- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Sustainability Insights Framework on AWS
Guidance for Sustainability Insights Framework on AWS
Overview
How it works
Overview
The SIF is composed of a suite of modules focusing on a specific set of features. This conceptual architecture shows these modules and their interactions.
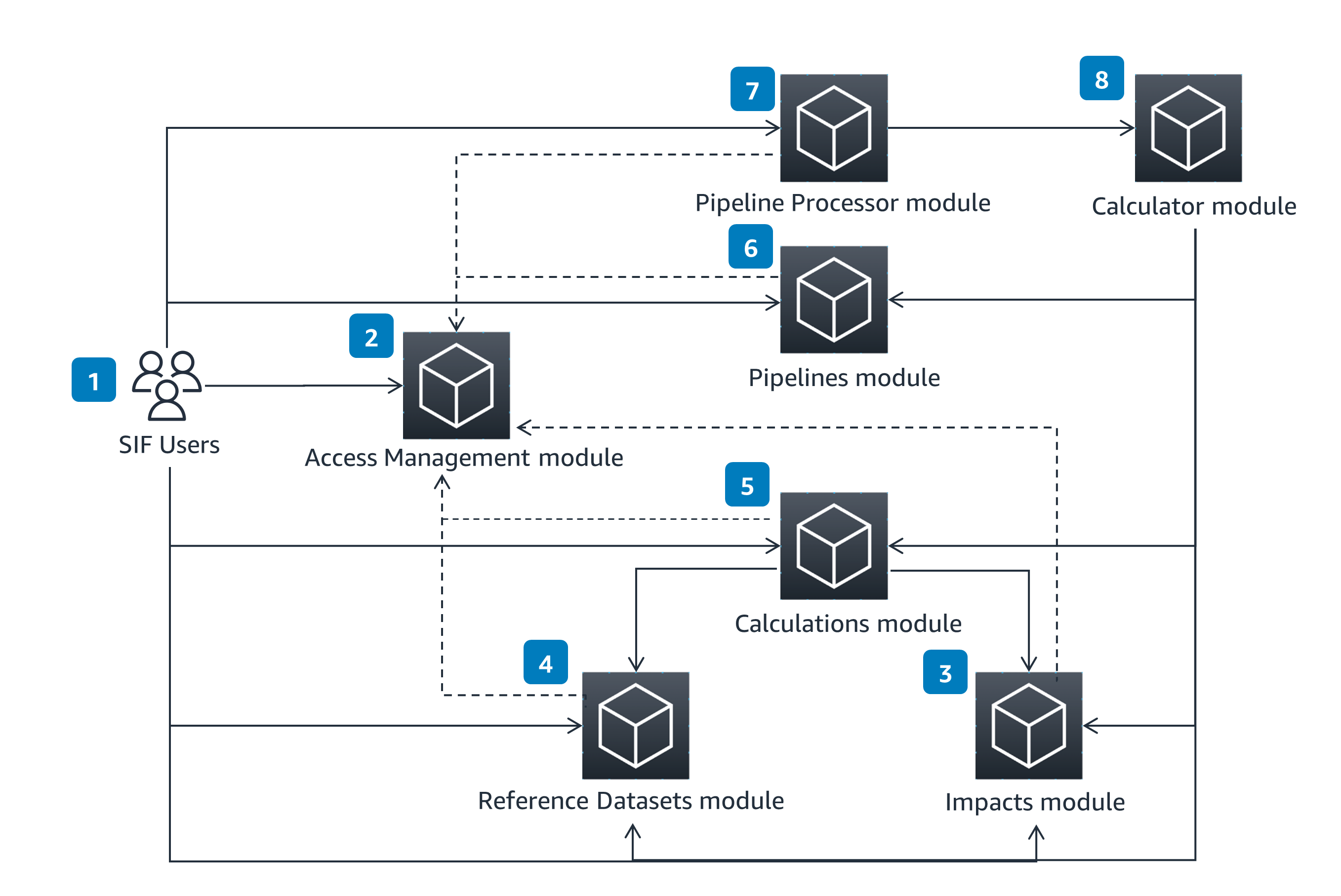
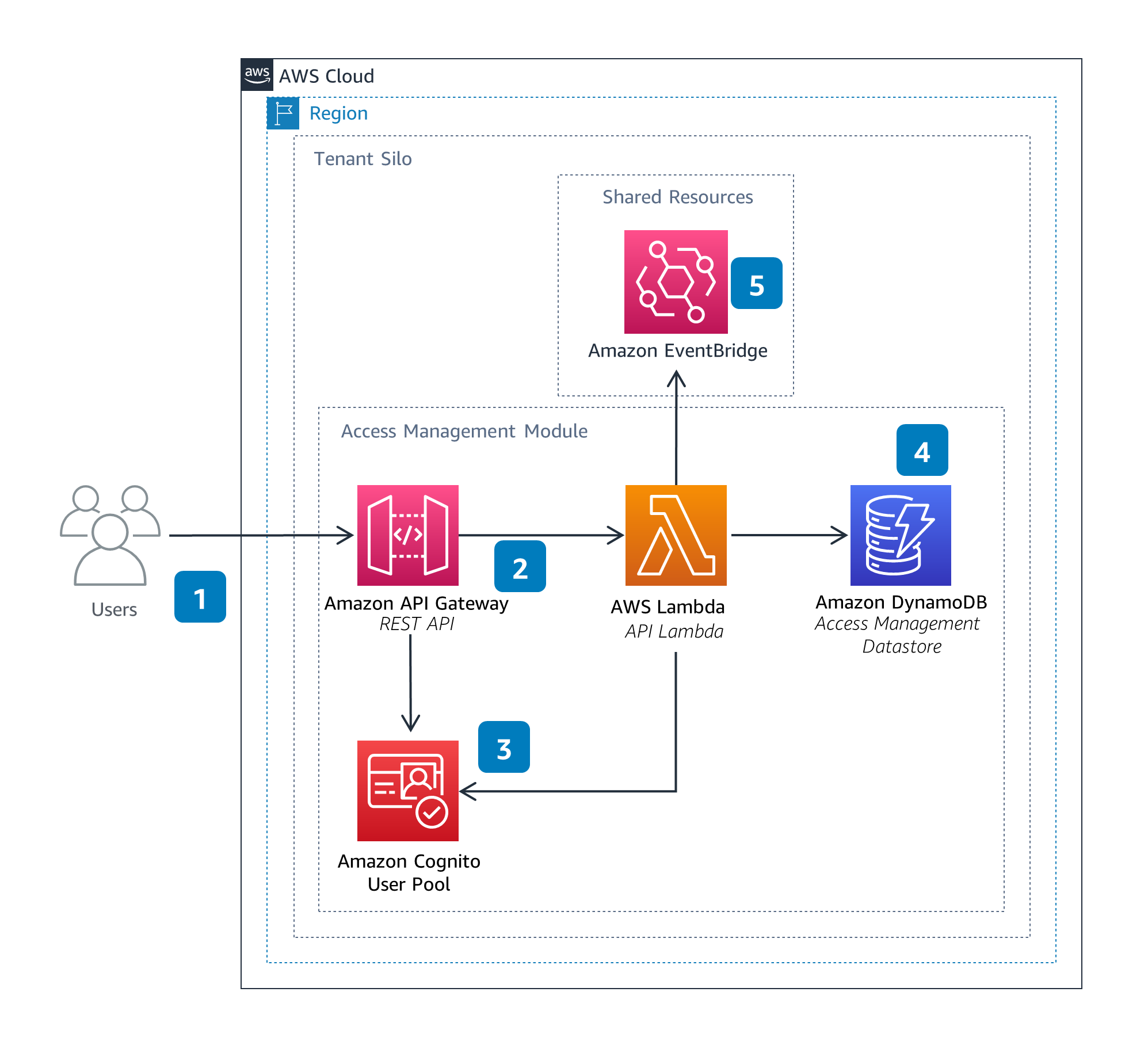
Access Management
The Access Management Module uses the concepts of users and groups to allows for permissions management and segregation of resources within SIF. SIF users can define users and groups through an external REST API.
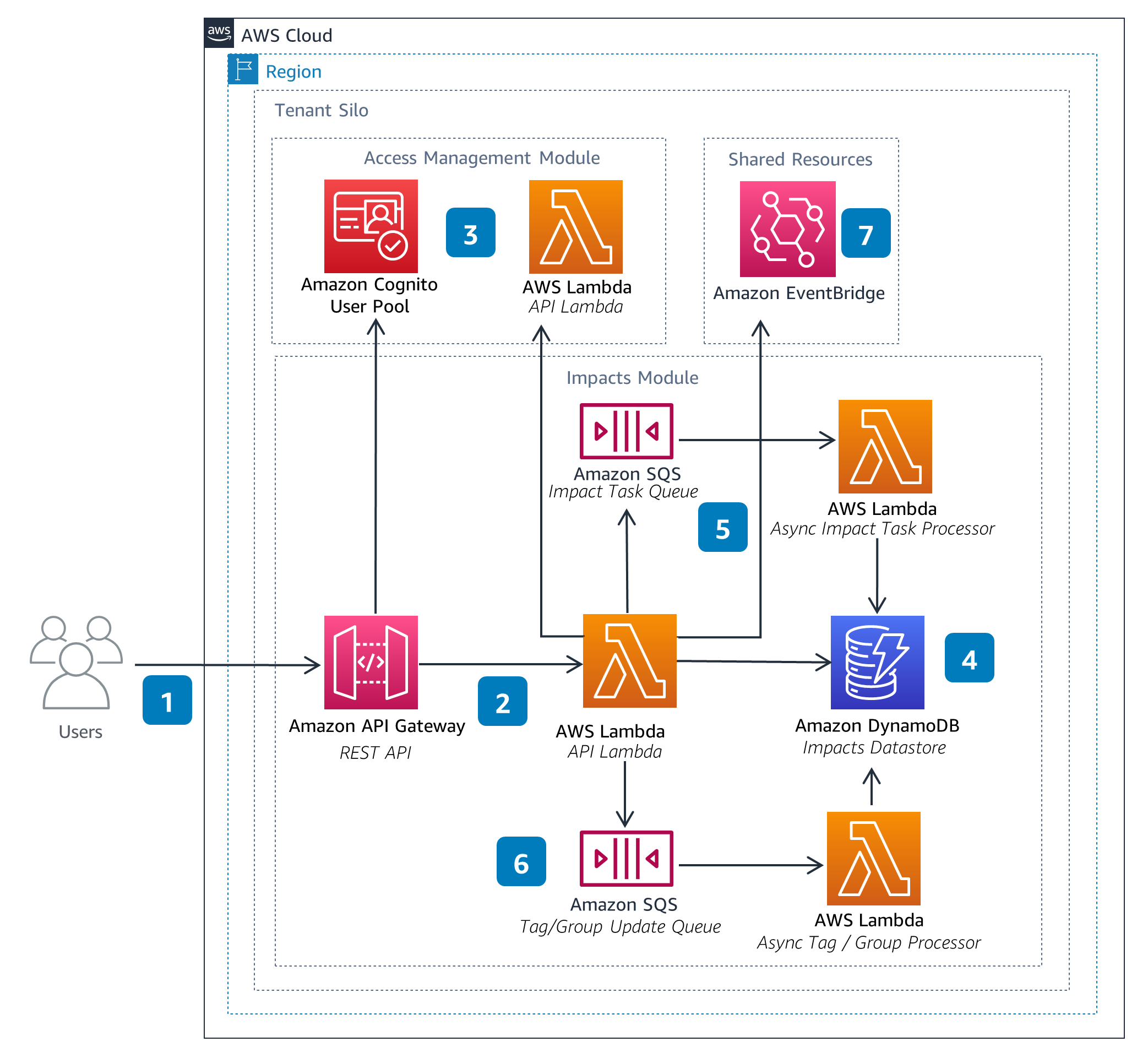
Impacts
The Impacts Module enables users to manage impact-related resources. These resources can be referenced from within the Calculations and Pipelines modules when performing data processing calculations, such as emissions.
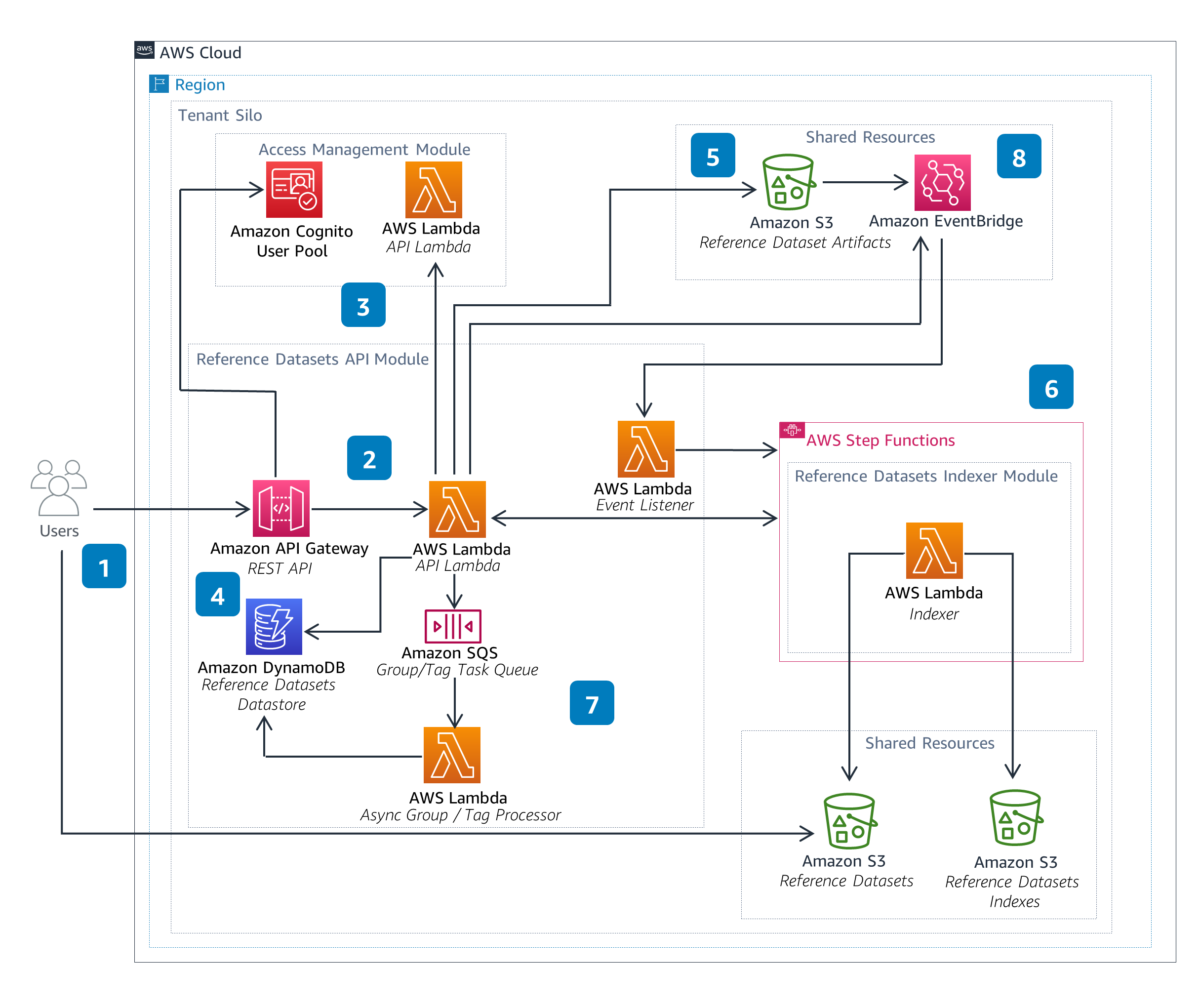
Reference Datasets
The Reference Datasets Module enables users to manage datasets, such as lookup tables. These datasets can be referenced from within the Calculations and Pipelines modules when performing data processing calculations, such as emissions.
How it works (continued)
Calculations
The Calculations Module enables users to define and manage equations or functions. These equations or functions can then be referenced in other Calculations or Pipelines modules when performing data processing calculations, such as emissions.
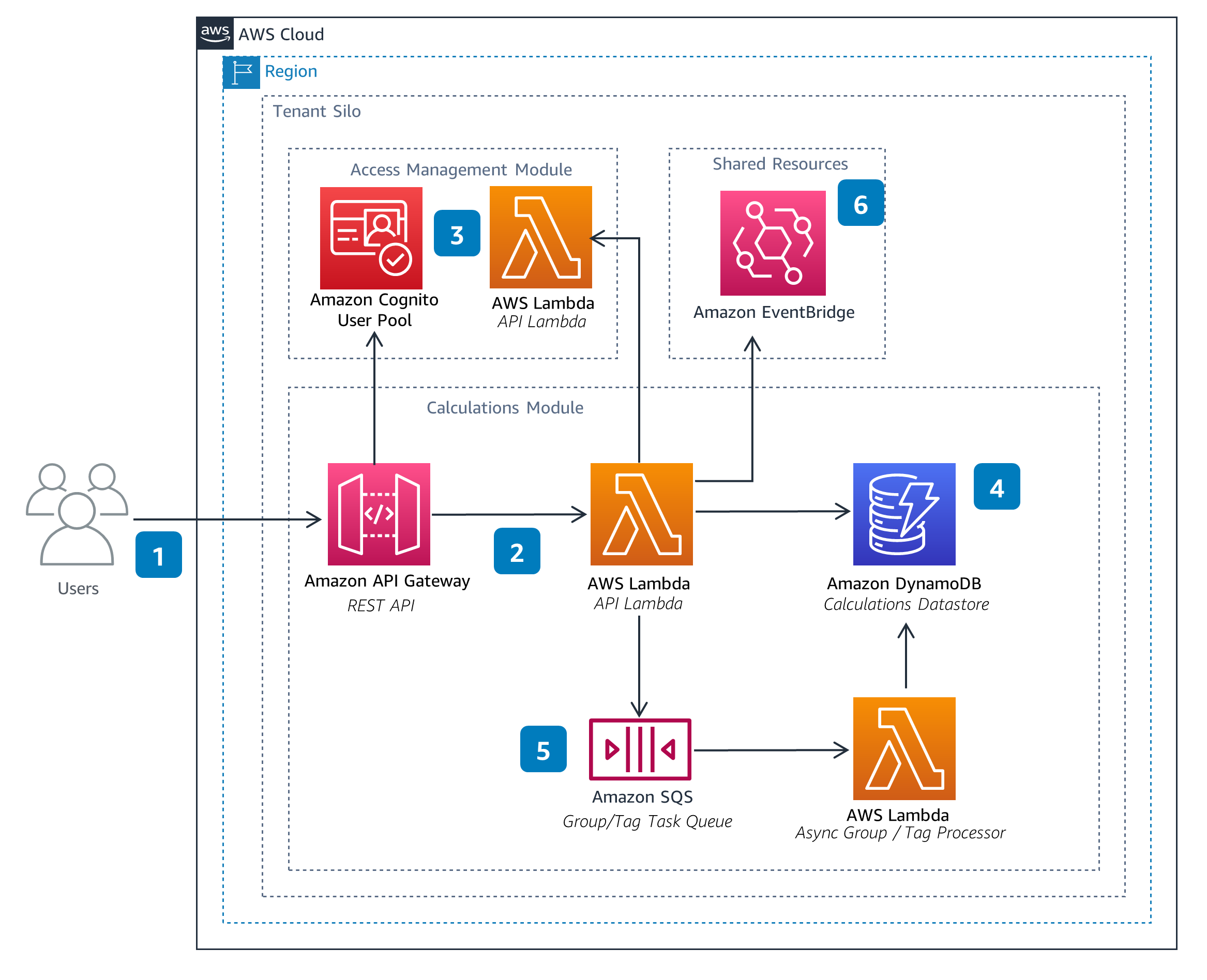
Pipelines
The Pipelines Module enables users to manage Pipeline configurations. These configurations define data processing pipelines used to perform calculations, such as emissions. A Pipeline can be configured to aggregate outputs across executions and groups into metrics. Metrics capture key performance indicators (KPIs), such as total emissions over time.
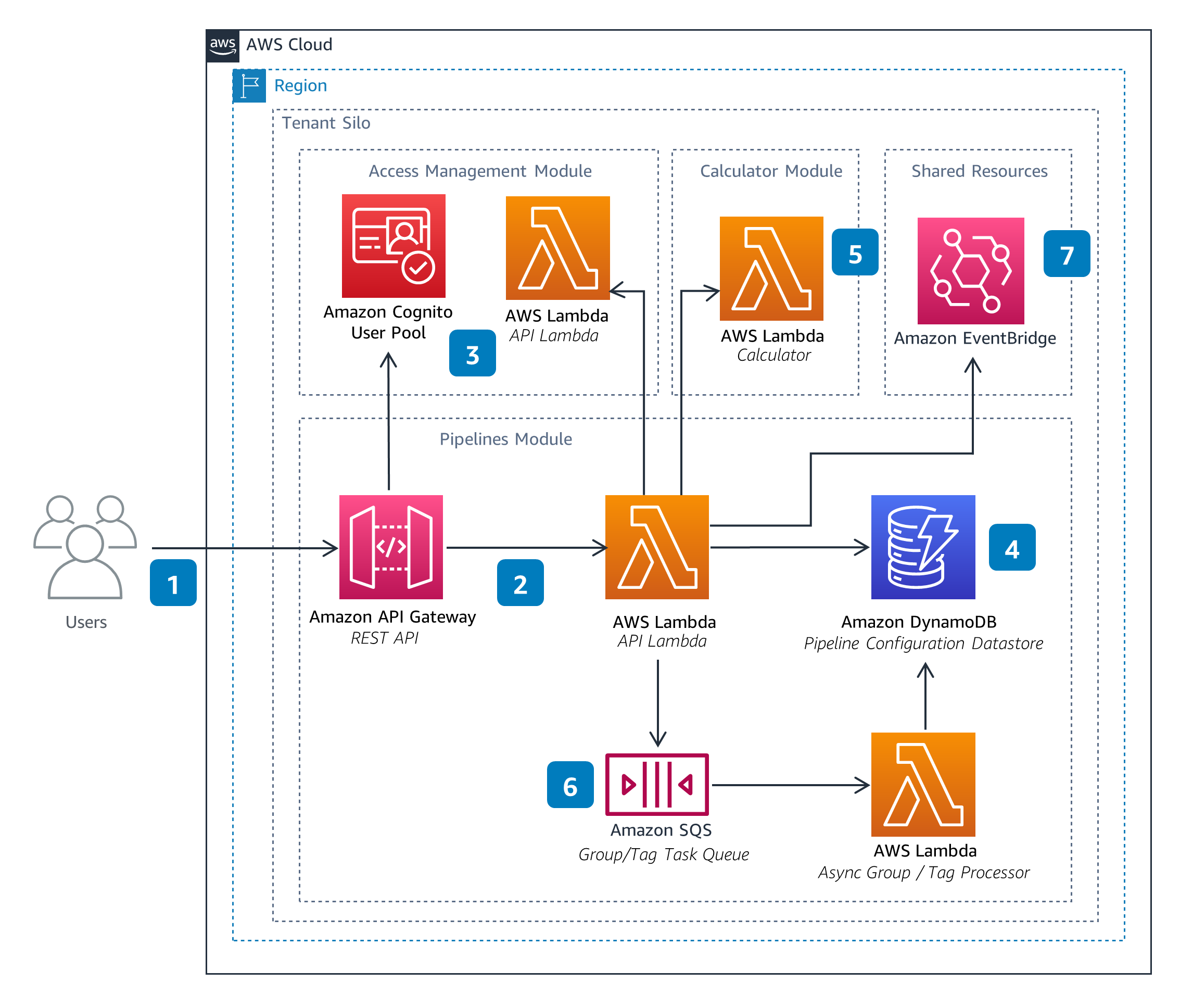
Pipeline Processor
The Pipeline Processor Module is responsible for the orchestration of Pipelines. This includes starting a pipeline execution in response to input files provided by a user and performing any aggregations defined in the pipeline configuration. The Pipeline Processor module also provides the status of pipeline executions.
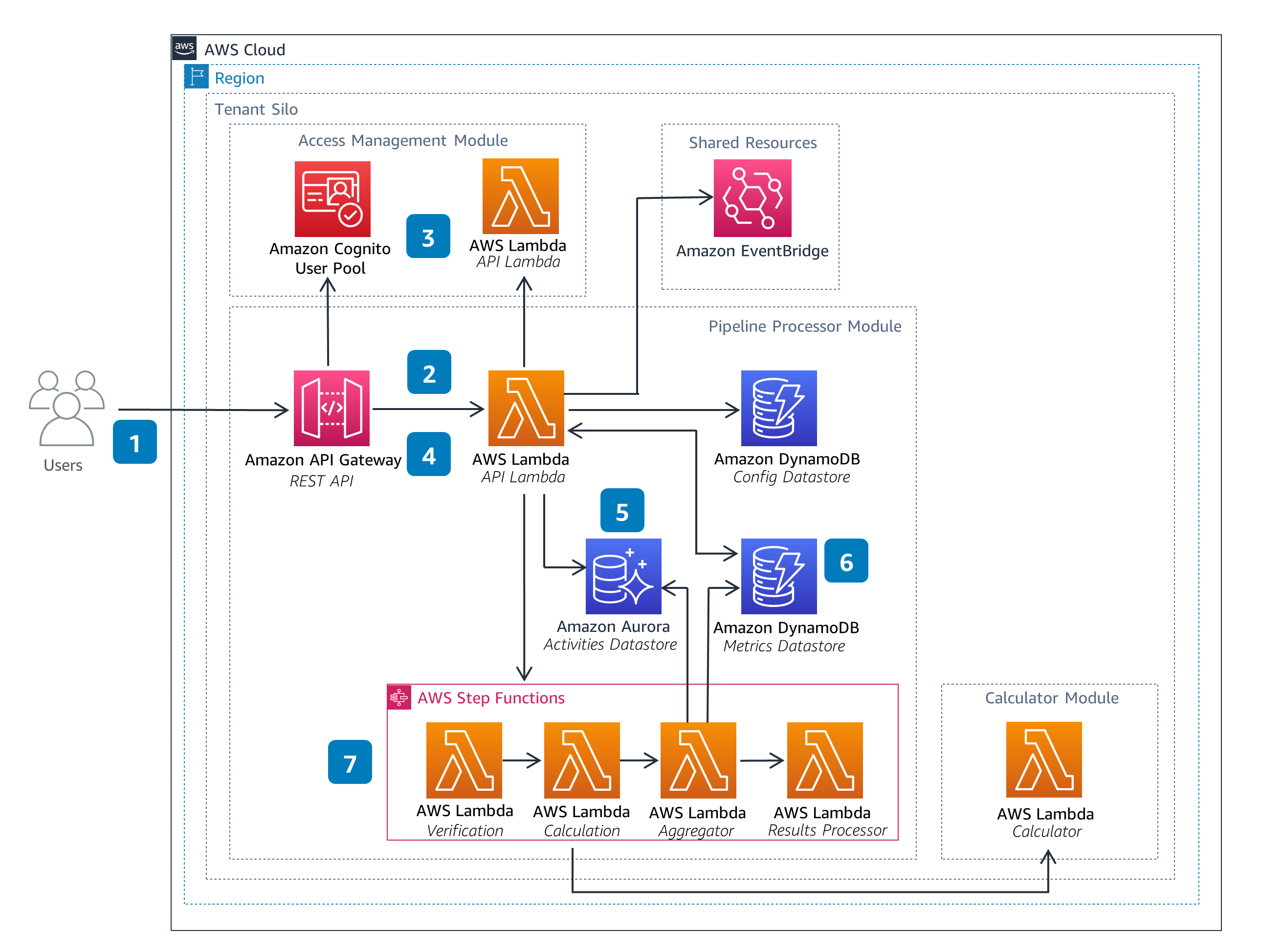
Calculator
The Calculator Module is a backend component which parses and executes the operations defined within a pipeline. This can include arithmetic operations or lookups of resources, such as Reference Datasets and Impacts.
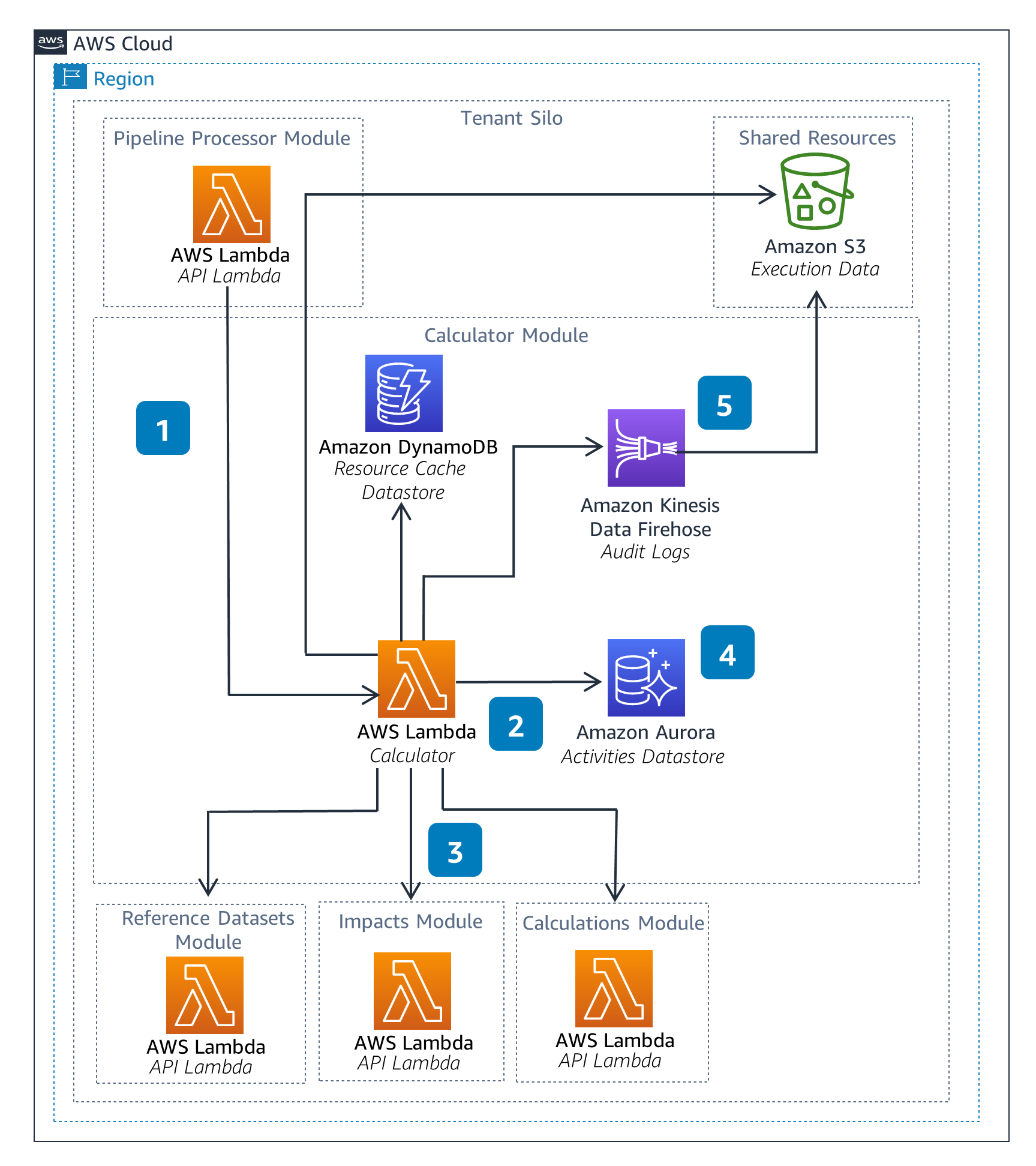
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
Deployments for infrastructure and application code changes can be done through AWS CloudFormation and the AWS Cloud Development Kit (AWS CDK). Integration tests exist for all of the modules in addition to tests for end-to-end scenarios. These tests can be run to verify deployments.
The infrastructure components of this Guidance were selected to help secure your workloads and minimize your security maintenance tasks. Amazon Cognito and the Access Management module are utilized for user authentication and authorization, respectively. Database services use encryption at rest, where permissions are set between tenants and tenant data is separated. Both external and internal interfaces are implemented in services that require TLS (HTTPS/SSL) to enforce data encryption in transit. Customer managed keys in AWS Key Management (AWS KMS) are used to encrypt data in Kinesis Data Firehose.
For a workload to perform its intended function correctly and consistently, managed services including Lambda (for computing), API Gateway (for API), and Amazon SQS (for messaging) are used. This ensures that your core services are deployed across multiple Availability Zones.
Key components in this Guidance are split into separate microservices with clear REST interfaces defined between the services. Retries with backoff limits are implemented in clients between services, allowing for reliable application-level architecture.
Deployment of this Guidance can be done through infrastructure as code (IaC). This makes it possible to deploy one-off deployments and hooks in continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. Parameters and environment variables for the applications are handled through standard mechanisms such as AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store.
Database services in this Guidance were chosen based on the access patterns and use cases required. DynamoDB was chosen for the NoSQL datastore use cases, and Aurora Serverless v2 was chosen for the data layer requiring relational access patterns. Additionally, deployment of this Guidance can be done through IaC. Customers can quickly deploy and test this Guidance with their data and use case, and they can terminate services just as quickly when they are done. Customers are able to select their preferred AWS Region to deploy this Guidance using the provided IaC tooling.
To help you build and operate cost-aware workloads, this Guidance gives you the option to enable a flexible pricing model. Compute Savings Plans can be enabled for Lambda to help reduce your costs. You can also assign cost-allocation tags to organize your resources and track your AWS costs on a detailed level. To help you scale using only the minimum resources, this Guidance utilizes services in layers. The compute layer uses Lambda while the data layer incorporates the auto scaling capabilities for Aurora and DynamoDB, ensuring resources are scaled based on demand.
Primary services within the architecture, such as Lambda, DynamoDB, and Aurora, offer automated scaling, which optimizes resource utilization. These services can scale from zero to peak demands to ensure the minimum provisioned capacity is used to meet demand. This Guidance also follows a serverless architecture, in which compute can be scaled up and down with demand.
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages