Démarrer avec AWS
Créer une application web sans serveur
avec AWS Lambda, Amazon API Gateway, AWS Amplify, Amazon DynamoDB et Amazon Cognito
Module 3 : Backend service sans serveur
Vous utiliserez AWS Lambda et Amazon DynamoDB afin de créer un processus backend pour la gestion des requêtes pour votre application Web.
Présentation
Dans ce module, vous utiliserez AWS Lambda et Amazon DynamoDB afin de créer un processus backend pour la gestion des requêtes pour votre application Web. L'application de navigation que vous avez déployée dans le premier module permet aux utilisateurs de demander l'envoi d'une licorne à un emplacement de leur choix. Pour répondre à ces demandes, le code JavaScript qui s'exécute dans le navigateur devra invoquer un service exécuté dans le cloud.
Présentation de l'architecture
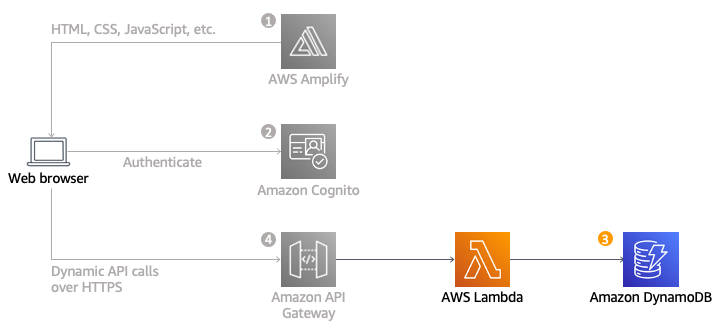
Vous allez mettre en œuvre une fonction Lambda qui sera invoquée chaque fois qu'un utilisateur demande une licorne. La fonction sélectionnera une licorne dans la flotte, consignera la demande dans une table DynamoDB, puis répondra à l'application frontend avec des détails sur la licorne envoyée.
La fonction est invoquée à partir du navigateur en utilisant Amazon API Gateway. Vous allez mettre en œuvre cette connexion dans le module suivant. Pour ce module vous allez simplement tester votre fonction de manière isolée.
Temps nécessaire
30 minutes
Services utilisés
Mise en œuvre
-
Création d'une table Amazon DynamoDB
Utilisez la console Amazon DynamoDB pour créer une table DynamoDB.
- Dans la console Amazon DynamoDB, cliquez sur Créer une table.
- Saisissez Rides pour le Nom de la table. Ce champ est sensible à la casse.
- Saisissez RideId pour la Clé de partition, puis sélectionnez Chaîne comme type de clé. Ce champ est sensible à la casse.
- Dans la section Paramètres du tableau, vérifiez que les paramètres par défaut sont sélectionnés, puis cliquez sur Créer une table.
- Sur la page Tables, attendez la fin de la création de votre table. Lorsqu'elle est terminée, le statut passe sur Active. Sélectionnez le nom de votre table.
- Dans l'onglet Vue d'ensemble > Informations générales de votre nouvelle table, cliquez sur Informations supplémentaires. Copiez l'ARN. Vous l'utiliserez dans la section suivante.
-
Création d'un rôle IAM pour votre fonction Lambda
Un rôle IAM est associé à chaque fonction Lambda. Ce rôle définit avec quels autres services AWS la fonction peut interagir. Dans le cadre de ce didacticiel, vous devrez créer un rôle IAM qui autorise votre fonction Lambda à écrire des journaux dans Amazon CloudWatch Logs et à accéder en écriture à votre table DynamoDB.
- Dans la console IAM, cliquez sur Rôles dans le panneau de navigation de gauche, puis sélectionnez Créer un rôle.
- Dans la section Type d'entité de confiance, sélectionnez Service AWS. Dans Cas d'utilisation, sélectionnez Lambda, puis cliquez sur Suivant.
Remarque : la sélection d'un type de rôle crée automatiquement une stratégie d'approbation pour votre rôle qui permet aux services AWS d'assumer ce rôle en votre nom. Si vous créez ce rôle en utilisant la CLI, AWS CloudFormation ou un autre mécanisme, spécifiez directement une stratégie d'approbation. - Saisissez AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole dans la zone de texte du filtre et cliquez sur Entrée.
- Cochez la case en regard du nom de la stratégie AWSLambdAbasicExecutionRole et cliquez sur Suivant.
- Saisissez WildRydesLambda comme Nom de rôle. Ne modifiez pas les autres paramètres par défaut.
- Sélectionnez Créer un rôle.
- Dans la zone de filtre de la page Rôles, saisissez WildryDesLambda et sélectionnez le nom du rôle que vous venez de créer.
- Dans l'onglet Autorisations, sous Ajouter des autorisations, cliquez sur Créer une stratégie en ligne.
- Dans la section Sélectionner un service, saisissez DynamoDB dans la barre de recherche, puis cliquez sur DynamoDB dès qu'il apparaît.
- Cliquez sur Sélectionner les actions.
- Dans la section Actions autorisées, saisissez PutItem dans la barre de recherche et cochez la case en regard de PutItem lorsqu'il apparaît.
- Dans la section Ressources, avec l'option Spécifique sélectionnée, cliquez sur le lien Ajouter ARN.
- Cliquez sur l'onglet Texte. Collez l'ARN de la table que vous avez créée dans DynamoDB (étape 6 de la section précédente), puis cliquez sur Ajouter des ARN.
- Cliquez sur Suivant.
- Saisissez DynamoDBWriteAccess pour le nom de la stratégie et sélectionnez Créer une stratégie.
-
Création d'une fonction Lambda pour gérer les requêtes
AWS Lambda exécutera votre code en réponse à des événements, tels qu'une requête HTTP. Au cours de cette étape, vous allez créer la fonction principale qui traitera les demandes d'API de l'application web pour envoyer une licorne. Dans le module suivant, vous utiliserez Amazon API Gateway pour créer une API RESTful qui exposera un point de terminaison HTTP qui peut être appelé à partir des navigateurs de vos utilisateurs. Vous connecterez ensuite la fonction Lambda créée dans cette étape à cette API afin de créer un backend totalement fonctionnel pour votre application Web.
Utilisez la console AWS Lambda pour créer une nouvelle fonction Lambda appelée RequestUnicorn qui traitera les demandes d'API. Utilisez l'exemple de mise en œuvre requestUnicorn.js suivant pour le code de votre fonction. Copiez-collez-le simplement à partir de ce fichier dans l'éditeur de la console AWS Lambda.
Assurez-vous de configurer votre fonction de manière à utiliser le rôle IAM WildRydesLambda que vous avez créé à la section précédente.
- Dans la console AWS Lambda, cliquez sur Créer une fonction.
- Gardez la carte Créer à partir de zéro sélectionnée par défaut.
- Saisissez RequestUnicorn dans le champ Nom de la fonction.
- Sélectionnez Node.js 16.x pour l'Exécution (les versions les plus récentes de Node.js ne fonctionneront pas dans ce didacticiel).
- Sélectionnez Utiliser un rôle existant dans le menu déroulant Modifier le rôle d'exécution par défaut.
- Sélectionnez WildRydesLambda dans le menu déroulant Rôle existant.
- Cliquez sur Créer une fonction.
- Descendez jusqu'à la section Source du code et remplacez le code index.js présent dans l'éditeur de code par le contenu de requestUnicorn.js. Le bloc de code suivant affiche le fichier requestUnicorn.js. Copiez et collez ce code dans l'onglet index.js de l'éditeur de code.
const randomBytes = require('crypto').randomBytes; const AWS = require('aws-sdk'); const ddb = new AWS.DynamoDB.DocumentClient(); const fleet = [ { Name: 'Angel', Color: 'White', Gender: 'Female', }, { Name: 'Gil', Color: 'White', Gender: 'Male', }, { Name: 'Rocinante', Color: 'Yellow', Gender: 'Female', }, ]; exports.handler = (event, context, callback) => { if (!event.requestContext.authorizer) { errorResponse('Authorization not configured', context.awsRequestId, callback); return; } const rideId = toUrlString(randomBytes(16)); console.log('Received event (', rideId, '): ', event); // Because we're using a Cognito User Pools authorizer, all of the claims // included in the authentication token are provided in the request context. // This includes the username as well as other attributes. const username = event.requestContext.authorizer.claims['cognito:username']; // The body field of the event in a proxy integration is a raw string. // In order to extract meaningful values, we need to first parse this string // into an object. A more robust implementation might inspect the Content-Type // header first and use a different parsing strategy based on that value. const requestBody = JSON.parse(event.body); const pickupLocation = requestBody.PickupLocation; const unicorn = findUnicorn(pickupLocation); recordRide(rideId, username, unicorn).then(() => { // You can use the callback function to provide a return value from your Node.js // Lambda functions. The first parameter is used for failed invocations. The // second parameter specifies the result data of the invocation. // Because this Lambda function is called by an API Gateway proxy integration // the result object must use the following structure. callback(null, { statusCode: 201, body: JSON.stringify({ RideId: rideId, Unicorn: unicorn, Eta: '30 seconds', Rider: username, }), headers: { 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*', }, }); }).catch((err) => { console.error(err); // If there is an error during processing, catch it and return // from the Lambda function successfully. Specify a 500 HTTP status // code and provide an error message in the body. This will provide a // more meaningful error response to the end client. errorResponse(err.message, context.awsRequestId, callback) }); }; // This is where you would implement logic to find the optimal unicorn for // this ride (possibly invoking another Lambda function as a microservice.) // For simplicity, we'll just pick a unicorn at random. function findUnicorn(pickupLocation) { console.log('Finding unicorn for ', pickupLocation.Latitude, ', ', pickupLocation.Longitude); return fleet[Math.floor(Math.random() * fleet.length)]; } function recordRide(rideId, username, unicorn) { return ddb.put({ TableName: 'Rides', Item: { RideId: rideId, User: username, Unicorn: unicorn, RequestTime: new Date().toISOString(), }, }).promise(); } function toUrlString(buffer) { return buffer.toString('base64') .replace(/\+/g, '-') .replace(/\//g, '_') .replace(/=/g, ''); } function errorResponse(errorMessage, awsRequestId, callback) { callback(null, { statusCode: 500, body: JSON.stringify({ Error: errorMessage, Reference: awsRequestId, }), headers: { 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*', }, }); }9. Cliquez sur Déployer.
-
Validation de votre mise en œuvre
Pour ce module, vous allez tester la fonction que vous avec créée à l'aide de la console AWS Lambda. Dans le module suivant, vous ajouterez une API REST avec API Gateway de manière à pouvoir invoquer votre fonction à partir de l'application basée sur navigateur que vous avez déployée dans le premier module.
- Dans la fonction RequestUnicorn que vous avez créée à la section précédente, cliquez sur Test dans la section Source du code, puis sélectionnez Configurer l'événement de test dans le menu déroulant.
- Conservez la sélection par défaut Créer un nouvel événement.
- Saisissez TestRequestEvent dans le champ Nom de l'événement.
- Copiez et collez l'événement de test suivant dans la section Événement JSON :
{ "path": "/ride", "httpMethod": "POST", "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Authorization": "eyJraWQiOiJLTzRVMWZs", "content-type": "application/json; charset=UTF-8" }, "queryStringParameters": null, "pathParameters": null, "requestContext": { "authorizer": { "claims": { "cognito:username": "the_username" } } }, "body": "{\"PickupLocation\":{\"Latitude\":47.6174755835663,\"Longitude\":-122.28837066650185}}" }5. Sélectionnez Save (Enregistrer).
6. Dans la section Source du code de votre fonction, cliquez sur Test et sélectionnez TestRequestEvent dans le menu déroulant.
7. Dans l'onglet Test, sélectionnez Test.
8. Dans le message Réussite de l'exécution de la fonction qui apparaît, développez le menu déroulant Détails.
9. Assurez-vous que la fonction se présente comme suit :
{ "statusCode": 201, "body": "{\"RideId\":\"SvLnijIAtg6inAFUBRT+Fg==\",\"Unicorn\":{\"Name\":\"Rocinante\",\"Color\":\"Yellow\",\"Gender\":\"Female\"},\"Eta\":\"30 seconds\"}", "headers": { "Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*" } }





