- What is Cloud Computing?›
- Cloud Computing Concepts Hub›
- Networking & Content Delivery
What’s the Difference Between SSL and TLS?
What's the difference between SSL and TLS?
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a communication protocol, or set of rules, that creates a secure connection between two devices or applications on a network. It’s important to establish trust and authenticate the other party before you share credentials or data over the internet. SSL is technology your applications or browsers may have used to create a secure, encrypted communication channel over any network. However, SSL is an older technology that contains some security flaws. Transport Layer Security (TLS) is the upgraded version of SSL that fixes existing SSL vulnerabilities. TLS authenticates more efficiently and continues to support encrypted communication channels.
What are the similarities between SSL and TLS?
Both SSL and TLS are communication protocols that encrypt data between servers, applications, users, and systems. They authenticate two parties connected over a network so they can exchange data securely.
Taher Elgamal led the development of SSL and released SSL 2.0 publicly in 1995. The purpose of SSL was to keep communication secure over the World Wide Web. After SSL moved through various iterations, Tim Dierks and Christopher Allen created TLS 1.0 in 1999 as the successor to SSL 3.0.
Terminology
TLS is the direct successor to SSL, and all versions of SSL are now deprecated. However, it’s common to find the term SSL describing a TLS connection. In most cases, the terms SSL and SSL/TLS both refer to the TLS protocol and TLS certificates.
Purpose
TLS is a secure communication protocol that enables encryption and authentication, and this was true for SSL before it was deprecated. TLS and SSL both use digital certificates that facilitate the handshake process and establish encrypted communications between a browser and a web server.
Usage in HTTPS
HTTP is a protocol or set of communication rules for client-server communication over any network. HTTPS is the practice of establishing a secure SSL/TLS protocol on an insecure HTTP connection.
Before it connects with a website, your browser uses TLS to check the website’s TLS or SSL certificate. TLS and SSL certificates show that a server adheres to the current security standards. You can find evidence about the certificate within the browser address bar. An authentic and encrypted connection displays https:// instead of http://. The additional s stands for secure.
Key differences: SSL vs. TLS
While the purposes of SSL and TLS are very similar, these communication protocols are distinct in how they operate. These changes developed over time as SSL moved through various versions before it was succeeded by TLS.
SSL/TLS handshakes
A handshake is a process in which a browser authenticates a server’s SSL or TLS certificate. This process authenticates both parties, then exchanges cryptographic keys.
An SSL handshake was an explicit connection, while a TLS handshake is an implicit one. The SSL handshake process had more steps than the TLS process. By removing additional steps and reducing the total number of cipher suites, TLS has sped up the process.
Alert messages
Alert messages are how SSL and TLS protocols communicate errors and warnings. In SSL, there are only two alert message types: warning and fatal. A warning alert indicates that an error has occurred, but the connection can continue. A fatal alert indicates that the connection must be terminated immediately. Additionally, SSL alert messages are unencrypted.
TLS has an additional alert message type called close notify. The close notify alert signals the end of the session. TLS alerts are also encrypted for additional security.
Message authentication
Both SSL and TLS use message authentication codes (MACs), a cryptographic technique for verifying the authenticity and integrity of messages. By using a secret key, the record protocol generates the MAC as a fixed-length code and attaches it to the original message.
The SSL protocol uses the MD5 algorithm—which is now outdated—for MAC generation. TLS uses Hash-Based Message Authentication Code (HMAC) for more complex cryptography and security.
Cipher suites
A cipher suite is a collection of algorithms that create keys to encrypt information between a browser and a server. Typically, a cipher suite includes a key exchange algorithm, a validation algorithm, a bulk encryption algorithm, and a MAC algorithm. Several algorithms in TLS were upgraded from SSL due to security concerns.
What is the difference between SSL certificates and TLS certificates?
At present, all SSL certificates are no longer in use. TLS certificates are the industry standard. However, the industry continues to use the term SSL to refer to TLS certificates.
TLS certificates have iterated upon SSL certificates and improved them over time. The final function of SSL certificates and TLS certificates hasn’t changed.
Should you replace SSL certificates with TLS certificates?
Due to slow cultural change, most TLS certificates are incorrectly named SSL certificates. Even if your certificate brands itself as an SSL certificate, it will already support both SSL and TLS protocols.
However, it’s important to note that TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 were also formally deprecated in 2021. By June 2023, all Amazon Web Services clients must support TLS 1.2 or later. Remember that certificates are not the same thing as a protocol. You should make sure your server configuration supports TLS protocols.
Summary of differences: SSL vs. TLS
|
SSL |
TLS |
|
|
Stands For |
SSL means Secure Sockets Layer. |
TLS means Transport Layer Security. |
|
Version History |
SSL is now replaced with TLS. SSL moved through versions 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0. |
TLS is the upgraded version of SSL. TLS has moved through versions 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3. |
|
Activity |
Every SSL version is now deprecated. |
TLS versions 1.2 and 1.3 are actively used. |
|
Alert Messages |
SSL has only two types of alert messages. Alert messages are unencrypted. |
TLS alert messages are encrypted and more diverse. |
|
Message Authentication |
SSL uses MACs. |
TLS uses HMACs. |
|
Cipher Suites |
SSL supports older algorithms with known security vulnerabilities. |
TLS uses advanced encryption algorithms. |
|
Handshake |
An SSL handshake is complex and slow. |
A TLS handshake has fewer steps and a faster connection. |
How can AWS support your SSL/TLS requirements?
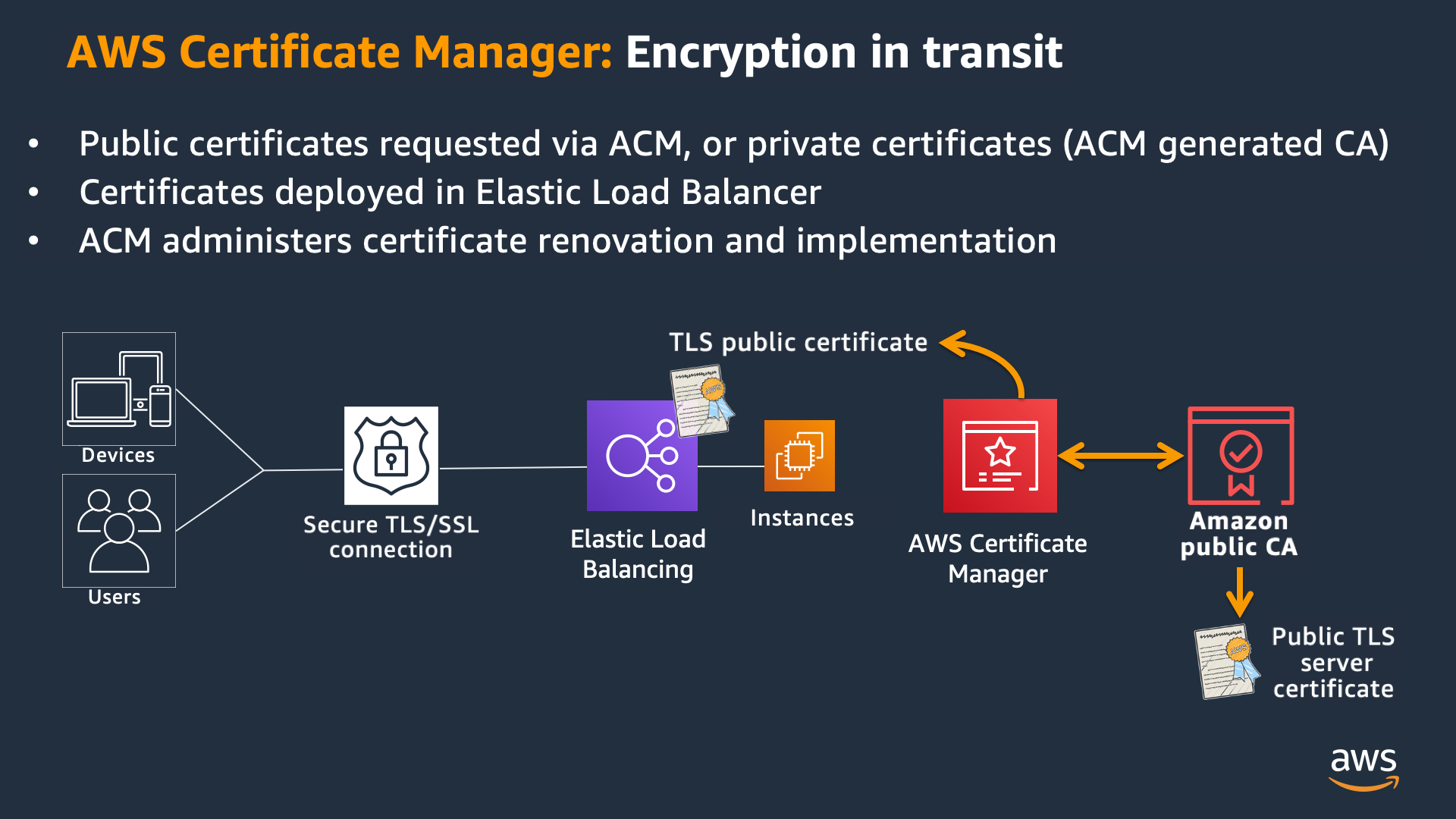
At Amazon Web Services (AWS), we offer AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) to help you meet your SSL/TLS requirements. With ACM, you can provision, manage, and deploy public and private SSL/TLS certificates.
Here are other ways you can benefit with ACM:
- Protect your internal resources with secure communication on private networks. For example, protect your servers, mobile and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and applications.
- Maintain SSL/TLS certificates, including certificate renewals, with automated certificate management.
- Use no-cost certificates with integrated AWS services.
Get started with SSL/TLS certificate management on AWS by creating a free account today.