End-to-end RAG deployment using Amazon Bedrock and Elastic Cloud
Deploy a RAG-enabled conversational agent using Elastic to automate the generation and storage of vector embeddings from your S3-stored data using AWS Lambda
Overview
- Enterprise-scale similarity search capabilities
- Secure data handling through PrivateLink integration
- Unified platform for both full-text and vector search
- Automated vector embedding generation from your S3 data
Deploy the solution
Introduction
Large Language Models (LLM) and conversational interfaces are a top area of development and innovation across most organizations today. For LLMs to become truly valuable to organizations and their users, it is indispensable to provide the model with custom, proprietary and sensitive information.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a frequently used mechanism to enrich the knowledge available to LLMs with custom data that the model can leverage as part of its response generation.
RAG can be used to extend the power of LLMs from general response generation to domain specific knowledge and improved user experience, all depending on the data used to enrich the LLM context.
Everything from internal knowledge bases to financial or healthcare analysis relying on highly sensitive, proprietary and protected data can be achieved using retrieval augmented generation, resulting in improved accuracy and relevance in generated responses, reduced model hallucinations and an overall improvement to user experience, all while being generally cost-effective to implement.
An out-of-the-box optimized RAG solution for AWS
RAG’s popularity is driven by the relative simplicity of its implementation, requiring no direct training or tweaking of models themselves, and allowing for real-time access to data that may be rapidly updated and proprietary.
Retrieval Augmented Generation does not come without challenges though, as it requires data pipelines that will process and store data in a format that is suitable for Large Language Models to incorporate as part of its generation process. The efficiency and timeliness of these pipelines, as well as the capabilities of the underlying storage technology and the selection of LLMs to use, are key components that directly impact the overall value that users can derive from a RAG based solution.
This solution relies on carefully selected technologies to solve these challenges, while keeping a minimal number of moving parts.
The tutorial below provides detailed information about how the solution works and complete instructions. This solution expands on and implements the concepts exposed in the technical article: LLM and RAG in practice: A conversational interface for your searchable data.
Solution overview
Components required for Retrieval Augmented Generation
Let’s investigate the various components and capabilities required for building a solution that relies on RAG:
Similarity search:
Retrieval Augmented Generation traditionally relies on similarity search, a method for finding data that looks for objects that resemble a query object, returning data that looks similar together with a similarity score. Similarity search takes place prior to submitting a user’s input to a model and is used to include related data to the context the model is using to generate its response.Vector storage:
For similarity search to work, data must be represented in a format that enables finding, ranking and retrieving complex objects within large datasets given some similarity search algorithm. Vectorized embeddings serve this purpose by representing data as a list of numbers (a vector).Data pipeline:
Producing vector embeddings for data requires some form of pipeline that will take data in its original format, parse it and represent it in numeric form. Chunking (splitting data into small pieces) is also a usual requirement that data pipelines must handle.Large language model:
A model is what ultimately uses the data returned by the similarity search, together with its internal knowledge, to generate a response. There are numerous LLMs that can be used, each model best suited for some specific use case.
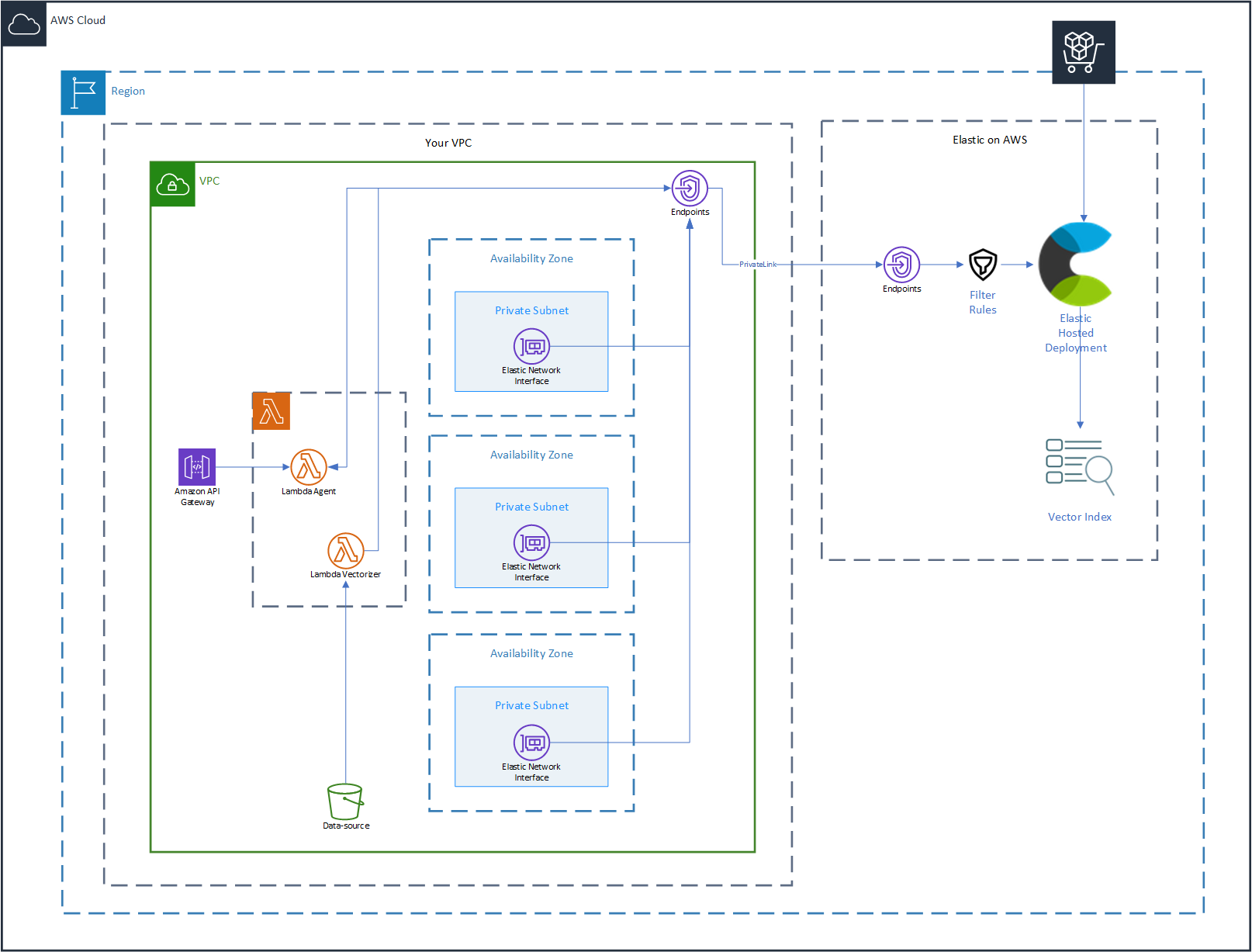
Architecture
Elastic Cloud for vector storage
Elastic has been long chosen for its powerful query and at-scale storage of huge datasets. Thanks to its integration with technologies such as Apache Lucene, Elastic has also become a key go-to solution for vector storage and similarity searches. Using Elastic for vectorized data allows organizations to unify their data and use a common platform for full-text search as well as vectorized data similarity searches.
Subscribing to Elastic Cloud in AWS Marketplace makes deploying Elastic even easier thanks to the free trial available as well as the Quick Launch integration which automates the deployment of a full Elastic environment in AWS, enabling secure connectivity over PrivateLink.
Amazon S3 for data storage
Data in organizations comes in many formats, from Word Documents or PDFs, to presentations, spreadsheets and everything in between. Amazon S3 is the leading provider of object storage, with unrivaled availability and durability, reasons for its widespread use across most organizations.
Infinitely scalable, S3 is an ideal component to act as data sink for any and all information you want to make available as knowledge for your RAG implementation, all while directly integrating with other AWS services such as AWS Lambda which we’ll cover next.
AWS Lambda integrated with S3
On demand and just in time execution of containerized business logic with per second billing and direct integration with S3 makes AWS Lambda one of the most efficient means to process data without having to deploy complex data extraction and transformation mechanisms.
Acting as the target for S3 triggers, AWS Lambda will execute the necessary tasks to load, split and store vectorized embeddings of data on Elastic.
Amazon Bedrock and Titan Models
Amazon Titan models have been chosen for this solution template due to their versatility, performance and Amazon Bedrock integration. Amazon Bedrock provides a fully managed solution to develop and scale generative AI applications, providing access to a wide variety of foundational models, including of course Amazon Titan models. Amazon Titan models excel in tasks like text generation, summarization and question answering scenarios, which directly align with the objectives of this template.
API Gateway
Exposing the solution for users to be able to ask questions related to the data added to the S3 bucket requires an API. Amazon API Gateway also provides fully managed and direct integration with AWS Lambda, dramatically simplifying exposing an interface to users that can infinitely scale and requires zero additional infrastructure.
Deploying this template
The template is fully codified using Terraform and will deploy all the resources you need to have a fully functional environment as seen in the architecture diagram, all with a single terraform apply.
Development environment requirements
Terraform v1.10 or later
AWS CLI
Prerequisites
Sign up for Elastic in AWS Marketplace and complete the quick launch procedure.
Request access to the Amazon Bedrock Titan Models.
Generate an API Key for your Elastic Cloud account and use it as value for an environment variable called EC_API_KEY.
Create a Amazon Secrets Manager secret with the username and password to your Elastic deployment.
Terraform module description
All solution template modules are written using Terraform and are available in the following repository:
Data source
The data source module creates an S3 bucket and enables VPC access to the bucket using S3 VPC Endpoints. The data source module generates an S3 bucket uniquely named to with the corresponding Elastic deployment ID as suffix.
Private link
The private link module creates an Amazon PrivateLink connection with the Elastic cloud service and establishes a VPC endpoint for secure communication with the Elastic deployment. The module also creates a Filter Rule for your Elastic deployment allowing connections only through the VPC endpoint and the necessary Route53 resources required to reach the Elastic deployment using an internal-only hostname.
Lambda vectorizer
The lambda vectorizer module deploys a containerized AWS Lambda function which uses LangChain and Amazon Bedrock to generate and store vector embeddings in an Elastic vector index. The module also grants all necessary IAM permissions and configures the S3 data source to trigger the function whenever documents are added, fully automating the vector embedding generation process.
Lambda agent
The lambda agent module receives a question and uses LangChain with Amazon Bedrock and Elastic to query for related knowledge from the Elastic vector store and provide it as context for Amazon Bedrock to generate a response.
API Gateway
The API gateway module provides a HTTP interface to the lambda agent function, enabling users to submit questions via POST requests and get a response.
Deployment steps
Make sure you have satisfied the Prerequisites section.
Clone the solution template repository
Create a terraform.tfvars file at the root of the repo with the following values:
deployment_id: The unique ID of your Elastic deployment.
elasticsearch_connection_secret: The name of the previously created secret storing access credentials to your elastic deployment.

Run terraform init – this will copy all modules required by the solution.
Run terraform plan – this step will show you all resources to be created by the solution template.
Run terraform apply – this will deploy the full solution in your AWS account.
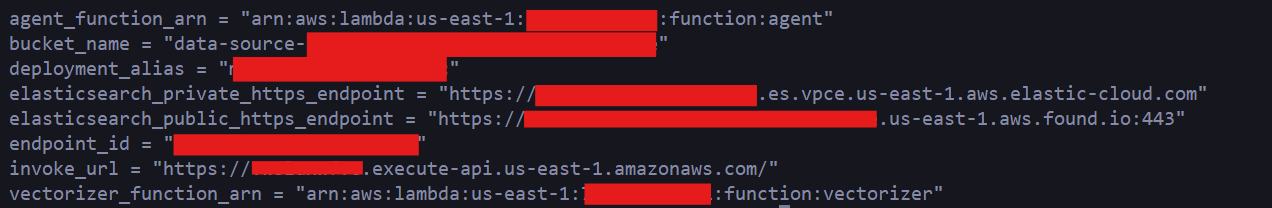
Take note of the outputs generated by the solution. You will find the name of the S3 bucket (bucket_name) as well as the URL (invoke_url) to use when asking the solution questions about your data:
Exploring and using the solution
You’ll notice there is one deployment in your Elastic Cloud account, click Open to inspect its contents.
Click on Elasticsearch, this will take you to an interface that allows you to explore Indices and other types of data stored in your Elastic deployment.
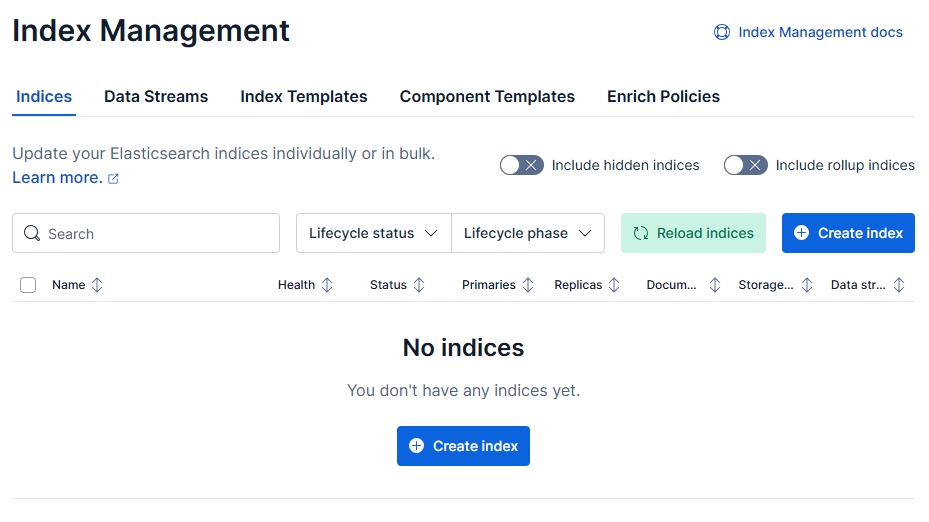
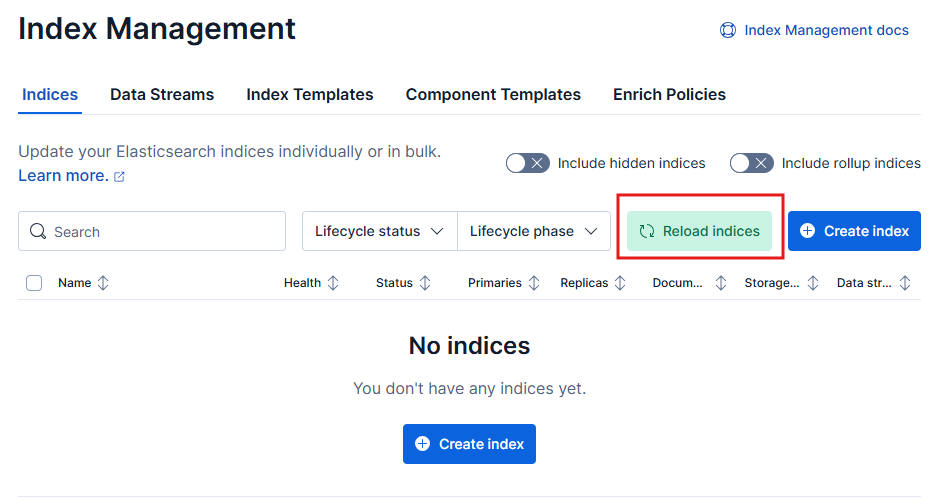
If you click on Index management, you will notice that there are no Indices in your elastic cluster.
Now, let’s generate some vectorized embeddings. We’re going to use AWS Marketplace Cloud-native DevOps eBook as an example, click this link to download it in PDF format.
Go to the S3 Service in your AWS Console and look for a bucket named data-source-{your elastic deployment id}.
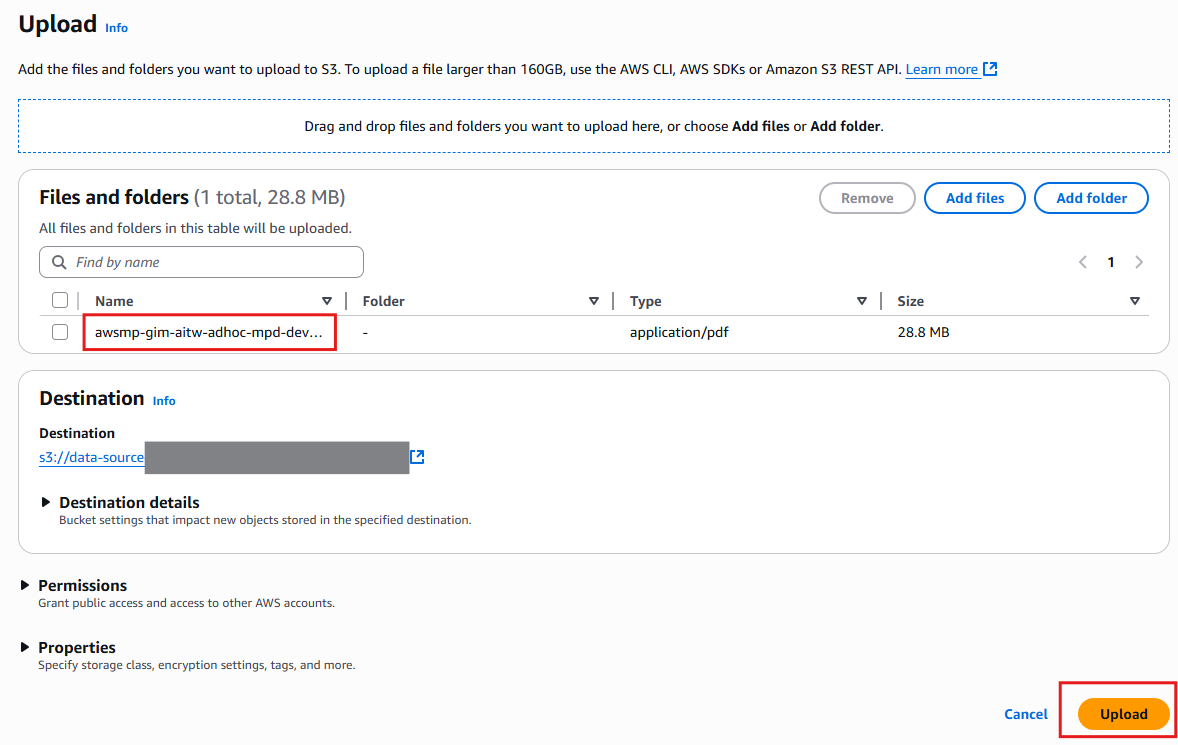
Click on your bucket and select Upload.

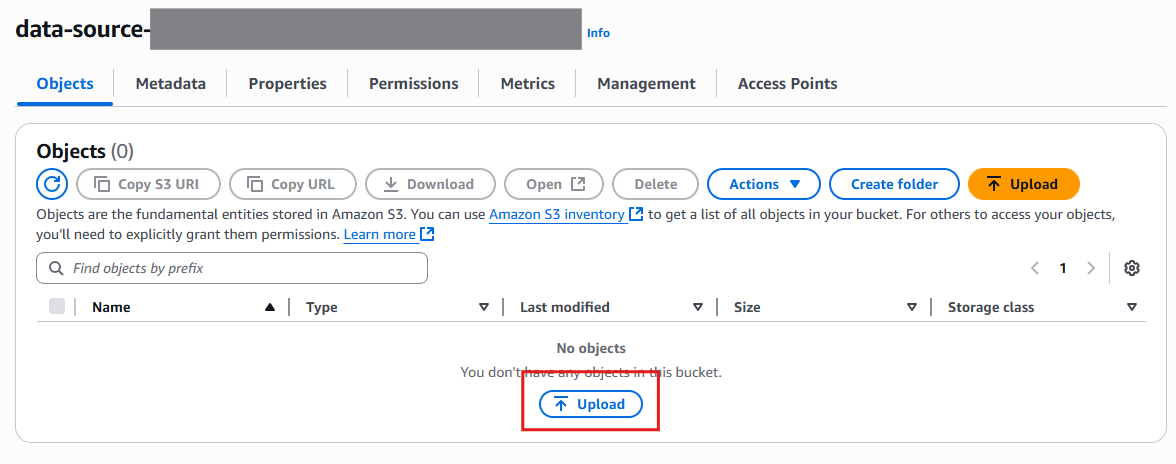
Drag and drop the AWS Marketplace Cloud-Native DevOps PDF you downloaded into the bucket, and click on Upload.
Now let’s look at the vectorizing function we have deployed as part of this solution, running in AWS Lambda. Go to the AWS Lambda service in your AWS Console
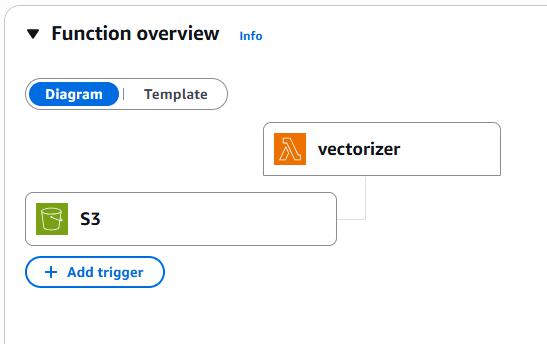
Click on the function named vectorizer. Here you can see how S3 is configured to trigger it when objects are uploaded.

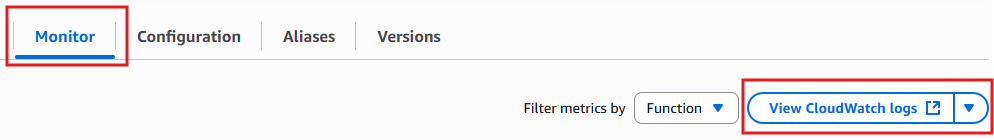
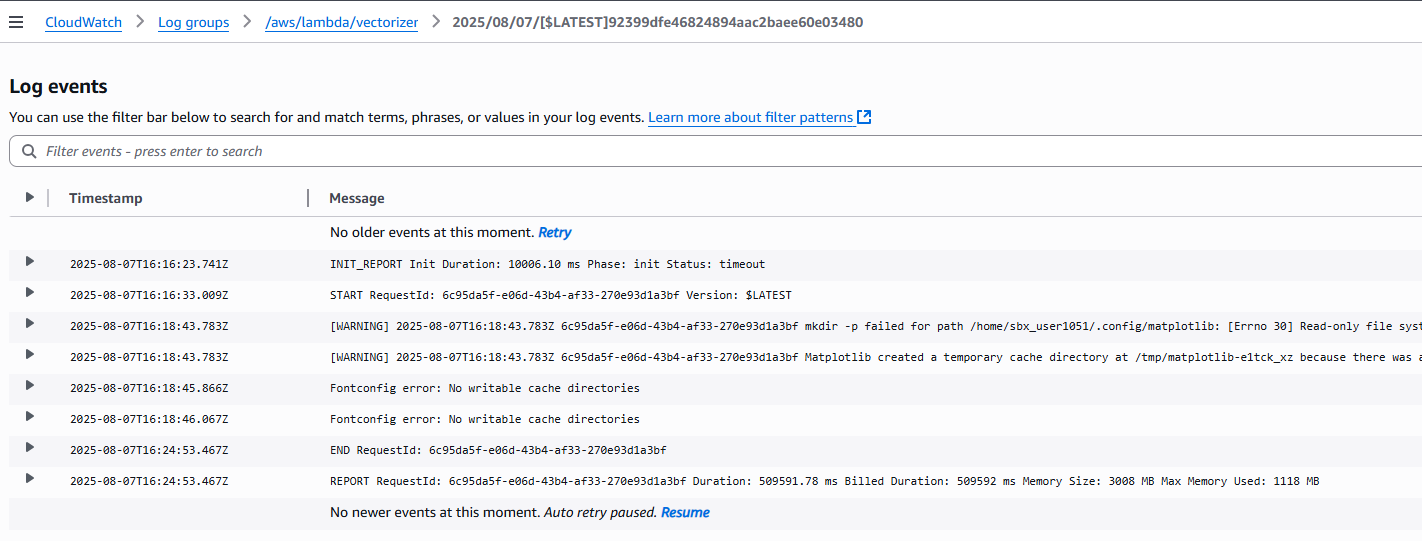
To inspect the logs of the running function you can click on Monitor and View CloudWatch logs.
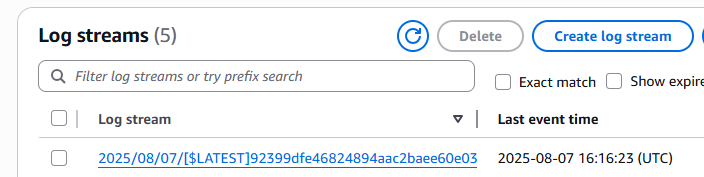
Click on the most recent Log stream (confirm that the Last event time is not in the past) – you will see the lambda function initialize and generate some output.
Now go back to Elastic Index Management and click Reload indices.
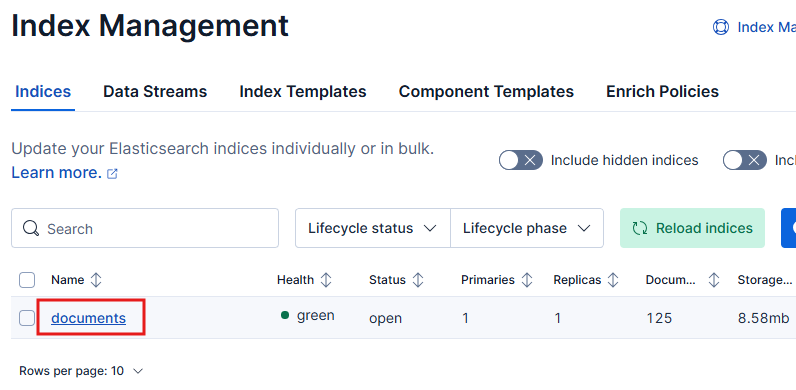
A new index named documents will now exist, holding the vectorized embeddings of the PDF ebook you’ve just uploaded.
Now, let’s ask the LLM a question about our data, we will do that using CURL from your terminal, you can also use Postman or other similar tools. Select API gateway from the available services in your AWS console.
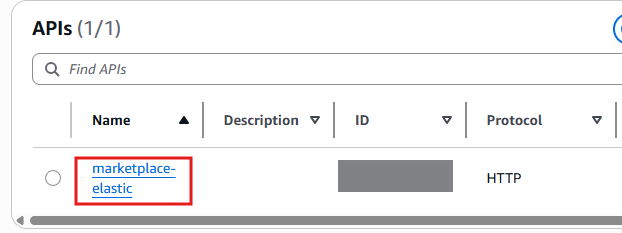
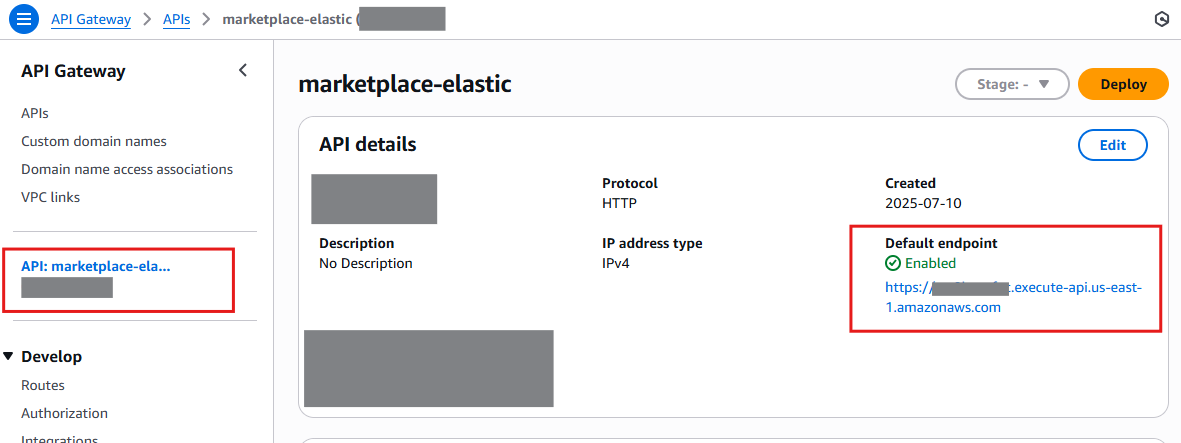
Look for an API named marketplace-elastic, click on it and look for the default endpoint URL. This value will be unique to your API, copy it.
Now open up a terminal and run the following cURL command, making sure to modify it to use your unique endpoint. Notice that there is a /agent path in the URL that you must append to your endpoint.

After a few seconds, you will get a response! LLMs are not deterministic so the response you get may vary.

Now try it with your own data! Upload a PDF, wait for the vectors to be created, and then ask a question in Elastic Playground using the Elastic managed LLM.
Troubleshooting
Q: I get an “Internal Server Error” after running multiple consecutive questions.
A: Amazon Bedrock has a rate limit to the number of calls you can make to it, ask for a quota increase if needed.
Why AWS Marketplace for on-demand cloud tools
Free to try. Deploy in minutes. Pay only for what you use.