Obayashi Corporation Develops Scalable HPC/HTC for Environmental Analysis (Simulations) in Urban Development, Making HPC Wind Environment Analysis up to 640 Times Faster
Learn how Obayashi Corporation uses AWS HPC and serverless solutions to achieve 640x faster wind analysis and streamline urban environmental simulations.
Benefits
Overview
Obayashi Corporation is one of Japan’s leading construction management companies, providing construction and urban development services both domestically and internationally. Environmental analysis plays a critical role in ensuring optimal design and safety for its construction and urban planning projects, but it requires substantial computational power.
To meet these demands, Obayashi turned to Amazon Web Services (AWS) to build a flexible and scalable analysis system. Using AWS, the company accelerated its high-performance computing (HPC) analysis of urban wind environments by up to 640 times and leveraged serverless high-throughput computing (HTC) to achieve CPU performance comparable to GPU processing.
About Obayashi Corporation
While primarily focused on construction in Japan, Obayashi Corporation operates globally in construction and engineering services, land development, green energy, and new business initiatives. As part of its medium-term Business Plan 2022, the company aims to “realize a sustainable society” in line with its corporate philosophy. To achieve this, Obayashi is driving innovations and strengthening its core business through three main strategies: deepening its core construction expertise, advancing technological and business innovations, and expanding its business portfolio to support long-term growth.
Opportunity | Overcoming Computational Challenges for Environmental Impact Analysis in Urban Development
Obayashi Corporation’s group vision is “MAKE BEYOND—Transcending the Art and Science of Making Things”. Its goal is to expand beyond its current business boundaries by integrating advanced technology into projects. In urban development, structures don’t just define physical space—they also influence the surrounding environment. For example, buildings can create wind patterns that impact pedestrian spaces, alter views and visibility from nearby structures, and affect how sunlight heats ground surfaces. As part of its urban development projects and high-rise building construction, the company requires these environmental factors to be thoroughly assessed.
To perform these assessments, Obayashi Corporation’s design department relies on 3D models to conduct environmental analysis, which demands significant computational resources. However, completing these analyses quickly has been challenging in its existing PC-based environment. “Our employees solely relied on PCs for analysis,” says Hirotsugu Ueda, Assistant Manager of Advanced Design, Design Solutions Department in Design Division of Obayashi Corporation. “They can secure the resource of few PCs at most. While our R&D team had a small HPC environment, they needed to request assistance from dedicated staff, making frequent use difficult.”
Furthermore, the team faced several issues with their analysis workload. Urban environment analysis begins with downloading the PLATEAU 3D city model, an open urban model data overseen by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism. They then combine data from PLATEAU with computer-aided design (CAD) data of the planned building to create a visualized model for analysis. The next step involves defining the requirements for analysis based on metrological data and generating a mesh for simulation. Following that, the team conducts analysis, evaluates results, visualizes the data, and compiles a report. Each of these steps was manual, leading to long coordination times between departments.
“The first challenge is obtaining data from PLATEAU,” says Ueda. “We need to download 3D urban models for planned sites using publicly available data from the website. After that, we must convert the data format—CityGML—into one compatible with construction simulation, such as the OBJ format. With around 210 cities in Japan, converting all the data, even when automated, takes over 200 hours. When the 3D model data is combined with analysis data, it amounts to gigabytes or even terabytes. These massive datasets are challenging to process and analyze on PCs, which is why we started considering cloud-based solutions.”
Solution | Building a Computing Environment with AWS Batch and Lambda
Ueda began developing open-source analysis tools and testing various cloud services in 2020, prioritizing computational efficiency and ease of use. The company ultimately chose Amazon Web Services (AWS) as the most comprehensive and advanced solution. “AWS stood out for the variety and stability of its computational resources,” says Ueda. “We could use up to 30 to 50 nodes per job, which was remarkable back in 2020.”
The business implemented Amazon Elastic Cloud Compute (Amazon EC2) Spot Instances to lower costs and used AWS Lambda to instantly scale up to thousands of computational resources, boosting efficiency. The availability of extensive technical documentation also meant Obayashi Corporation could save on training costs.
In 2021, the team developed an analysis tool, initially using it for wind analysis. To process the data, they used AWS Lambda and AWS Batch to convert information from PLATEAU into the OBJ format and stored the results in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3), making the converted data easily searchable. This approach significantly reduced the time needed to access 3D city models across Japan.
Each step of the analysis was then modularized using containers to streamline the process. The team leveraged fully managed AWS Batch for HPC analysis, which enabled large-scale parallel processing, while AWS Lambda handled high-throughput computing (HTC) analysis for high-speed serverless distributed processing. Standardizing each analysis component using containers and automating the entire workflow through AWS Step Functions allowed them to seamlessly switch between HPC and HTC processes as required.
“When we considered fully automating the process,” Ueda explains, “we explored AWS Batch and AWS Lambda. Modularizing the process with containers allowed us to flexibly allocate computational resources as needed. While building the workflow for the analysis module, we discovered AWS Step Functions. Six months later, AWS released the GUI-based AWS Step Functions Workflow Studio, which made it easier to build workflows exactly as we wanted. From there, we expanded our simulation products from wind analysis to include insolation analysis and viewshed assessment.”
Outcome | Accelerating 3D Model Processing and Large-Scale Analysis Efficiency
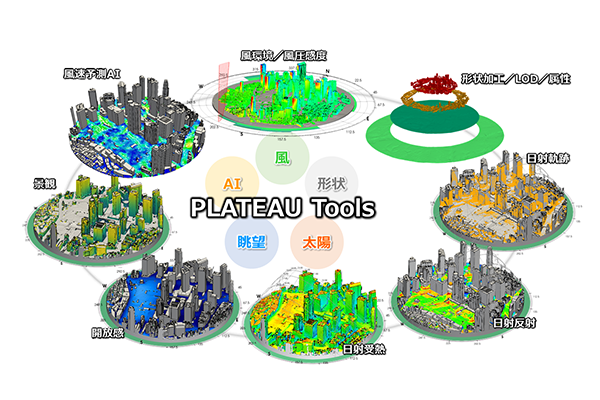
The company launched a suite of cloud analysis tools on AWS, named PLATEAU Tools, which can now be used whenever needed for various analyses. The current system functions as a program-based backend, primarily used by Ueda's team, which uses its AWS expertise to acquire PLATEAU models and perform environmental analyses.
Previously, it took 200 hours to download and convert PLATEAU data. With the new tools, the process is now 40 times faster, taking just 5 hours. The analysis itself has also been significantly accelerated. HPC analysis of urban wind environments, which requires extensive computational resources, is now 15 to 40 times faster per node with 48 cores. Simultaneous analysis of 16 wind directions is now 240 to 640 times faster.
For HTC analysis, the team uses serverless distributed computing to evaluate the viewshed from ground level and building facades. In one assessment, 300 million rays were generated and split into 3,000 segments to analyze intersections with objects, completing the process in under a minute.“
Not all simulations are suitable for GPUs,” says Ueda. “It’s extremely valuable to use existing CPU-based programs for large-scale distributed processing. With AWS Lambda functionality to quickly start and launch thousands of instances simultaneously, we were able to achieve GPU-level performance using only CPUs.”
AWS Step Functions have fully automated the analysis process, reducing tasks that previously took days or weeks to just minutes or hours. This shift has significantly boosted work efficiency and lightened the team’s workload.
Currently, PLATEAU Tools function as a backend solution, but the company is working on a web-based user interface to make them accessible to architects without AWS expertise. The goal is to extend the tools' usability to other simulations and expand the general user base.
“We want to make the tools more accessible for architects,” says Ueda. “We’re currently adding features for use in the early stages of design, such as route searches and street views. Our goal is to transform PLATEAU Tools into design and analysis solutions that streamline design workflows. We’re also exploring ways to integrate them with 3D modeling tools and PLATEAU data, enabling us to perform analyses within 3D urban models that include the proposed structure. In the future, we may develop add-ins for CAD software, allowing users to conduct analyses directly within their CAD programs.”
* PLATEAU Tools received the Mad Data Scientist Award at the PLATEAU AWARD 2022, a contest hosted by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism of Japan, recognizing services, applications, and content that leverage 3D urban models.
Learn More
Architecture Diagram

The analysis process was very challenging but leveraging cloud resources allowed us to fully automate and significantly speed up this process. With PLATEAU tools, we aim to drive digital transformation in design and analysis.
Yasuo Ichii
Director, Obayashi CorporationAWS Services Used
Get Started
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages