How was this content?
- Learn
- The latest generative AI trends to address the climate crisis
The latest generative AI trends to address the climate crisis
In the Paris Climate Agreement of 2015, global nations signed up to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2050. With that date just 26 years away, the race to transition to clean technologies has never been more pressing. The effects of climate change are already being felt with more frequent wildfires, extreme heat, flooding, and crop failure. The shift to a net-zero economy will need to be as big as the industrial revolution. Where that revolution gradually unfolded over 180 years, this one will need to happen in just 26 years. Luckily, innovators today have access to advanced technology and artificial intelligence (AI) that can accelerate the transition to net zero.
On AWS, startups are using generative AI to address this challenge. Earlier this year, we shared how the first wave of climate tech startups are using generative AI to more efficiently manage their operations, deploying it to rapidly unlock important information contained in long and complicated documents. Now, climate tech startups are using generative AI to accelerate product development, save money for their customers, and prove what’s possible at a previously unimaginable scale.
Emerging generative AI trends in climate tech
- Developing Foundation Models (FM) based on real world data, including the natural world, weather, material science, and others.
- Using generative AI to discover and design new science, including the development of sustainable materials, genetic mapping, and more.
- Optimizing business operations to save time and money through enhancements to categorization, document ingestion, and automation.
- Creating synthetic data to train machine learning (ML) models when data isn’t readily available.
- Using Small Language Models (SLM), specialized smaller models that have their capacity concentrated on a specific target task, to optimize generative AI workloads for environmental sustainability and cost.
How Insilico uses generative AI to discover and design sustainable materials

Insilico Medicine is a global clinical-stage biotechnology company powered by generative AI that initially focused on accelerating drug discovery. It has since expanded its platform to discover and design sustainable materials and agrochemicals. Insilico initially built Pharma AI, which uses generative AI to identify targets and rapidly generate and optimize molecules to develop and advance its own pipeline of programs to clinical trials in record time. Insilico also offers the Pharma.ai platform as SaaS products hosted on AWS. On average, in the pharmaceutical industry, the journey from target identification to clinical candidate selection involves synthesizing and testing thousands of compounds and takes more than 4.5 years. Insilico's generative AI approach allows for precise multiparametric optimization, typically reducing the average number of synthesized molecules per program to fewer than 100 from hit identification to preclinical candidate nomination in only 12-18 months. In addition to making the process faster and more affordable, the process is approximately 10 times less wasteful than the traditional approach. Together with Amazon, Insilico Medicine has also built what they believe to be the largest molecule dynamics data set in the world generated using High Performance Computing (HPC) on AWS with Amazon EC2, Amazon FSx, Amazon S3 and Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA). A unique dataset that can be leveraged in multiple ways to enhance the accuracy and speed of small molecule drug discovery and development.
Insilico is now applying its generative AI platform to discover and design sustainable materials. Their platform uses Amazon SageMaker to train new Foundation Models quickly and generate optimized molecular structures. SageMaker enables parallel processing of complex computational tasks, seamlessly scales resources for model evaluation, and provides Insilico with on-demand access to cutting-edge GPUs and CPUs. To get started in sustainable materials, Insilico partnered with a large global agricultural technology company to create greener, safer, more effective herbicides. Herbicides are important for protecting crops and enabling farmers to grow food affordably, but they can harm the surrounding environment. Working closely, they leveraged Insilico’s generative AI-powered small molecule generative chemistry technology and expertise to design and optimize potential active herbicides more quickly and better for the environment and human health.
Insilico is not stopping there. They recently announced the launch of the Generative AI for Environmental Sustainability Consortium, with the mission to develop open source cutting-edge generative AI technologies for environmental sustainability. It is an open source platform for scientists and academic labs to contribute models and data to advance the fields of 1) carbon capture 2) hydrogen storage, 3) agrichemistry, and 4) base oils and lubricants. Scientists can submit models for review. The platform offers a benchmarking system so that scientists can understand which models are best for which purposes.
NET2GRID deploys generative AI to help utility companies accelerate the energy transition
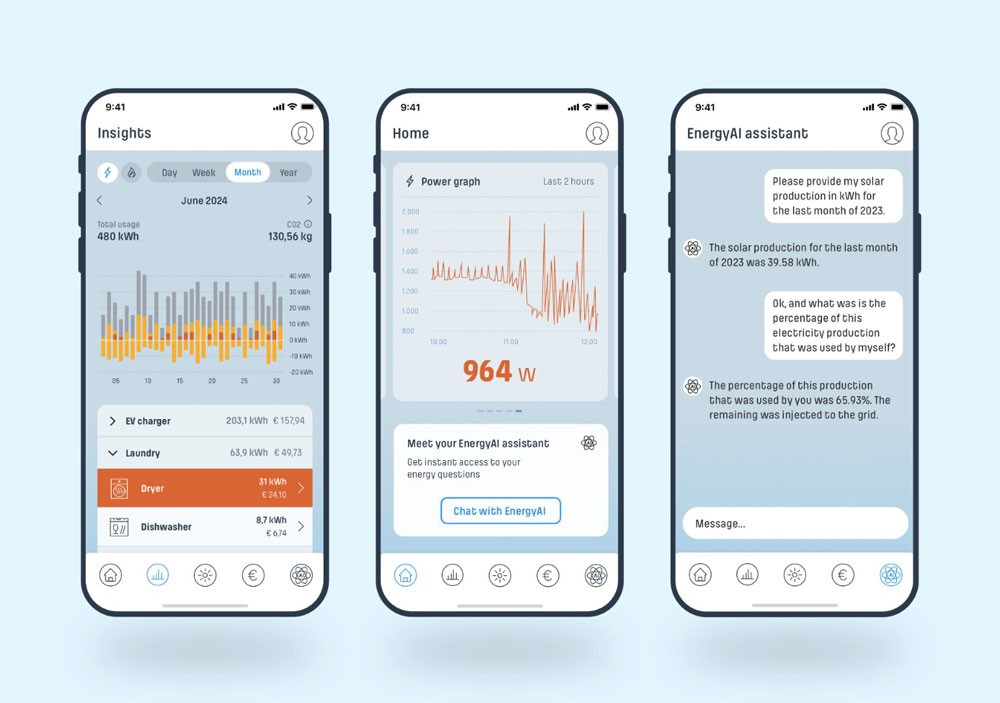
The electric grid’s complexity is growing rapidly as energy providers shift to intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind, which produce different amounts of electricity during different times of the day. This variability, coupled with climate change-driven extreme weather creates extreme electricity demand and pricing spikes. If not managed well, spikes can lead to grid instability. A Wall Street Journal study indicates that incidences of prolonged blackouts have doubled since 2013. In addition, the IEA’s World Energy Outlook 2022 found that energy prices have surged by 30% in the last decade, causing customers to seek ways for energy bill reduction.
NET2GRID’s EnergyAI platform uses generative AI to enable utilities to provide their customers with energy usage insights and recommendations that reduce costs, balance the grid, and avoid outages. EnergyAI Assistant helps utility customers easily understand their energy usage, cut costs, and improve efficiency. The system is powered by large language models (LLMs) that leverage analytics APIs to provide utility customers with personalized insights and recommendations on energy consumption. It empowers households and businesses with advanced energy analytics and forecasting that was previously prohibitively expensive and only available to industry experts. The system can identify the energy usage of specific appliances and historic energy use so that utility customers know where to find savings. It also offers sophisticated forecasting of future energy consumption and electricity pricing so that users can avoid peak rates and reduce costs.
NET2GRID uses Amazon Sagemaker for fine-tuning and deploying scale-based LLMs based on Llama 7B. They use AWS Inferentia2, AWS’ custom high-performance machine learning inference chip, for cost-effective and energy-optimized deployment of AI models. Finally, they use AWS Lambda functions to run code responding to specific triggers or events, ensuring the assistant remains responsive and efficient without needing continuous server management.
Implementing the EnergyAI Assistant offers benefits for both energy providers and their customers. The assistant significantly enhances the customer experience by providing quick, personalized responses to energy-related questions. Available around the clock, this level of support can help improve customer satisfaction and help them reduce their energy usage. This in turn helps utilities manage the grid and avoid costly outages. The technology also helps energy providers cut their cost-to-serve by up to 25% through more efficient first-level customer support. Additionally, the insights generated by the assistant can reduce market analysis and survey costs by as much as 20%, leading to significant cost savings.
Connect Earth helps bank customers make climate-informed purchasing decisions using generative AI
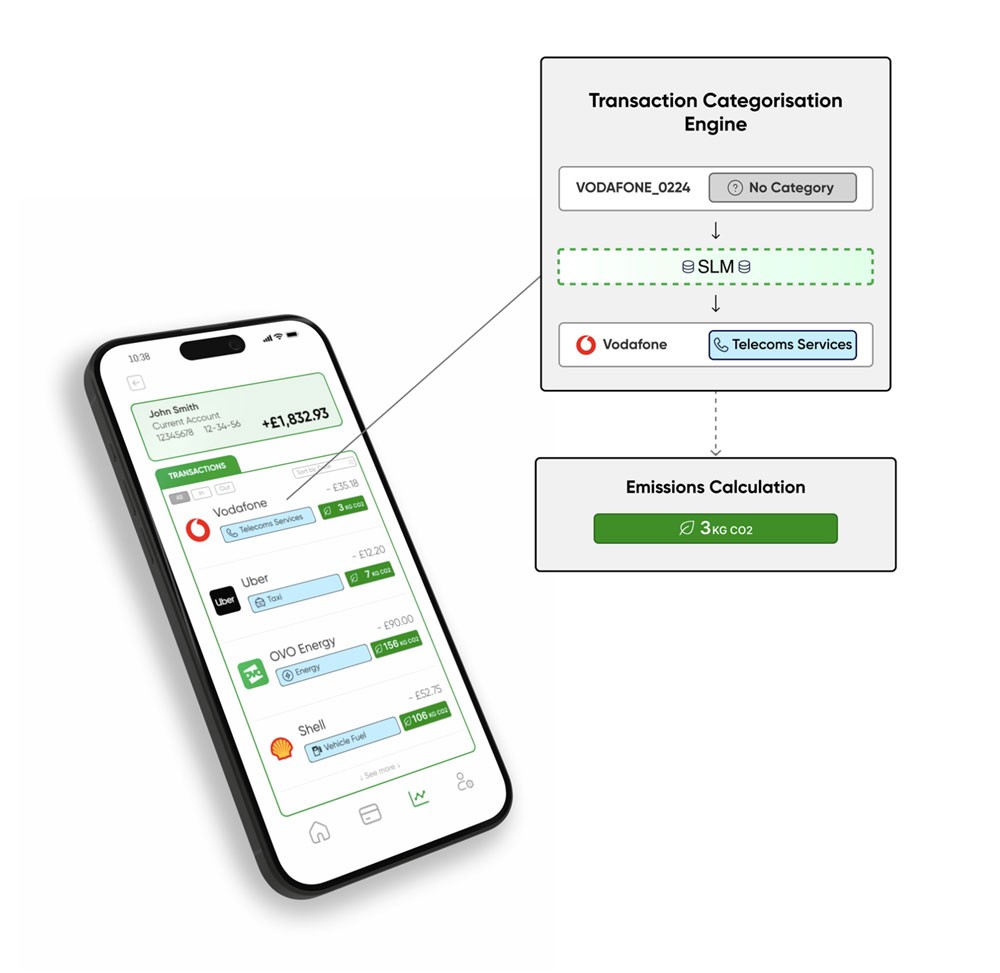
As the world races to get to net-zero greenhouse gas emissions, greenhouse gas reporting is now mandatory in 40 countries, including the UK, many EU member states, Australia, Japan, and the US. According to CDP, a nonprofit that runs global disclosure systems, more than 23,000 companies, representing two third of global market capitalization, report emissions data to them. More than 10,000 companies have publicly announced greenhouse gas reduction goals, including Amazon and the 500+ signatories of the Climate Pledge to get to net-zero emissions by 2040, which Amazon co-founded. To enable these efforts, Connect Earth provides a suite of AI-driven API tools that help financial services institutions and customers calculate and reduce greenhouse emissions.
Connect Earth uses generative AI on AWS to seamlessly integrate environmental impact assessment into everyday banking. By analyzing a comprehensive set of data points—including transaction descriptions, bank-provided categories, dates, currencies, and regional information—the system not only categorizes transactions with precision but also associates each one with its corresponding estimated carbon emissions. This approach empowers bank customers with a clear understanding of their personal and business carbon emissions, enabling them to make environmentally conscious purchasing decisions and take active steps to reduce their carbon footprint.
Connect Earth integrates generative AI on AWS in three ways. First, generative AI is used to categorize and label transactions to estimate the carbon footprint, a formerly manual process. Connect Earth fine-tunes DistilBERT for sequence classification, a distilled version of BERT that has 40% fewer parameters, runs 60% faster, and preserves over 95% of BERT’s performance. Second, when data is not accessible or regulation restricts usage, synthetic data is generated to train its models, using Small Language Models (SLMs) such as Mistral 8x7B via AWS Bedrock. Finally, Connect Earth is exploring open-source SLMs, such as Llama 7B for extracting data from unstructured inputs to feed into its model, to deliver impressive results with a fraction of the computational resources of a Large Language Model (LLM). By embracing energy-efficient algorithms and SLMs, Connect Earth is reducing costs and following AWS best practices for optimizing Machine Learning workloads for Sustainability. Connect Earth stack is deployed on AWS serverless computing: APIs are powered by AWS Lambda and models are deployed on Amazon SageMaker Serverless Inference. This scalable infrastructure enables Connect Earth to process millions of transactions per day.
Through this generative AI pipeline, the company estimates that they are now doubling the number of transactions for which they provide carbon data, and will soon enable the calculation of emissions for unstructured data sources, such as invoices. Bank customers receive additional benefit as well: previously, accountants manually categorized spending to determine carbon emissions estimates, taking 10-20 hours per company per year. Now that process has been eliminated, saving bank customers time and money.
Start building now, with AWS and generative AI
AWS is committed to helping startups speed up the fight against the climate crisis by leveraging generative AI. Through the AWS suite of tools, startups can quickly develop solutions to enable the discovery of more sustainable materials, reduce the timeline for scientific discovery, speed up operations and lower costs, or even generate synthetic data. Together, we will all lead the charge to fight climate change.
Find out how AWS can help your startup take advantage of the transformative power of generative AI, by learning more about Amazon Bedrock and the AWS Startups program.

Lisbeth Kaufman
Lisbeth Kaufman is the Founder and Head of the Climate Tech Startups BD team at Amazon Web Services. Her mission is to help the best Climate Tech startups succeed and reverse the global climate crisis through access to AWS’ cloud technology. Her team has technical resources, go to market support, and non-dilutive funding to help climate tech startups overcome obstacles and scale. With expertise at the intersection of climate and startups, Lisbeth was Founder and CEO of KitSplit.com, a sharing economy company called “the Airbnb of Cameras” by Forbes, and LucidHome.co, easy-to-understand climate risk reports for any address in the U.S. Before she was a founder, Lisbeth worked on climate policy as an energy/environment/agriculture policy advisor in the U.S. Senate. There she built a first-of-its-kind energy efficiency retrofit program and wrote a clean energy bill for farmers that got passed into law. Lisbeth has a BA from Yale and an MBA from NYU Stern where she was a Dean's Scholar. As a mentor at Techstars, Venture for Climate, and the Entrepreneurs Roundtable Accelerator Lisbeth mentors climate tech founders on product, growth, fundraising, as well as making strategic connections to teams at AWS and Amazon.

Benoit de Chateauvieux
Benoit de Chateauvieux is a Startup Solutions Architect at AWS, based in Montreal, Canada. As a former CTO, he enjoys helping startups build great and sustainable products using the cloud. Outside of work, you’ll find Benoit in canoe-camping expeditions, paddling across Canadian rivers.
How was this content?