Como estava esse conteúdo?
- Aprenda
- Guia para startups sobre GenAIOps na AWS, parte 3: rumo à excelência em produção
Guia para startups sobre GenAIOps na AWS, parte 3: rumo à excelência em produção

Na Parte 1 e na Parte 2, estabelecemos as bases de GenAIOps para a transição do MVP para a implantação inicial em produção. Se você implementou essas práticas, provavelmente já está vendo resultados: adoção crescente, clientes pagantes e sinais de adequação do produto ao mercado que todo fundador sonha em alcançar. Mas o sucesso traz novos desafios.
A simplicidade que serviu às suas fases iniciais agora enfrenta pressões de escalabilidade: manter a confiabilidade à medida que os volumes de solicitações aumentam, garantir desempenho consistente em diferentes workloads de usuários e gerenciar a complexidade que acompanha o crescimento. A Parte 3 mostra como lidar com as demandas de escalabilidade sem sacrificar a velocidade de inovação.
Evoluindo seu pipeline
Alcançar a excelência em produção não se resume apenas a gerenciar mais tráfego. Trata-se de construir um pipeline que funcione de forma confiável, eficiente e previsível em escala. Isso significa automatizar processos manuais, estabelecer experimentação e implantação sistemáticas e implementar observabilidade para entender não apenas o que está acontecendo, mas também o porquê. Conforme ilustrado abaixo, essa evolução ocorre por meio de mudanças operacionais ao longo de seis estágios do pipeline — desde os fundamentos que levaram você do MVP à adequação do produto ao mercado até os sistemas automatizados que possibilitam um crescimento sustentável. Vamos explorar como evoluir cada estágio.
.jpg)

Engenharia e gerenciamento de dados: transição para ativos de dados em evolução contínua
Com o tráfego de produção agora em execução, é hora de transformar conjuntos de dados estáticos em recursos continuamente enriquecidos, impulsionados pela interação real dos usuários.
Mineração sistemática de logs de produção: expandir os conjuntos de dados de seleção de modelos e avaliação de prompts de centenas de exemplos curados para milhares de casos de teste reais. Coletar exemplos de alto valor para ajuste fino, como conversas que exigem intervenção humana e consultas que demonstram comportamentos desejados. Usar o Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth Plus para curar exemplos de produção para ajuste fino supervisionado.
Pipeline automatizado de dados para RAG: substituir atualizações manuais de fontes de dados para bases de conhecimento por fluxos de trabalho orientados a eventos usando o Amazon EventBridge. Fluxos de trabalho envolvendo documentos, imagens, áudio e vídeos podem ser automatizados em escala usando o Amazon Bedrock Data Automation. Quando consultas não conseguirem recuperar contexto relevante ou apresentarem baixas pontuações de confiança, capturar automaticamente essas falhas como casos de teste de avaliação de RAG.
Recursos úteis:
- Feedback humano de alta qualidade para suas aplicações de IA generativa com o Amazon SageMaker Ground Truth Plus
- Crie um aplicativo multimodal baseado em RAG usando o Amazon Bedrock Data Automation e Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases

Desenvolvimento e experimentação: promover a iteração sistemática
À medida que sua operação escala, é necessário evoluir do protótipo manual para a experimentação sistemática. Isso envolve executar testes em paralelo em toda a sua pilha de IA para descobrir melhorias continuamente.
Otimização contínua de modelos e prompts: tornar o dimensionamento adequado de modelos uma prática contínua, reavaliando as escolhas à medida que novos modelos surgem ou os requisitos mudam. Escolher sistemas multimodelo que correspondam automaticamente a complexidade da tarefa à capacidade do modelo. Estender essa eficiência aos prompts por meio de roteamento dinâmico com modelos especializados com base na classificação da consulta, no contexto do usuário e no histórico de desempenho. Acompanhar métricas de desempenho multidimensionais — precisão, latência e custo — para decisões orientadas por dados sobre o dimensionamento adequado de modelos ou a troca de variantes de prompts.
Fluxos de trabalho de refinamento de contexto: estabelecer processos de otimização repetíveis para recuperar conhecimento externo e personalizar modelos. Para otimização de RAG, implementar experimentação estruturada testando estratégias avançadas de chunking e abordagens de recuperação (busca híbrida, filtragem por metadados, reformulação de consultas, re-ranking), iterando com base na precisão da recuperação e na latência. Otimizar o tamanho de embedding testando, por exemplo, 768 ou 512 em comparação com 1536 dimensões para reduzir custos de armazenamento e latência de recuperação, mantendo a precisão. Para personalização de modelos, aproveitar o Amazon Bedrock para simplificar os fluxos de trabalho — usar pré-treinamento contínuo para adaptar modelos a vocabulário específico de domínio ou ajuste fino supervisionado para melhorar o desempenho em tarefas específicas. O Amazon SageMaker AI oferece maior controle sobre o treinamento à medida que as necessidades crescem.
Estabelecer ciclos regulares de otimização para evoluir os sistemas de contexto junto com sua aplicação, desde revisões mensais de desempenho de RAG até avaliações trimestrais de personalização de modelos.
Orquestração de agentes para fluxos de trabalho complexos: à medida que seus agentes lidam com workloads de produção diversos, arquiteturas de agente único atingem limites de complexidade. Agentes que tentam tratar tanto consultas de faturamento quanto solução de problemas técnicos enfrentam dificuldades devido a contextos e conjuntos de ferramentas conflitantes. Monitorar as taxas de conclusão por complexidade da tarefa: se seu agente tem sucesso em 85 por cento das tarefas que exigem 2–3 chamadas de ferramentas, mas cai para 45 por cento quando há 5 ou mais chamadas, você identificou o limite para decomposição. Implantar sistemas multiagente especializados, nos quais um agente de roteamento delega questões de faturamento a agentes de pagamento e problemas técnicos são encaminhados a agentes de suporte.
O Amazon Bedrock AgentCore aborda os desafios de escalabilidade em produção ao oferecer isolamento de sessões para usuários simultâneos, runtimes estendidos para raciocínio complexo e observabilidade unificada entre seus agentes. Para proteger contra custos descontrolados, implementar mecanismos de timeout para reduzir a probabilidade de falhas por bloqueio em fluxos de trabalho e execuções agênticas.
Experimentação sistemática sem caos em produção: executar vários experimentos simultaneamente depende do isolamento dos testes e da proteção do tráfego de produção. Para controlar implantações de componentes de IA, implantar sinalizadores de recursos por meio do AWS AppConfig, permitindo testar novas estratégias de recuperação de RAG ou avaliar variantes de prompts simultaneamente entre segmentos de usuários.
Para garantir resultados confiáveis dos experimentos, comece criando ambientes de teste isolados que reflitam os dados e os padrões de tráfego de produção. Em seguida, estabeleça métricas padronizadas que cubram tanto aspectos técnicos, como precisão e latência, quanto métricas de comportamento do usuário, como satisfação e engajamento. Ao comparar experimentos, adote uma abordagem holística de avaliação. Por exemplo, ao comparar duas estratégias de recuperação de RAG, considere que uma pequena melhoria na precisão com melhor latência pode gerar maior satisfação geral do usuário do que um ganho maior de precisão com aumento da latência. Isso garante que os resultados experimentais reflitam o impacto no mundo real, e não apenas métricas isoladas.
Recursos úteis:
- Construindo aplicações de RAG escaláveis, seguras e confiáveis usando o Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases
- O Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases agora oferece suporte a parsing avançado, fragmentação e reformulação de consultas, proporcionando maior controle de precisão em aplicações baseadas em RAG
- Colaboração multiagente com vertentes

Teste e avaliação: criar ciclos de qualidade contínuos
Os testes manuais podem rapidamente se tornar difíceis de gerenciar, especialmente quando há entregas várias vezes por semana. A transição de um gate de pré-lançamento para um ciclo contínuo de feedback impulsiona iterações mais rápidas e evita que implantações inadequadas prejudiquem a confiança dos clientes.
Pipeline automatizado de avaliação: transformar as abordagens de avaliação da Parte 2 em suítes de testes automatizadas integradas ao seu pipeline de CI/CD. Cada implantação de código aciona automaticamente avaliações de componentes e de ponta a ponta — medindo precisão, conclusão de tarefas e qualidade das respostas. Identificar problemas decorrentes de atualizações da base de conhecimento ou de atualizações de dados fora dos ciclos de implantação ao agendar testes de regressão noturnos. Não se esqueça de definir limites de qualidade para bloquear implantações que aumentem a latência ou reduzam a precisão. Realimentar as falhas de teste no seu pipeline de dados também ampliará a cobertura de avaliação.
Estratégias de avaliação de IA responsável: a correção funcional não é suficiente — sistemas em produção precisam ser seguros e confiáveis. Estender os testes automatizados para incluir detecção de alucinações com verificações de fundamentação factual, resistência à injeção de prompt por meio de casos de teste adversariais e avaliação de conteúdo prejudicial. Outras estratégias para apoiar desempenho e segurança em escala incluem a realização regular de exercícios de red teaming para identificar comportamentos inseguros e a verificação pontual de saídas em produção com base em métricas de IA responsável.
Recursos úteis:
- Criar um pipeline automatizado de avaliação de soluções de IA generativa com o Amazon Nova
- Considerações para abordar as dimensões centrais de IA responsável em aplicações do Amazon Bedrock

Implantação e disponibilização: escalar com resiliência
À medida que o tráfego de produção escala, a implantação deve evoluir de simplesmente colocar as aplicações online para a implementação de estratégias que mantenham a confiabilidade e o desempenho.
Estratégias de implantação escaláveis: começar definindo requisitos de desempenho, incluindo throughput alvo, percentis de latência e limites de degradação. Em seguida, realizar testes de carga simulando tráfego sustentado, padrões de pico e fluxos de trabalho em várias etapas. Isso ajudará a identificar lacunas de desempenho, orientar decisões arquiteturais e validar os requisitos de infraestrutura.
Otimizar a eficiência de inferência por meio de padrões inteligentes de cache e disponibilização. Aproveitar o armazenamento de prompts em cache do Bedrock ajudará a reutilizar grandes blocos de contexto, reduzindo a latência e os custos. Alinhar os padrões de inferência aos requisitos, por exemplo, usando inferência em tempo real para aplicações interativas ou inferência em lote para análises offline, também reduzirá significativamente os custos.
Para arquitetar a pilha em escala, a inferência entre regiões do Amazon Bedrock encaminha automaticamente as solicitações entre as regiões da AWS mais adequadas para aumentar o throughput e a disponibilidade. Enquanto isso, o escalonamento automático de endpoints do SageMaker AI ajusta dinamicamente a capacidade, o Bedrock AgentCore Runtime oferece implantação segura de agentes em escala e o OpenSearch Serverless dimensiona automaticamente a capacidade de computação para bancos de dados vetoriais.
Padrões de implantação também podem reduzir riscos nas liberações, como implantações canário para expor 5–10 por cento do tráfego a novos modelos enquanto as métricas são monitoradas antes do rollout completo e implantações azul-verde, que permitem rollback instantâneo em caso de regressões.
Estratégias resilientes de disponibilização: além da escalabilidade, sistemas em produção precisam lidar com limites de cotas, falhas transitórias e cargas inesperadas sem degradar a experiência do usuário. Revisar proativamente as cotas do Amazon Bedrock, solicitando aumentos antes de atingir os limites. Implementar rate limiting usando o Amazon API Gateway para controlar as solicitações de entrada e garantir uso justo. Usar o Amazon SQS entre sua aplicação e os modelos para absorver a variabilidade de demanda e evitar rejeição de solicitações.
Ao configurar hierarquias de cascata de modelos — do modelo primário para o modelo de backup e, em seguida, para respostas em cache até respostas degradadas de forma controlada — é possível garantir que os usuários sempre recebam uma resposta, mesmo quando os caminhos ideais de disponibilização falham. Além disso, implementar circuit breakers para interromper solicitações a dependências com falha.
Recursos úteis:
- Otimizando a capacidade de resposta da IA: um guia prático para inferência otimizada para latência do Amazon Bedrock
- Projetando workloads de IA generativa para resiliência

Observabilidade e refinamento: impulsionar a melhoria contínua
Tornar a observabilidade a principal vantagem competitiva com um sistema de ciclo fechado, no qual insights acionam automaticamente refinamentos, criando uma aplicação que se aprimora continuamente.
Observabilidade unificada entre métricas técnicas e de negócio: a análise de correlação é fundamental para entender o comportamento do sistema como um todo. Para isso, criar painéis unificados que combinem métricas técnicas e de negócio — não apenas “Model A x Model B”, mas sim “Model A a US$ 0,02 por solicitação com 92 por cento de precisão x Model B a US$ 0,08 por solicitação com 94 por cento de precisão” — e, em seguida, acompanhar como cada um impacta a retenção de usuários em 30 dias. Projetar visões específicas por função a partir de telemetria compartilhada: a engenharia visualiza alertas de taxa de erro e tendências de latência; as equipes de produto veem taxas de conclusão e padrões de interação do usuário; os executivos acompanham custo por interação e correlações de ROI. Assim, quando o bot de atendimento ao cliente apresenta consultas 40 por cento mais longas durante lançamentos de funcionalidades ou quando padrões sazonais alteram a estrutura de custos em 60 por cento, a análise de correlação entre métricas revela a causa raiz.
Ciclos de melhoria em ciclo fechado: a verdadeira excelência em produção vem da criação de sistemas de ciclo fechado nos quais a observabilidade aciona refinamentos em todo o pipeline de GenAIOps, conforme mostrado na figura abaixo.
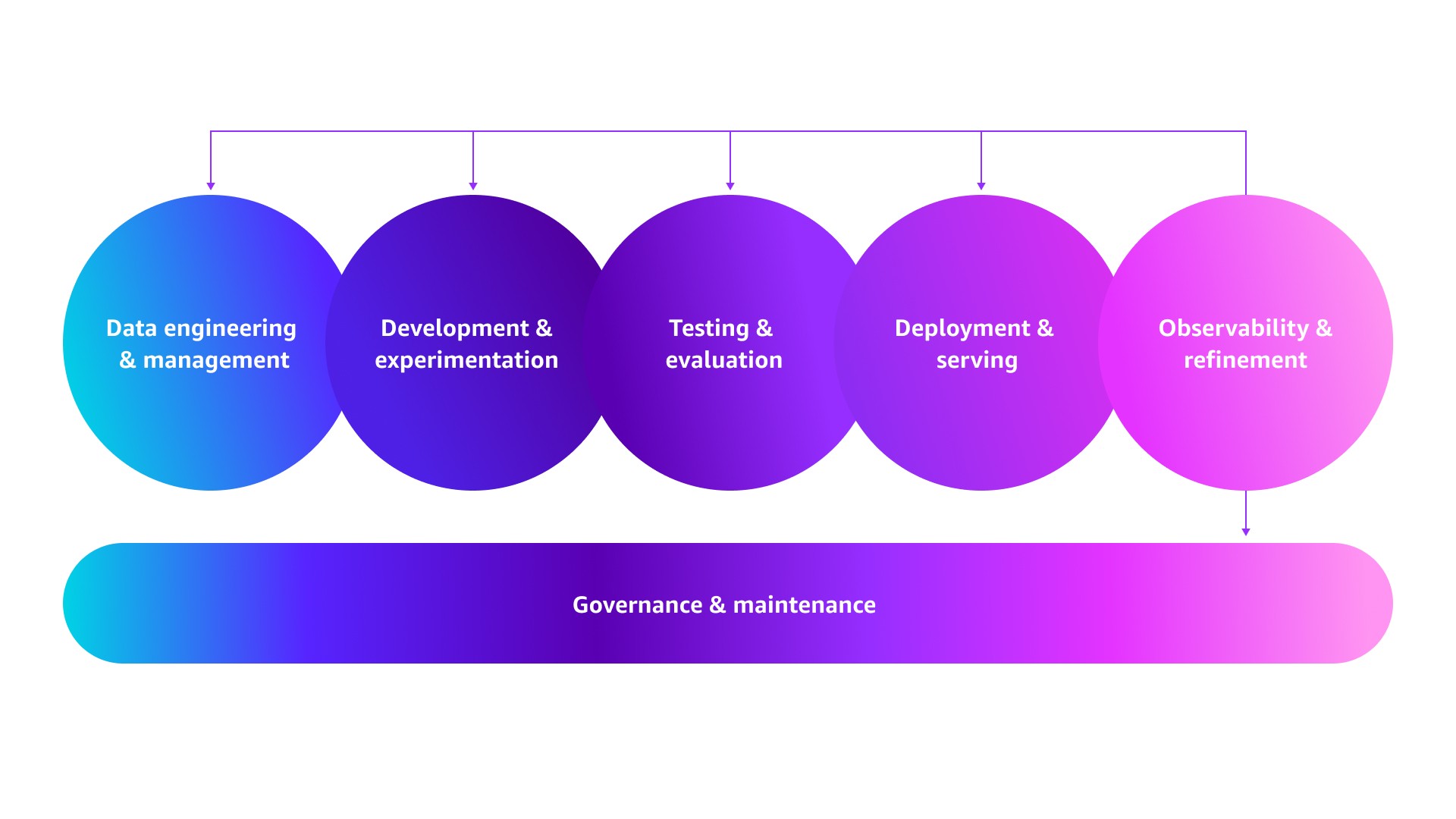
Por exemplo, a observabilidade do bot de atendimento ao cliente pode acionar as seguintes melhorias:
- Engenharia e gerenciamento de dados: quando a taxa de respostas com falha aumenta em 15 por cento para consultas de lançamento de produto, o Amazon EventBridge aciona a sincronização da base de conhecimento para ingerir a documentação mais recente a partir dos sistemas de origem.
- Desenvolvimento e experimentação: se as taxas de resolução do bot caírem em 20 por cento para consultas de faturamento, o sistema enfileira testes A/B para variantes de prompts especializadas em faturamento.
- Testes e avaliação: quando as falhas em conversas de rastreamento de pedidos aumentam em 25 por cento, casos de teste são gerados automaticamente a partir das interações com falha e adicionados às suítes de regressão.
- Implantação e disponibilização: quando a análise de traces mostra que 8 por cento dos fluxos de trabalho de agentes sofrem timeout em 30 segundos, mas são concluídos com sucesso em 45 segundos, as configurações de timeout são ajustadas.
- Governança e manutenção: quando os logs de implantação mostram que 40 por cento das liberações falham devido à ausência de permissões do IAM ou de pré-requisitos de infraestrutura, verificações de validação pré-implantação são adicionadas ao pipeline de implantação — identificando problemas de configuração antes que bloqueiem as liberações.
Recursos úteis:
- Capacite sua aplicação de IA generativa com uma solução abrangente de observabilidade personalizada
- Criar agentes de IA confiáveis com o Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Observability

Governança e manutenção: viabilizar a inovação segura
O framework de governança deve funcionar como um consultor de confiança que acelera a tomada de riscos inteligentes ao mesmo tempo em que evita erros dispendiosos. Transformar as barreiras de proteção da Parte 2 em uma vantagem competitiva por meio de práticas de IA responsável que constroem a confiança dos clientes.
Fluxos de trabalho automatizados de governança: substituir revisões manuais por automação inteligente, usando o AWS Step Functions para criar fluxos de aprovação nos quais atualizações de baixo risco, como refinamentos de templates de prompts, são implantadas automaticamente, enquanto atualizações de alto risco, como mudanças de modelos, acionam revisões humanas. Também é possível automatizar a documentação de conformidade, desde a captura de cadeias de aprovação até a manutenção de trilhas de auditoria. Quando implantações violam políticas, os fluxos de trabalho bloqueiam automaticamente a liberação e escalam para as partes interessadas.
Infraestrutura como código e rastreamento de linhagem: codificar toda a infraestrutura de IA, capturando o conhecimento de implantação em código versionado. Rastrear a linhagem de modelos usando o Registro de Modelos do Amazon SageMaker e a linhagem de dados usando os recursos do Amazon SageMaker Catalog. Documentar como os dados fluem dos documentos de origem por meio das etapas de processamento até as saídas dos modelos também cria trilhas de auditoria para apoiar depuração e conformidade, tornando tudo — desde os dados de treinamento até os resultados de inferência — rastreável.
Visibilidade operacional e responsabilização: criar painéis específicos por função no Amazon QuickSight que exponham métricas de governança. Estabelecer responsabilidades claras entre as equipes, com produto responsável por metas de desempenho, engenharia responsável pela confiabilidade, conformidade responsável pela segurança e governança coordenando entre as equipes.
Recursos úteis:
- Gerenciar de forma eficaz modelos fundacionais para aplicações de IA generativa com o Registro de Modelos do Amazon SageMaker
- Simplificar o caminho dos dados aos insights com novos recursos do Amazon SageMaker Catalog

Conclusão
Alcançar a excelência em produção não é um esforço pontual, é um processo contínuo de construir um pipeline que aprende com cada implantação, falha e interação do usuário. Essas melhorias sistemáticas se acumulam ao longo do tempo, criando vantagens competitivas que vão além do que é possível apenas entregar funcionalidades mais rapidamente.
Para dar o próximo passo, priorizar o estágio mais desafiador do pipeline — seja experimentos que demoram demais para serem validados, implantações complexas ou custos imprevisíveis. Depois de automatizar essa área, avançar para a próxima e continuar o processo. No fim, o que diferencia as startups líderes em IA não é o acesso a modelos melhores, mas sim um pipeline robusto de GenAIOps que aprimora continuamente a experiência do usuário.

Nima Seifi
Nima Seifi é arquiteto de soluções sênior na AWS, com escritório no sul da Califórnia, onde é especialista em SaaS e GenAIOps. Ele atua como consultor técnico para startups que utilizam a AWS. Antes da AWS, trabalhou como arquiteto de DevOps no setor de comércio eletrônico por mais de cinco anos, após uma década de trabalho em pesquisa e desenvolvimento em tecnologias de internet móvel. Nima possui mais de 20 publicações em revistas técnicas e conferências de renome e detém sete patentes nos Estados Unidos. Fora do trabalho, ele aprecia ler, assistir documentários e caminhar pela praia.
.jpg)
Pat Santora
Pat Santora é arquiteto de nuvem e tecnólogo da GenAI Labs, com mais de 25 anos de experiência na implementação de soluções em nuvem para empresas e startups. Ele lançou com êxito vários produtos desde o início, liderou projetos de reestruturação analítica e gerenciou equipes remotas com uma filosofia centrada na transparência e na confiança. Sua experiência técnica abrange planejamento estratégico, gerenciamento de sistemas e redesenho arquitetônico, complementada por interesses em IA generativa, analytics e Big Data.
.jpg)
Clement Perrot
Clement Perrot auxilia startups de primeira linha a acelerar suas iniciativas de IA, fornecendo orientação estratégica sobre seleção de modelos, implementação responsável de IA e operações otimizadas de machine learning. Empreendedor em série e premiado pela Inc 30 Under 30, ele traz profunda experiência na construção e escalabilidade de empresas de IA, tendo fundado e encerrado com êxito vários empreendimentos em tecnologia de consumo e IA empresarial.
Como estava esse conteúdo?