- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Event-Driven Application Autoscaling with KEDA on Amazon EKS
Guidance for Event-Driven Application Autoscaling with KEDA on Amazon EKS
Integrate KEDA with a Kubernetes cluster to achieve event-driven scalability
Overview
This Guidance demonstrates how to implement event-driven autoscaling for Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) applications using Kubernetes Event-Driven Autoscaler (KEDA). The Guidance shows how to scale deployments based on custom metrics, rather than solely CPU and memory utilization. KEDA integrates with Kubernetes, extending autoscaling capabilities for event-driven workloads. By following this Guidance, you can optimize resource provisioning, improve cost efficiency, and enhance the customer experience for your event-driven applications on Amazon EKS using custom metrics-based autoscaling with KEDA.
How it works
EKS Cluster
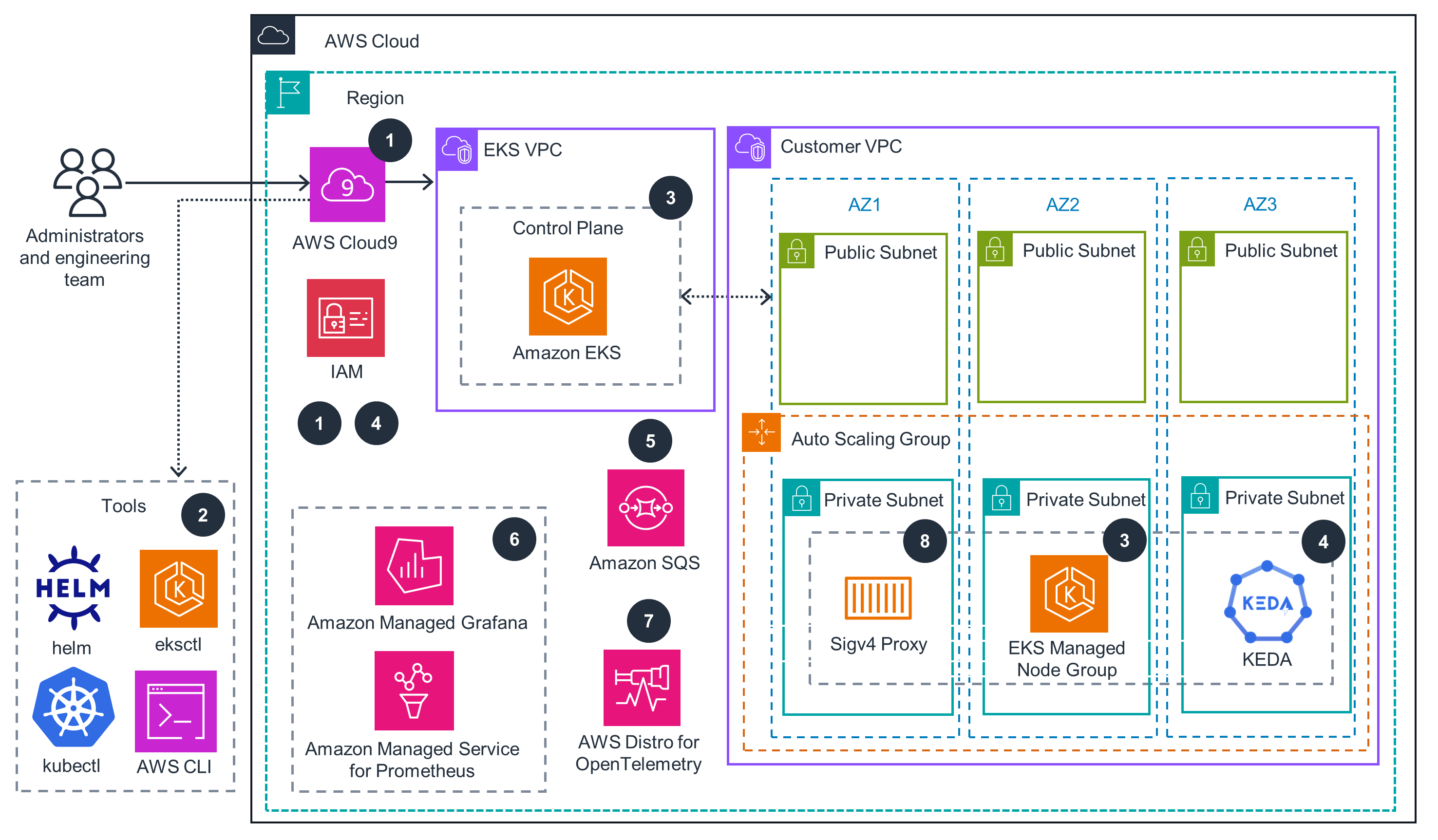
KEDA Overview
This architecture diagram shows an overview of how KEDA, the Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA), and external event sources work together. For KEDA scaling pods, open the next tab.
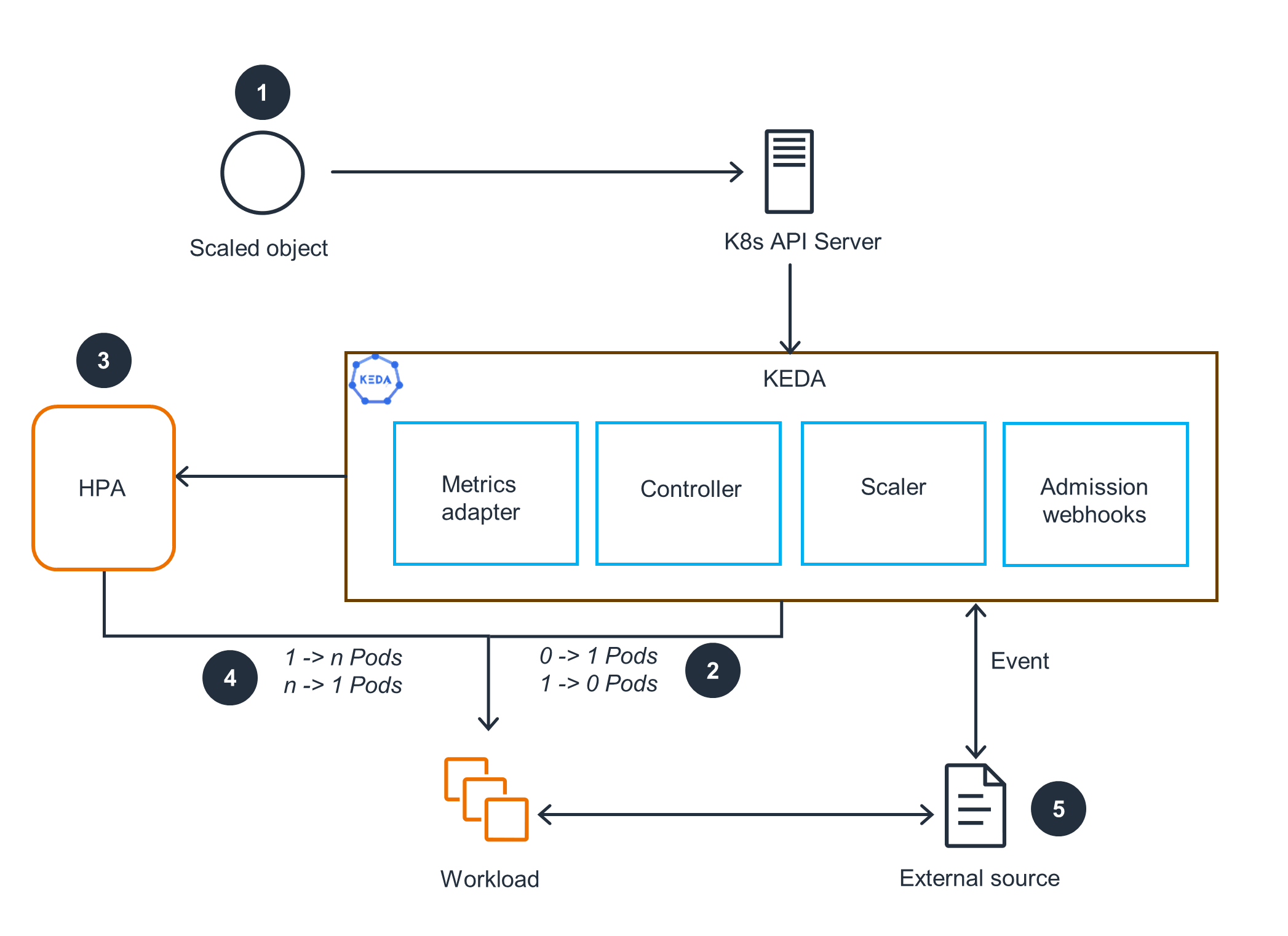
Scaling with KEDA
This architecture diagram shows KEDA scaling deployment pods based on custom metrics sources. For the EKS cluster, open the first tab.

Deploy with confidence
Everything you need to launch this Guidance in your account is right here
We'll walk you through it
Dive deep into the implementation guide for additional customization options and service configurations to tailor to your specific needs.
Let's make it happen
Ready to deploy? Review the sample code on GitHub for detailed deployment instructions to deploy as-is or customize to fit your needs.
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
This event-driven architecture allows you to define precise scaling rules, granting fine-grained control over how your applications respond to specific events or metrics. By using KEDA, you can enhance the efficiency, resource utilization, and responsiveness of your Kubernetes environment, driving operational excellence.
Use IAM roles to obtain temporary credentials, enabling access to diverse AWS services. For your Kubernetes-based applications, integrate with native authentication and authorization mechanisms to securely interact with the Kubernetes API server. By precisely defining IAM policies to grant the minimal necessary permissions, you effectively mitigate unauthorized access and strengthen the security of your environment.
Using pod topology spread constraints in Kubernetes can help you bolster availability and resilience of your applications. This feature enables you to control the distribution of your pods across different failure domains, such as hosts or Availability Zones. By ensuring a balanced and optimal spread, you minimize the impact of potential failures within a single domain, enhancing the overall integrity of your application.
The Amazon EKS cluster's multi-Availability Zone setup allows for low-latency performance. While inter-subnet traffic across Availability Zones may occur, the resulting latency is expected to have a minimal impact on your application's performance. In scenarios where even lower latency is required, you can direct traffic within a single Availability Zone to further optimize network performance.
KEDA's automated pod scaling capabilities can help provide cost savings. By using custom metrics to initiate scaling, you can support optimal pod availability to meet your application's needs, avoiding overprovisioning and unnecessary costs.
You can achieve sustainable resource management through Kubernetes HPA. KEDA uses this capability to effectively scale your workloads based on custom metrics so that only the required pods run. With access to over 60 different scalers, you can tailor the scaling behavior to your specific needs, maximizing the utilization of your deployed resources and preventing overallocation.
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages