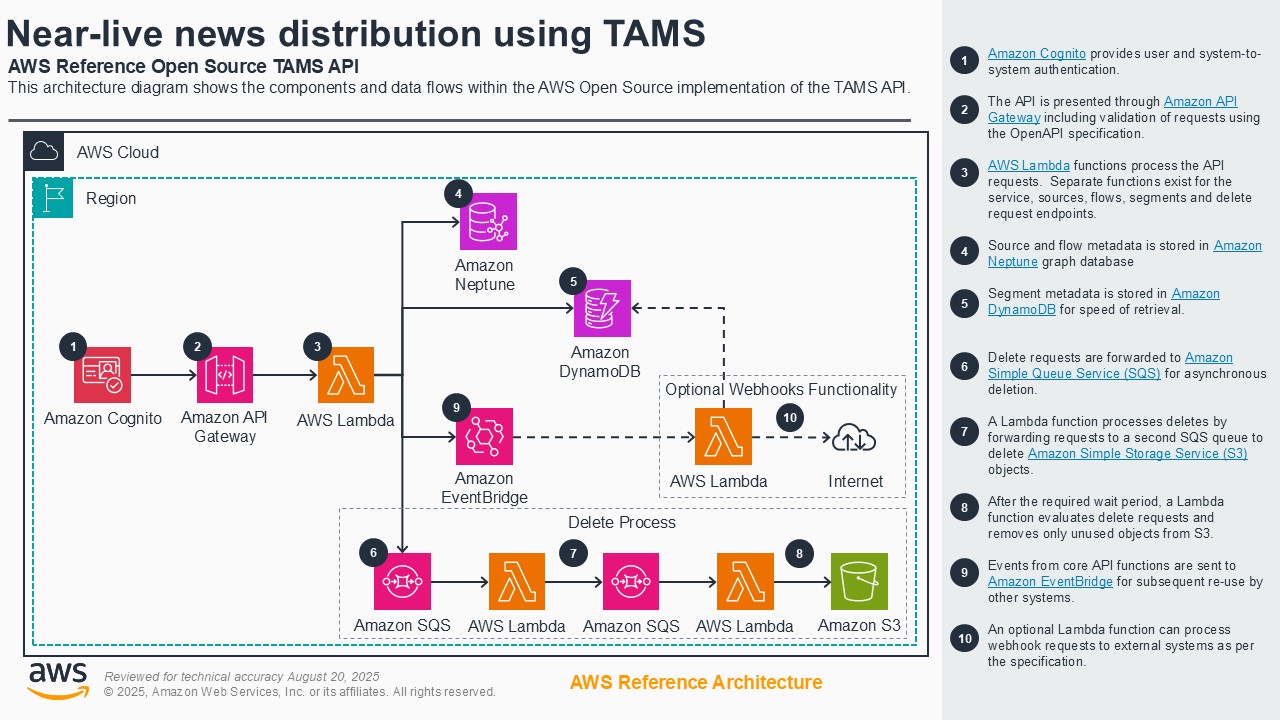
Near-live news distribution using TAMS
Distributing near-live news and sports content to partners remains inefficient, relying on costly, point-to-point delivery methods that create delays. We demonstrate how a news agency - Reuters - solves this by leveraging the open-source Time-Addressable Media Store (TAMS) API on AWS. In this live demonstration, Reuters publishes feeds of content from the UK Parliamentary Broadcasting Unit into TAMS, allowing its customers to immediately access, clip, and pull the segments they need on demand. This powerful, interoperable supply chain creates efficiency, while providing more flexible contribution and distribution of content.
Architecture diagram
Demo partners
Enhancing live production with AI
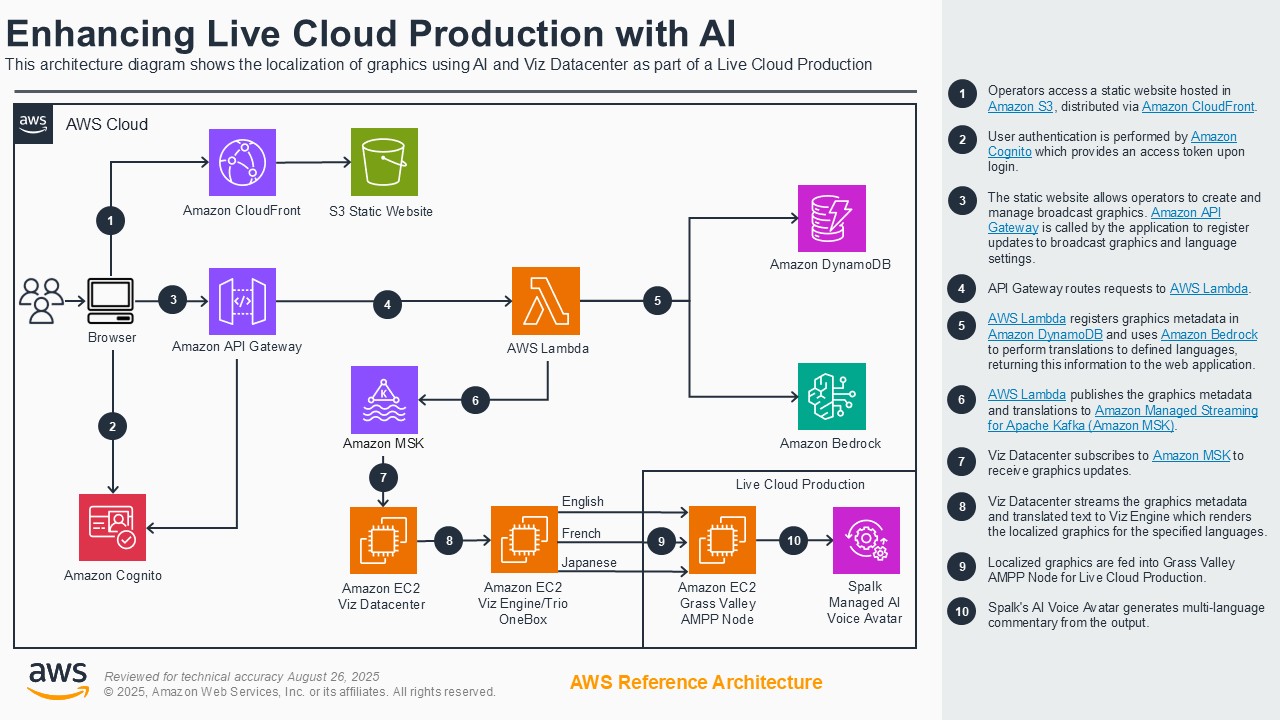
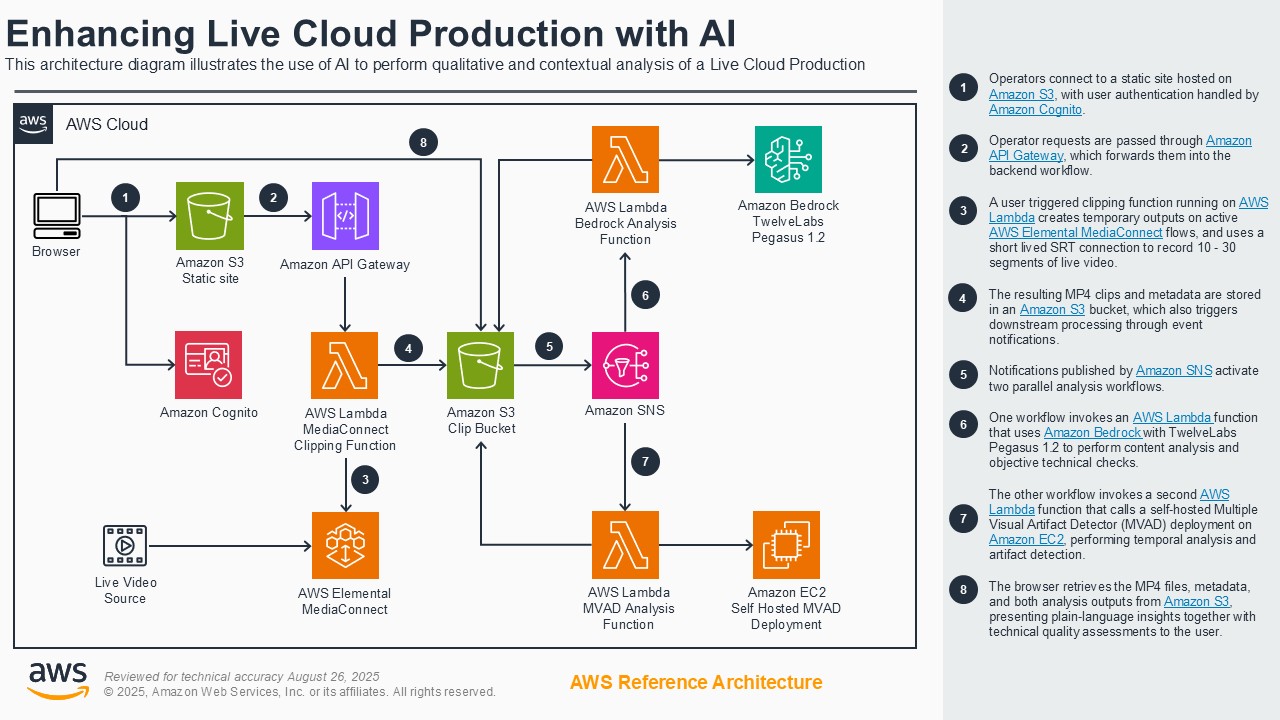
Customers face increasing challenges in creating customized variants of live content to support different markets and use-cases such as localization. Additionally, as customers migrate their broadcast workloads to the cloud, they require tools to ensure the quality of their live outputs. The enhancing live production with AI demonstration showcases how to address these challenges through two AI-powered systems powered by AWS and AWS Partner offerings. The demo features an innovative system for broadcast environments that combines automated graphics translation, leveraging Amazon Bedrock integrated with the Vizrt product family, along with AI-powered audio localization from Spalk to enable efficient multi-language broadcasting. This system handles localization of various broadcast graphics and audio tracks while supporting multiple languages. The second system in this demo focuses on video quality control through the Multiple Visual Artifact Detector (MVAD), co-developed by Amazon Prime Video and the University of Bristol. This tool analyzes video quality issues, detecting problems like frame distortion and blurring, while delivering plain-language insights with integration to AWS Elemental MediaConnect. Together, these systems demonstrate the ease of creating AI applications that enhance broadcast operations while maintaining human oversight, suitable for broadcasters of all sizes.
Architecture diagram
Disclaimer
References to third-party services or organizations on this page do not imply an endorsement, sponsorship, or affiliation between Amazon or AWS and the third party. Guidance from AWS is a technical starting point, and you can customize your integration with third-party services when you deploy them.
The sample code; software libraries; command line tools; proofs of concept; templates; or other related technology (including any of the foregoing that are provided by our personnel) is provided to you as AWS Content under the AWS Customer Agreement, or the relevant written agreement between you and AWS (whichever applies). You should not use this AWS Content in your production accounts, or on production or other critical data. You are responsible for testing, securing, and optimizing the AWS Content, such as sample code, as appropriate for production grade use based on your specific quality control practices and standards. Deploying AWS Content may incur AWS charges for creating or using AWS chargeable resources, such as running Amazon EC2 instances or using Amazon S3 storage.
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages