- What is Cloud Computing?›
- Cloud Computing Concepts Hub›
- Artificial Intelligence
What Is Cognitive Computing?
What Is Cognitive Computing?
Cognitive computing is the process of making software reason and “think” like a human. Humans' innate, advanced reasoning ability allows us to adapt to new situations and solve complex problems. For example, a human lost in the woods might move towards the water to survive or the traffic noise to find help. Similarly, cognitive computing aims to simulate human thought processes in software systems via perception, attention, and memory.
Traditional artificial intelligence (AI) systems can solve problems they are trained specifically for, such as analyzing data, making predictions, or generating text as the user directs. However, cognitive computing aims to take artificial intelligence further by teaching software systems to meet predetermined goals through independent decision-making in response to environmental changes.
Cognitive computing example
Consider an appointment-scheduling task for a specialist in your organization. New appointments should be made only in the afternoons when the specialist is available and has an existing relationship with the client. Appointments should also be made within 2 weeks of request. However, there are nuances to these conditions, such as
· Angry or upset clients receive early appointments, including in the mornings.
· Appointments may be requested beyond the two-week window.
· Certain long-term clients may require special considerations, like a personalized email once the booking is done.
Typically, AI can be trained to automate the task by fulfilling the primary conditions, but it cannot handle the nuances like a human professional would. However, cognitive computing is AI technology that can adjust conditions as needed to meet the goal of customer satisfaction while booking. For example, it might read the sentiment of the customer's message and prioritize their booking or schedule an early morning appointment to meet the needs of a long-term client.
What are the benefits of cognitive computing?
Cognitive computing brings various benefits to organizations.
Improve productivity
Human-AI teams can collaborate to perform complex tasks faster and more efficiently. For example, consider a cognitive computing solution assisting a human software developer. AI can review the code and highlight vulnerabilities or bugs for humans to fix. It can also keep track of environment changes, such as software updates or feature requests, and suggest new modifications as needed.
Improve complex decision-making
Traditional complex decision-making might require multiple people involved in the process, subject matter expertise, and the gathering and processing of other information relevant to the decision. Cognitive computing systems augment this process while keeping long-term goals in mind.
Support education and training
Cognitive computing technology can reduce the time and effort required to learn new information. It can quickly process and assimilate large structured and unstructured data sets and present the information systematically for human education and analysis. It can also acquire specialist or technical knowledge and support human effort in complex fields like quantum computing and genomic research.
What are the applications of cognitive computing?
Cognitive computing is designed to excel in applications requiring reasoning and simulation of human thought processes. These include problem-solving where there is ambiguity, the context has not been specified, or deep prior learning is a prerequisite.
We give some examples below.
Healthcare
Cognitive computing systems can be used within healthcare for better provider and patient outcomes. Within the healthcare setting, the applications of cognitive computing include:
· Customer service interactions
· Patient history amalgamation
· Personalized treatment options
· Patient monitoring and medication adjustments
· Real-time data analysis and forecasting for technicians and specialists.
Cybersecurity
Cognitive computing can be applied to many problems within the cybersecurity field. Cybersecurity suffers from a growing complexity problem as adversaries adjust techniques to evade cyber defenses. Within the cybersecurity field, cognitive computing can be used to:
· Monitor networks, assets, and endpoints for abnormal activities with a wide contextual scope and history
· Provide security teams with deep, contextual, real-time information on alerts
· Conduct quarantine activities automatically on high-risk events
IoT and IIoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) blend physical devices, environmental monitoring, and internet connectivity. Cognitive computing supports adaptive lighting, fitness trackers, and patient monitoring systems. It can also play a key role in energy management, predictive maintenance, and vehicle fleet monitoring systems
Some examples of cognitive computing applications in IoT and IIoT are:
· Offering complex feedback for patient monitoring systems
· Real-time, data-rich visualization of the state of industrial environments, including actionable alerts
· Autonomous aquatic vehicles for exploring and monitoring the deep ocean
How does cognitive computing work?
Cognitive computing works using neural networks that mimic the human brain. It combines multiple interdisciplinary machine learning algorithms or AI applications to perform a task. For example, a single cognitive computing app might combine natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, speech-to-text, and other specialty technologies. The types of artificial intelligence technologies required for a cognitive computing app depend on the task.
AI agents
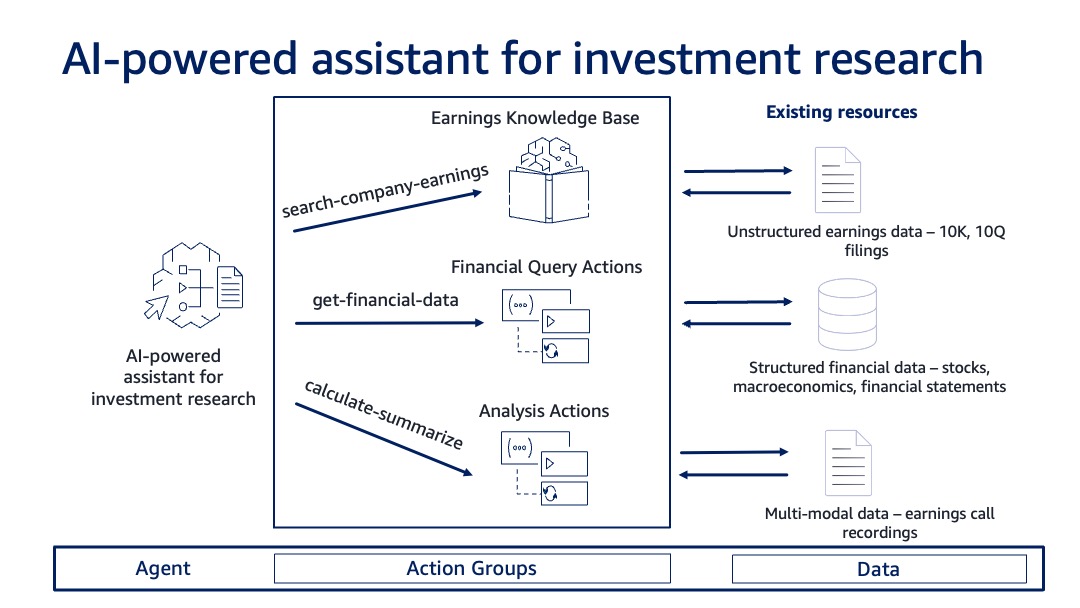
AI agents are the currently available, practical application of the cognitive computing model. An AI agent has a set of available tools (such as apps, plugins, or functions), as well as reasoning and planning abilities to use the tools to accomplish a goal.
For example, you can build an inventory management agent that determines product availability in the inventory system. The agent analyzes the task and breaks it into the correct logical sequence. It can call the necessary APIs to transact with the company systems and processes to complete the task, determining along the way if it can proceed or needs to gather more information.
Agents also have the ability to retain memory across interactions, offering more personalized user experiences and improved accuracy of multistep tasks. They can be used alone or in a team or hierarchical structure as needed.
Cognitive computing vs. AI
Cognitive systems are machine-based systems that mimic human cognition. The term cognitive computing indicates technologies that are a subset of the broader field of artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence is an umbrella term for all machine behavior that approximates a human. The cognitive AI focuses specifically on reasoning and decision-making. It attempts to perform tasks beyond the singular goals and processes of traditional ML/AI systems.
How can AWS support your cognitive computing requirements?
Generative AI services help you build cognitive computing apps and AI agents faster, smarter, scalably, and cost-effectively. Amazon Bedrock is a fully managed service that offers a choice of industry-leading foundation models (FMs) along with a broad set of capabilities needed to build generative AI applications. It provides the foundation of your cognitive computing apps and AI agents with fast integration, customization, fine-tuning, and deployment.
Amazon Bedrock Agents automates multistep tasks by seamlessly connecting with company systems, APIs, and data sources. Building an agent is straightforward and fast, and setup can be done in just a few steps. The AI agent can:
· Connect to your company’s data sources and augment the user request with the right information to generate an accurate response.
· Retain memory across interactions, offering more personalized and seamless user experiences.
· Dynamically generate and execute code in a secure environment.
· Create a prompt template based on user instructions, action groups, and knowledge bases.
You can also build and manage multiple specialized agents seamlessly working together to address increasingly complex business workflows. Each agent focuses on specific tasks under the coordination of a supervisor agent, which breaks down intricate processes into manageable steps for precision and reliability.
Get started with cognitive computing on AWS by creating an account today.