- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Building a SAP Cloud Data Warehouse on AWS
Guidance for Building a SAP Cloud Data Warehouse on AWS
Overview
This Guidance shows how to extract data and business logic from SAP systems to build a data warehouse that integrates the business context and logic embedded within the SAP system. Users can select functional areas such as Order-to-Cash (including customers, sales orders, customer deliveries, and invoices) and Procure-to-Pay (including vendors, purchase orders, good receipts, and vendor invoices).
Included are AWS CloudFormation templates that deploy the required data models, translating the technical data architecture into business-friendly terms and relationships. Additionally, this Guidance provides near real-time, simple, and adaptable data pipelines, with incremental change data capture (CDC) processes, conversion rules, and automatic inclusion of custom fields. This comprehensive approach delivers high-quality, contextual data to enable the creation of reports and the performance of advanced analytics with SAP and non-SAP data at speed, supporting data-driven decision making.
How it works
Overview
This architecture diagram shows how to build a cloud data warehouse on AWS by extracting data from SAP using the OData protocol. You can use the data warehouse to model and combine SAP data with that of other sources loaded into the data warehouse. The next two tabs show metadata replication and data marts, respectively.
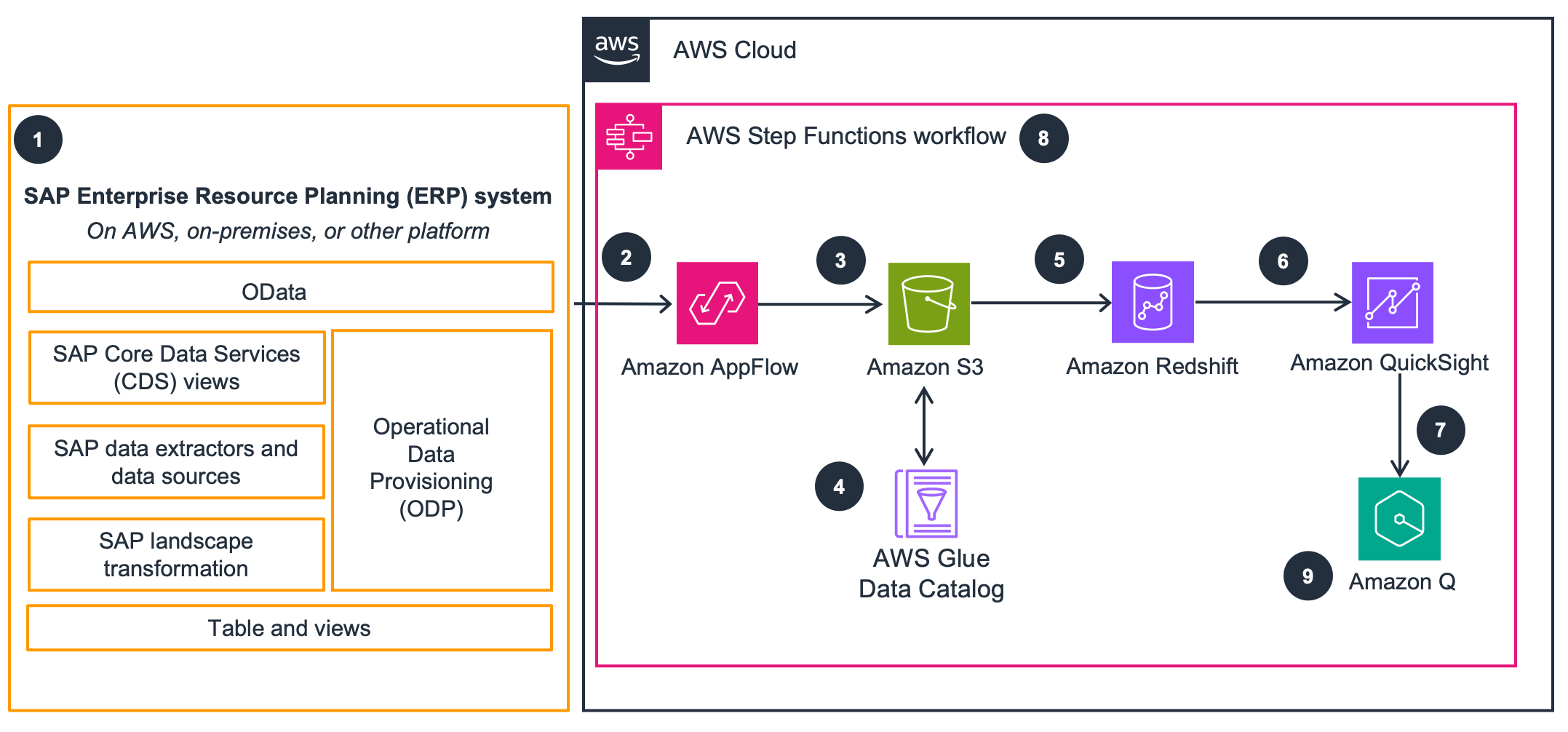
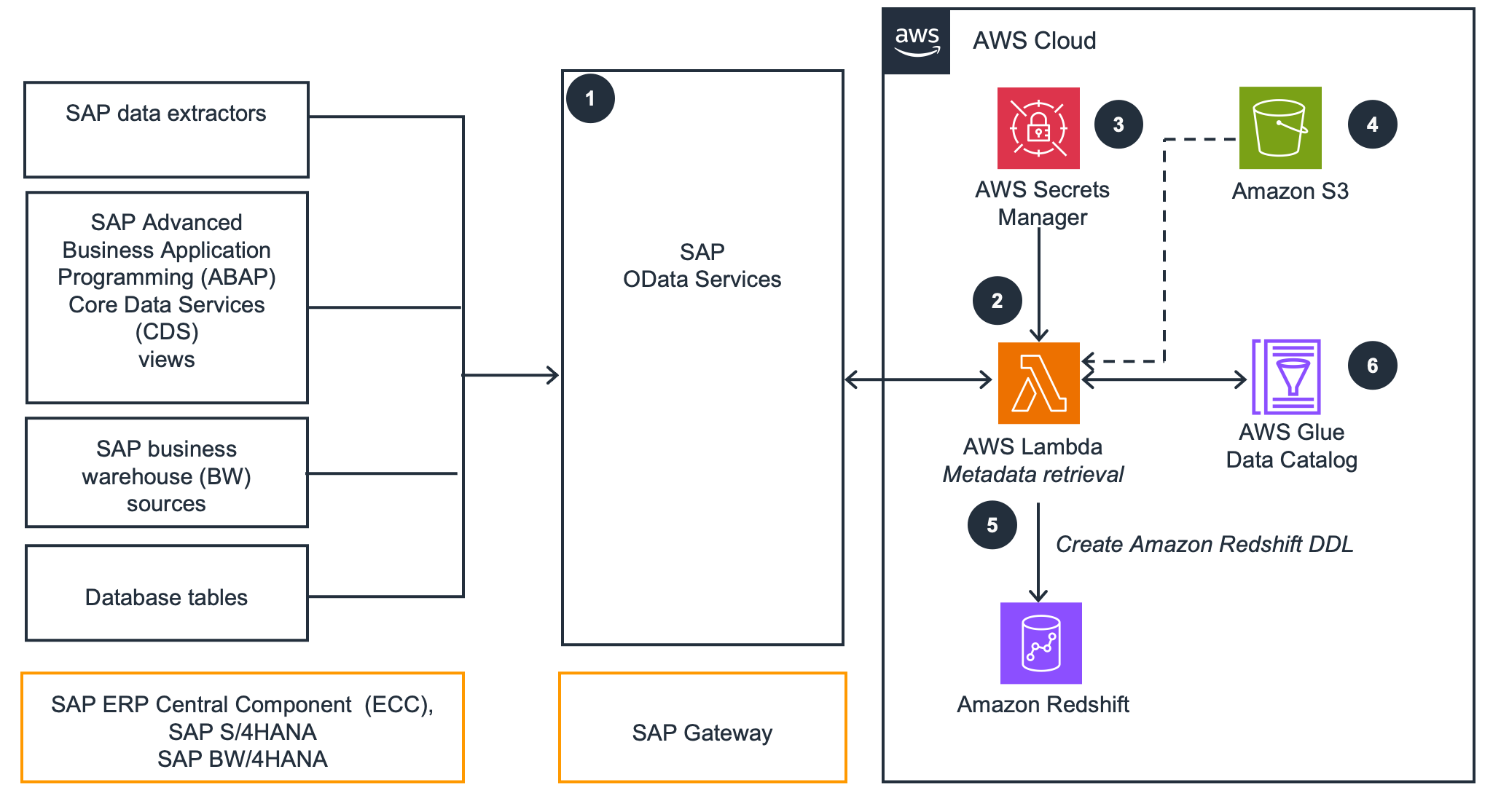
SAP metadata replication
This architecture uses Amazon Lambda and SAP OData to replicate metadata and create Amazon Redshift Data Definition Language (DDL) tables. A Python script with PyOdata queries SAP OData sources and generates DDL to create tables in Amazon Redshift and the AWS Glue Data Catalog.
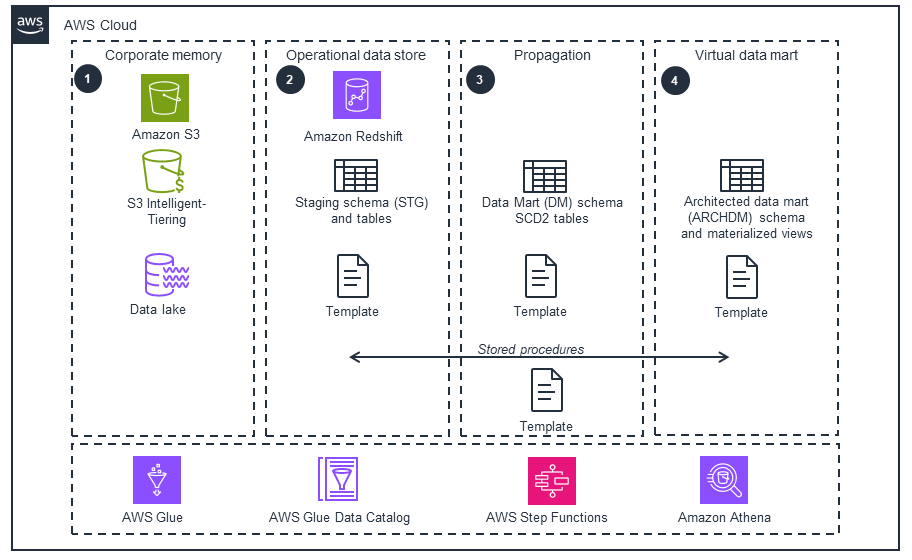
Amazon Redshift data marts
This architecture diagram illustrates how the Redshift data mart layers are used. With the Slowly Changing Dimension Type 2 (SCD2) data modeling technique, you have the full history of your data movements that you can query.
Get Started
Deploy this Guidance
Use sample code to deploy this Guidance in your AWS account
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
Observability is derived from the managed services used for data processing, with process-level metrics, logs, and dashboards available through Amazon CloudWatch. These services provide valuable insights into your operations, enabling the continuous improvement of your underlying processes and procedures.
The managed services used in this Guidance are granted access only to the specified data, with access to the SAP workload facilitated through Amazon AppFlow, which supports PrivateLink to create private data flows between AWS services. Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest, and data stored in Amazon S3 is secured from unauthorized access through the use of encryption features and access management tools. Moreover, the Amazon Redshift data warehouse cluster is isolated within your virtual private cloud (VPC).
These services support robust security measures, as the serverless components within the architecture are protected through AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)-based authentication for secure validation of user identities.
Amazon AppFlow is capable of handling large data volumes without the need to break them down into multiple batches, thereby enhancing the overall reliability of the data transfer process. Furthermore, Amazon Redshift offers several features, such as multi-Availability Zone (AZ) deployment, that serve to bolster the reliability of the data warehouse cluster. Amazon Redshift also continuously monitors the health of your system, automatically replicating data from failed drives and replacing nodes as necessary for fault tolerance. Lastly, all the serverless components in this Guidance are designed to be highly available, while the non-SAP components allow for automatic scaling.
By using Amazon S3 for the corporate data memory, the storage capabilities of this Guidance are optimized. The processing of the data is then performed within the Amazon Redshift environment. Additionally, to enhance performance and agility, multiple flows are configured in Amazon AppFlow for the different groups of business data.
By using serverless technologies, you pay only for the resources you use. To further optimize cost, extract only the business data group you need and minimize the number of flows being run based on the granularity of your reporting needs. Notably, the Amazon S3 Lifecycle configuration policies allow you to manage the objects so that they're stored cost-effectively throughout their lifecycle.
With managed services and dynamic scaling, you minimize the environmental impact of the backend services. As new features or capabilities become available for Amazon AppFlow, consider adopting those updates so that the data warehouse can continuously improve its efficiency and performance and meet your evolving business needs over time. Lastly, reducing the quantity and frequency of extraction improves sustainability, helps reduce cost, and improves the overall performance of your workloads.
Disclaimer
The sample code; software libraries; command line tools; proofs of concept; templates; or other related technology (including any of the foregoing that are provided by our personnel) is provided to you as AWS Content under the AWS Customer Agreement, or the relevant written agreement between you and AWS (whichever applies). You should not use this AWS Content in your production accounts, or on production or other critical data. You are responsible for testing, securing, and optimizing the AWS Content, such as sample code, as appropriate for production grade use based on your specific quality control practices and standards. Deploying AWS Content may incur AWS charges for creating or using AWS chargeable resources, such as running Amazon EC2 instances or using Amazon S3 storage.
References to third-party services or organizations in this Guidance do not imply an endorsement, sponsorship, or affiliation between Amazon or AWS and the third party. Guidance from AWS is a technical starting point, and you can customize your integration with third-party services when you deploy the architecture.
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages