- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Resilient Data Applications Using Amazon DynamoDB
Guidance for Resilient Data Applications Using Amazon DynamoDB
Improve application resiliency to guard against disruptions and outages
Overview
How it works
Primary
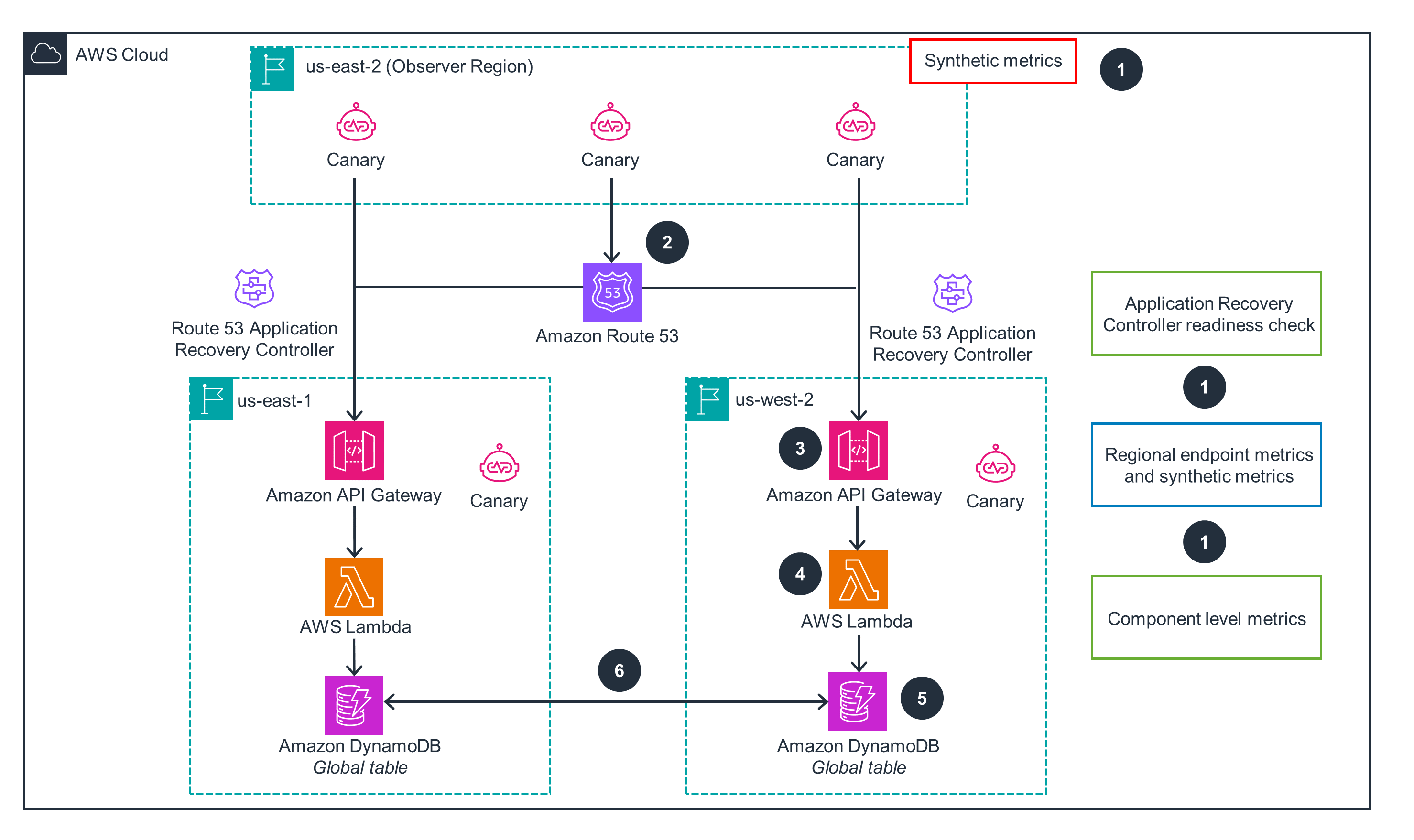
This architecture diagram shows how to set up and build a resilient, multi-Region application. For cross-Region failover and failback, open the other tab.
Cross-Region Failover and Failback
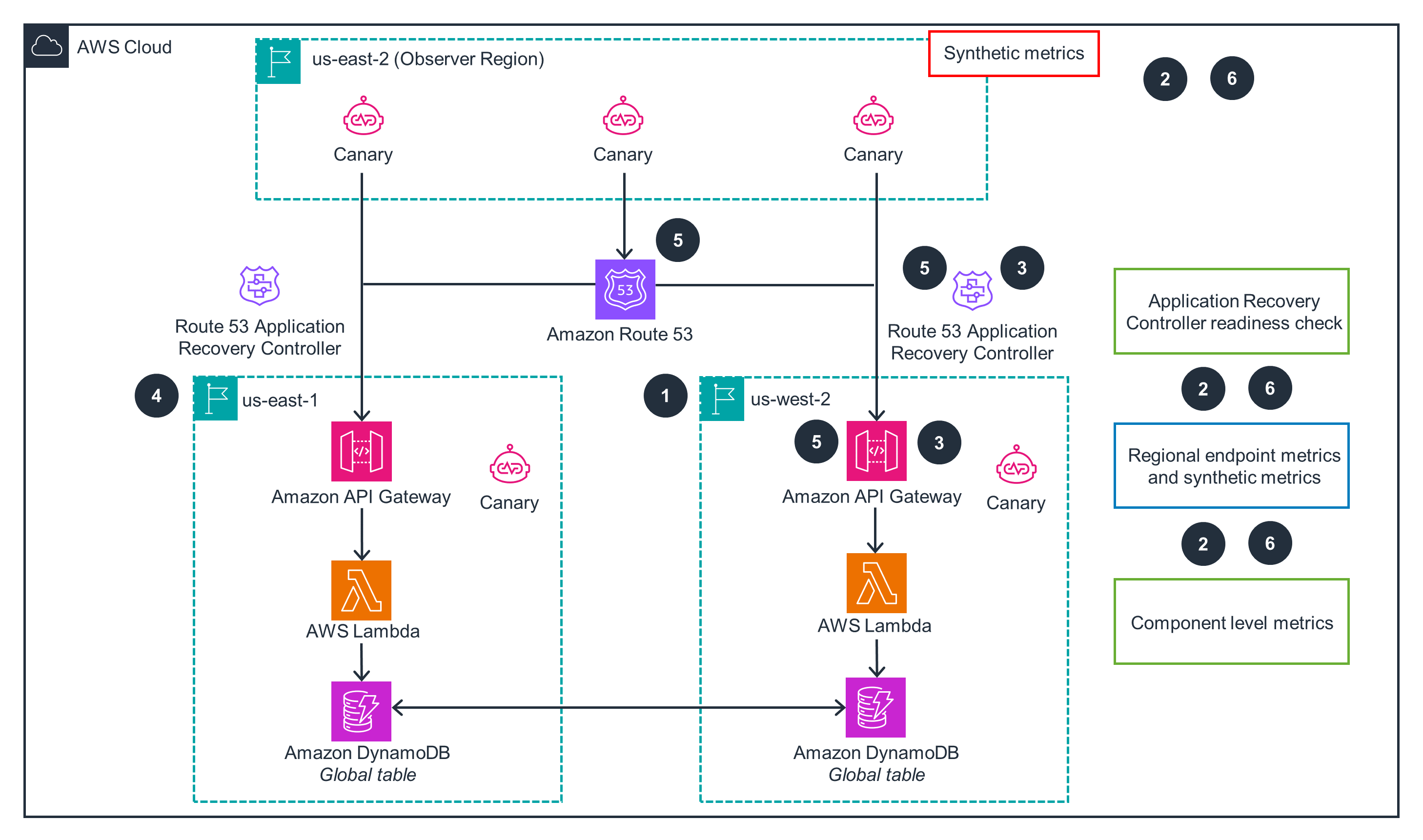
This architecture diagram shows how to perform cross-Region failover and failback in the event of an outage. For setup of the primary Region, open the other tab.
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
Amazon CloudWatch monitors the application's health through metrics from DynamoDB, Lambda, API Gateway, and Route 53. During incidents, metrics help assess user impact for evacuation decisions. CloudWatch Synthetics canaries simulate customer interactions, verifying user experience even without traffic. Canaries complement component metrics by revealing customer-facing issues. CloudWatch dashboards provide a unified view of performance for operations staff. Route 53 ARC checks application readiness. Post-failover, dashboards monitor the failover Region.
API Gateway HTTPS endpoints encrypt all communications. AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) implements the principle of least privilege, granting only the necessary permissions for services to function. DynamoDB encrypts data at rest and in transit, while CloudWatch logs are also encrypted, safeguarding your sensitive information. Adopting these security-focused AWS services mitigates the risk of data breaches and strengthens the overall security posture of your application.
DynamoDB global tables replicate your data across multiple AWS Regions. Automated failover with Route 53 routing and Route 53 ARC helps your application seamlessly continue operating in the event of a disruption. Lambda provides a scalable application layer, decoupling your services from provisioned compute resources. Real-time monitoring with CloudWatch and CloudWatch Synthetics canaries provide the information your team needs to make informed decisions during critical events. These AWS services help you build a robust and highly available application that can withstand unexpected failures.
Fully managed, serverless AWS services automatically scale to match your workload. DynamoDB, Lambda, API Gateway, and Route 53 dynamically allocate resources so your application can handle traffic surges and fluctuations without compromising the user experience. CloudWatch monitors your application's metrics, enabling you to identify and address performance bottlenecks. Route 53 automatically distributes traffic to the lowest latency Regions, improving responsiveness for your users.
AWS services automatically scale resources to match your application's needs. Lambda and DynamoDB only charge for the compute and storage resources you consume, eliminating the need for overprovisioning. API Gateway and Lambda work in tandem to launch your application logic only when valid API requests are received, so you pay only for the resources you use.
The serverless architecture diagram optimizes resource allocation, reducing the need for provisioned hardware and enabling efficient energy usage. API Gateway and Lambda launch only for valid requests, minimizing compute consumption. DynamoDB allocates storage as needed, preventing waste. Resources scale up during traffic spikes and failovers, then scale down when demand decreases. This automated, precise matching of supply to demand maximizes energy efficiency and reduces energy consumption.
Deploy with confidence
Ready to deploy? Review the sample code on GitHub for detailed deployment instructions to deploy as-is or customize to fit your needs.
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages