- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Deploying Harmonix on AWS
Guidance for Deploying Harmonix on AWS
Overview
How it works
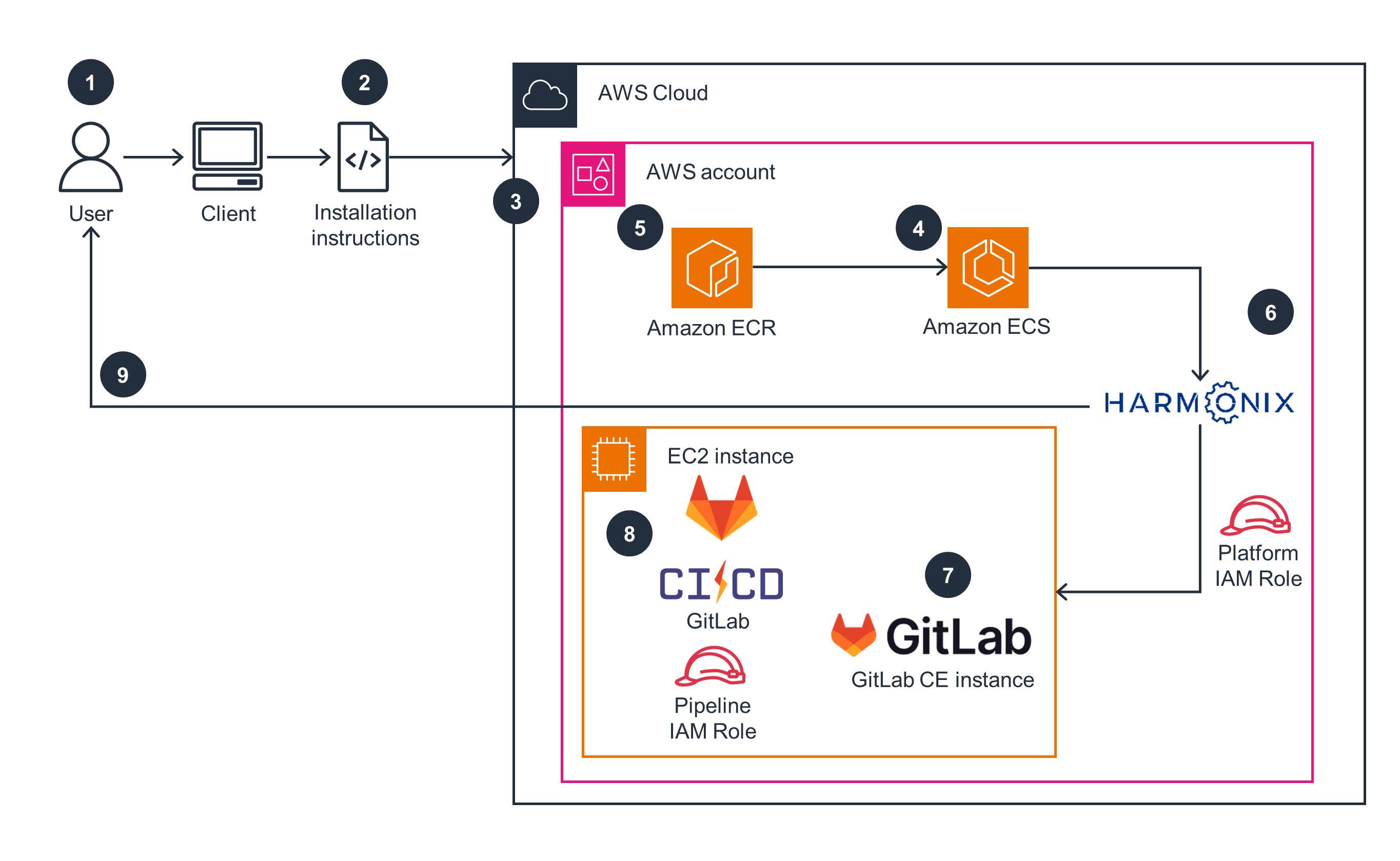
Provisioning the AWS account
This architecture diagram illustrates how to provision an AWS account after cloning Harmonix from GitHub.
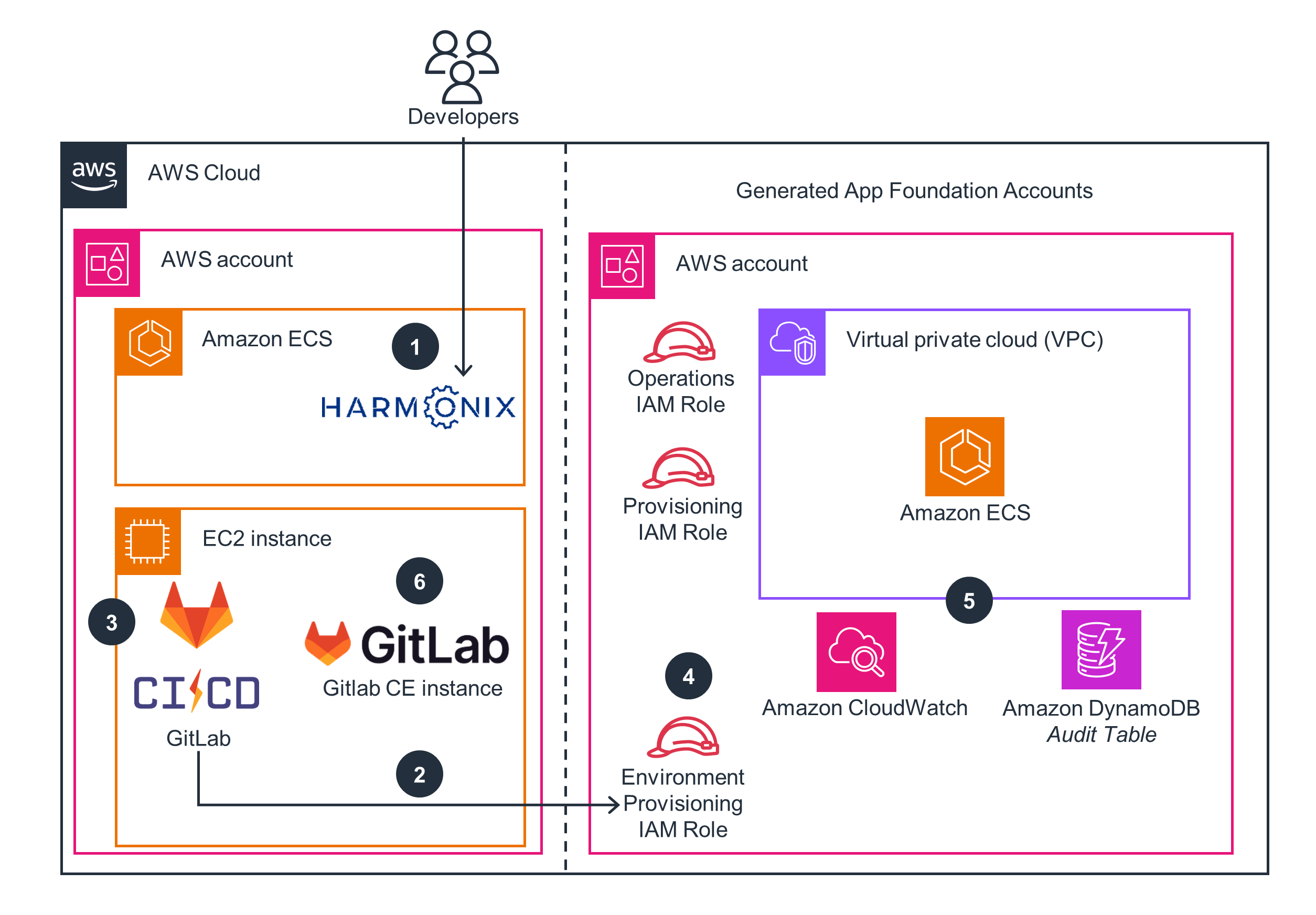
Provisioning an Amazon ECS environment
This architecture diagram shows how to provision an Amazon ECS environment using Harmonix on AWS.
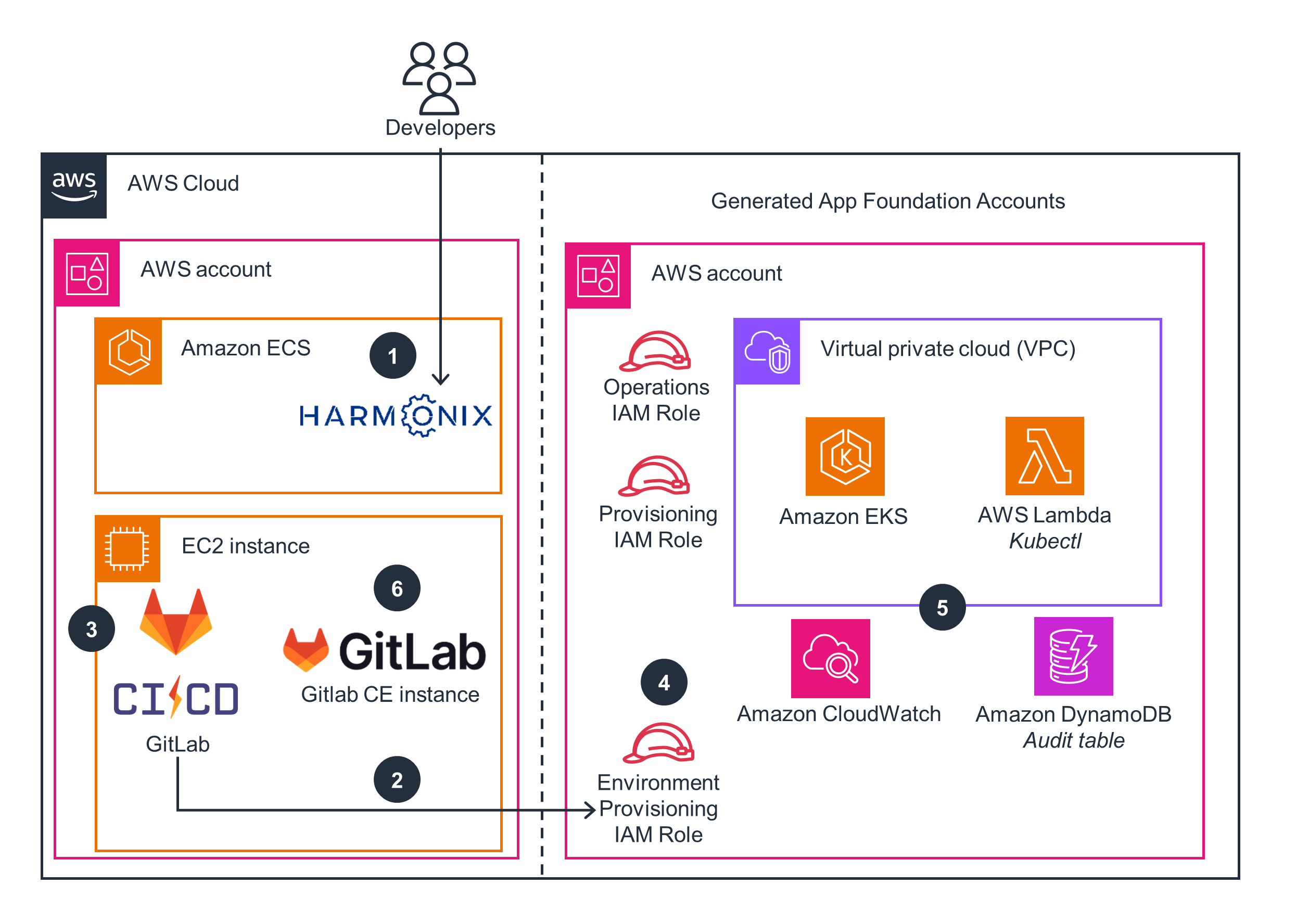
Provisioning an Amazon EKS environment
This architecture diagram shows how to provision an Amazon EKS environment using Harmonix on AWS.
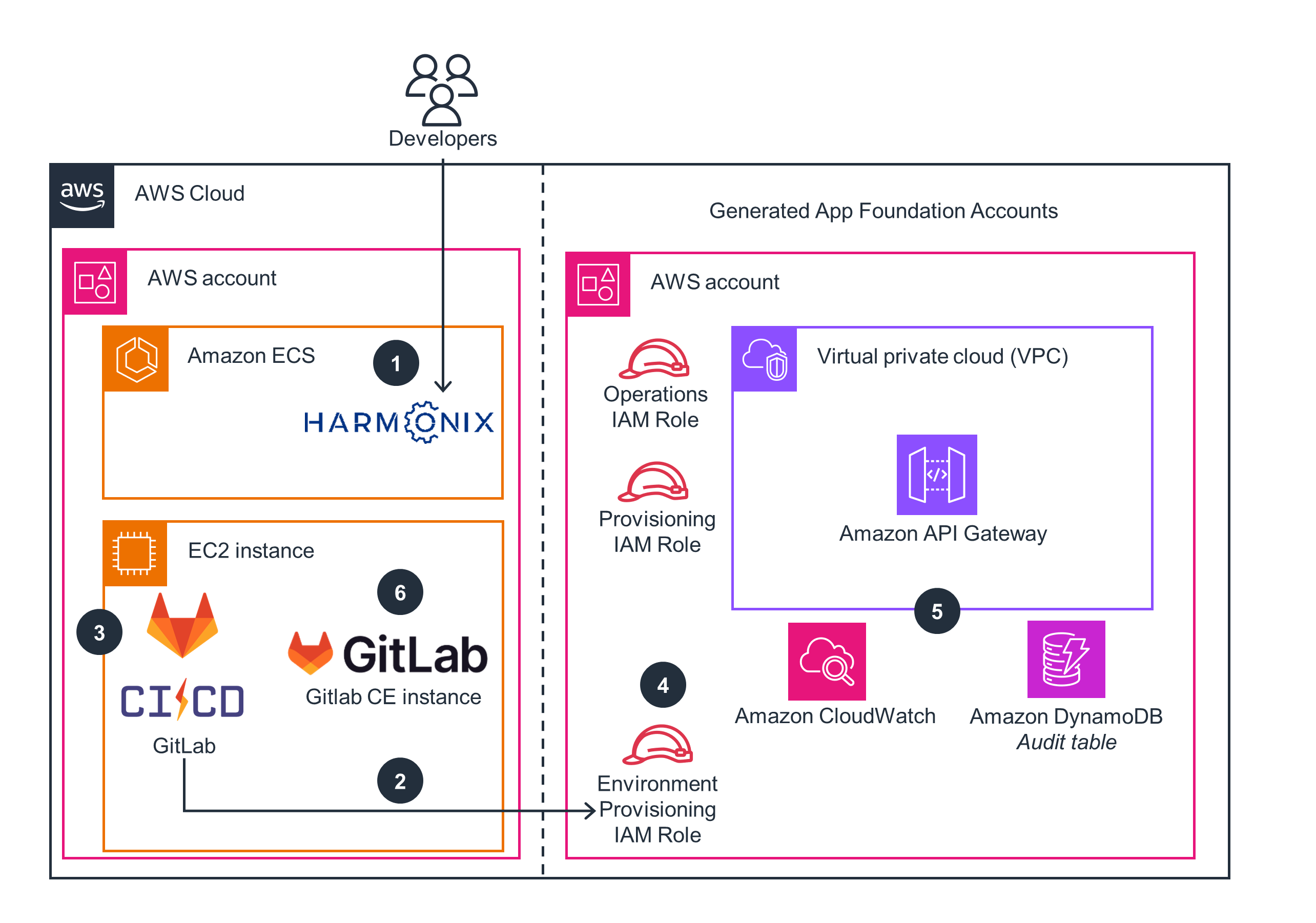
Provisioning a serverless environment
This architecture diagram shows how to provision a serverless environment with Amazon API Gateway using Harmonix on AWS.
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
CloudWatch provides logs and tracing for applications and infrastructure. DynamoDB audits requests executed outside of AWS, capturing user interactions in the GitLab pipeline API. CloudFormation maintains IAC orchestration, reducing deployment overhead. These services facilitate troubleshooting, support native cloud conventions for configuration management, and enable observation of numerous apps across multiple accounts. The composition provides isolated access control and segregated auditing, improving compliance, security, and operational efficiency.
Read the Operational Excellence whitepaperIAM limits permissions for infrastructure and application creation through specific roles, such as provisioning and operations. Access to environments requires assuming these roles. AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) provides encryption keys for each environment, used to encrypt all stored data. Appropriate roles are granted access to environment-specific keys. AWS Secrets Manager stores sensitive information using environment-specific AWS KMS keys, saving secrets with environment and application context.
Read the Security whitepaperWhile Harmonix on AWS currently uses a single site, you can run multiple sites ( ECS clusters) with route policies for improved reliability. Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) distributes requests across multiple ECS containers, sending traffic only to healthy containers. Amazon ECS maintains application and platform lifecycles, helping ensure that apps are running, scaling as needed, and provisioning new tasks on failure. These services provide resiliency and automatic recovery for apps and the platform, with automatic monitoring, recovery, and traffic redirection to appropriate running tasks.
Read the Reliability whitepaperAmazon ECS and Amazon EKS provide automatic scaling of desired tasks to help increase performance. Autoscaling groups, used with provisioned apps and ELB , improve performance by spinning up more app instances and distributing traffic across them. Lambda , a managed serverless compute service, offers automatic scaling when invoked through API, allowing serverless apps to benefit from performance increases during high traffic or demand.
Read the Performance Efficiency whitepaperServerless Lambda functions operate on a pay-as-you-go model, meaning you only pay for resources used. This allows you to scale up as necessary and optimize costs by only charging for active compute time. This eliminates the need for dedicated EC2 instances that may be underutilized during off-peak hours. Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS containerized services improve infrastructure utilization by running multiple jobs and containers on shared infrastructure, maximizing throughput and scaling tasks across multiple nodes when needed.
Read the Cost Optimization whitepaperAs managed services, Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS provide efficient application runtime environments, reducing redundant instances when no job is required. Serverless Lambda functions abstract hardware, allowing AWS to optimize existing infrastructure for more efficient runtimes instead of running underutilized hardware. By leveraging these services, you can optimize application execution, reduce costs, and decrease power consumption and emissions. This approach supports sustainability by maximizing resource utilization and minimizing idle infrastructure.
Read the Sustainability whitepaperDisclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages