- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Sustainability Data Management on AWS
Guidance for Sustainability Data Management on AWS
Overview
How it works
Overview
This architecture diagram illustrates how sustainability applications can both consume and produce data assets, incorporating key data management concepts to quickly share and extract trusted value from data across your organization. The subsequent slides cover user access, data discovery, and automated data asset registration workflows tailored for sustainability use cases.
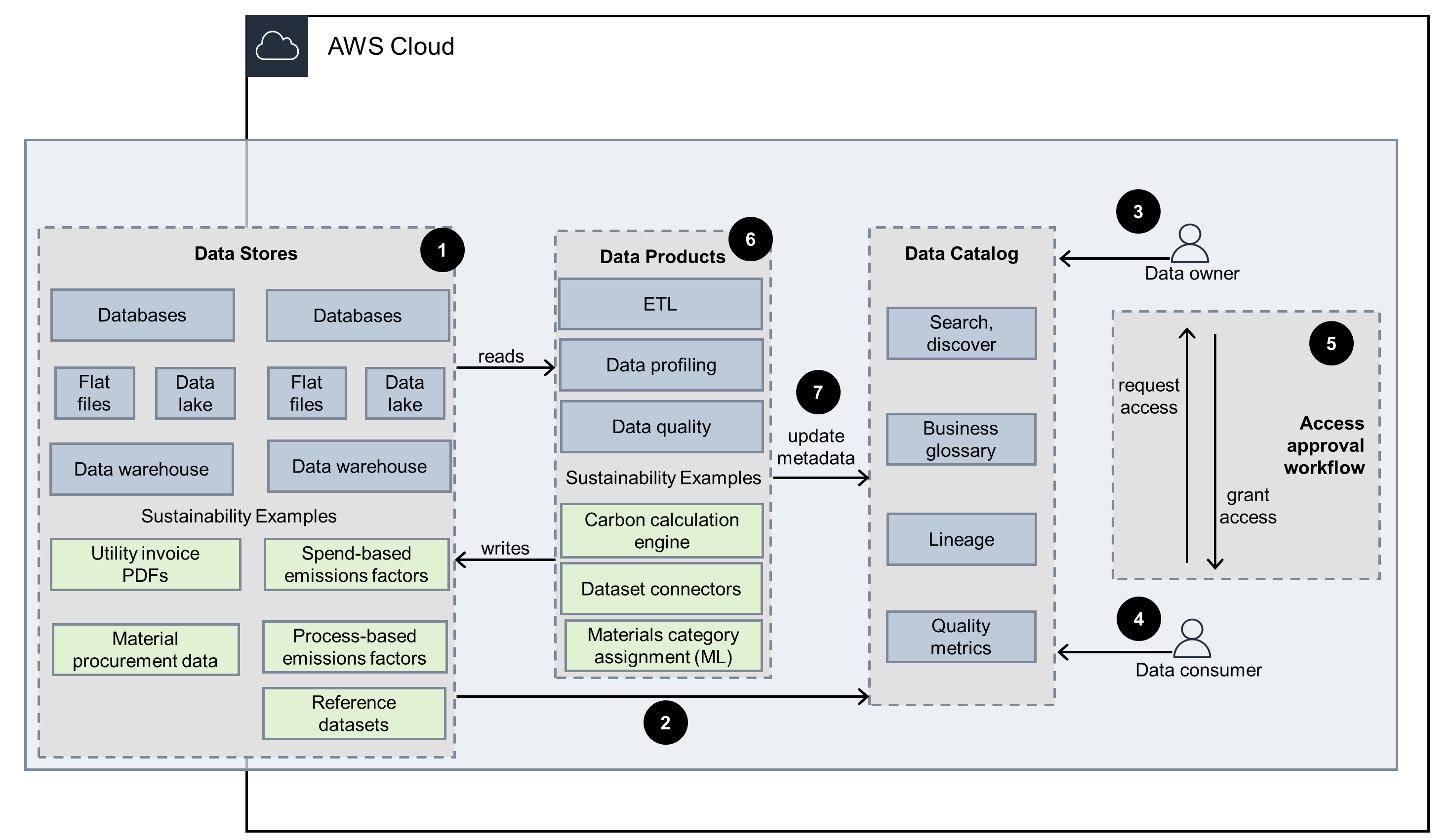
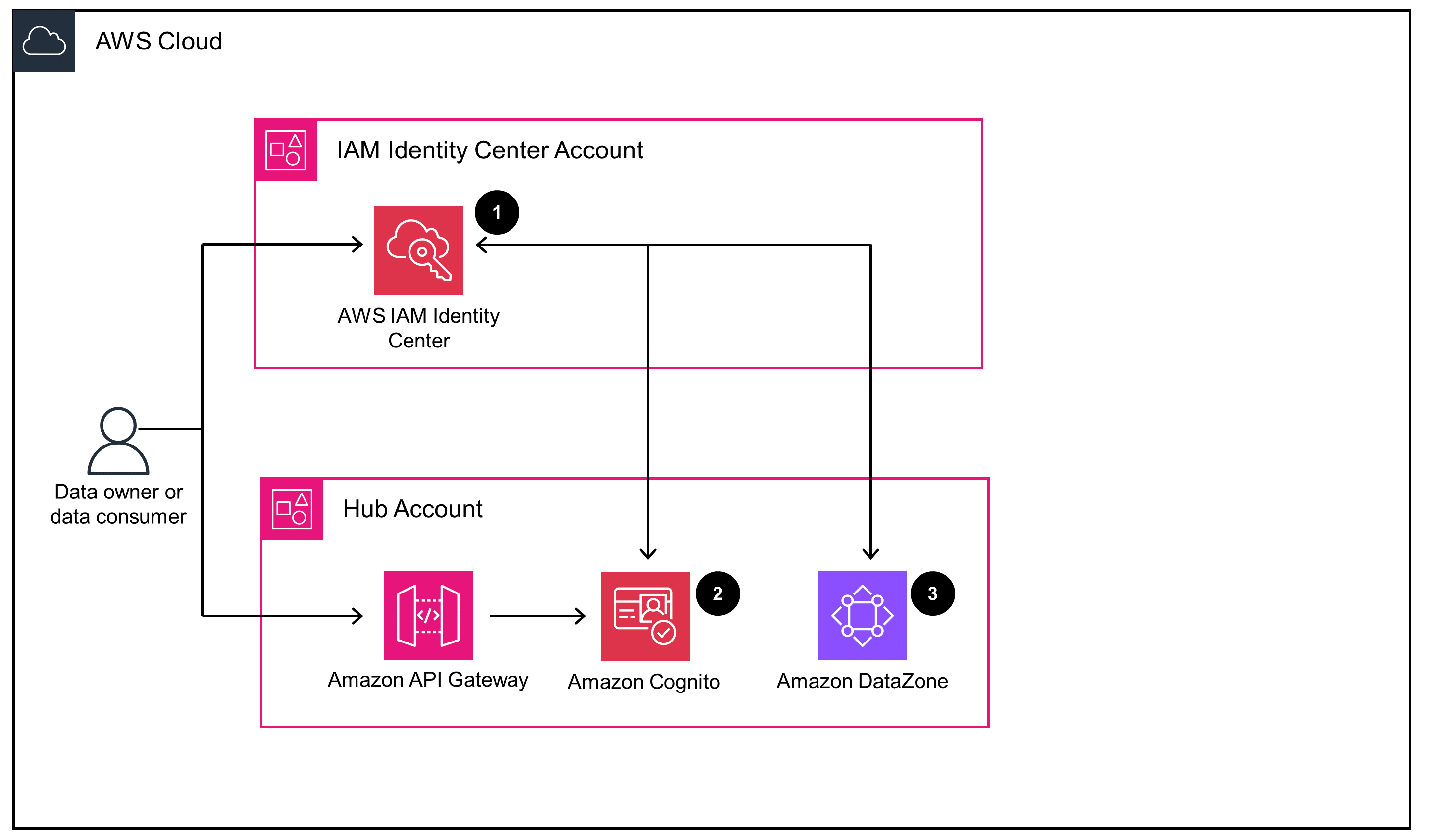
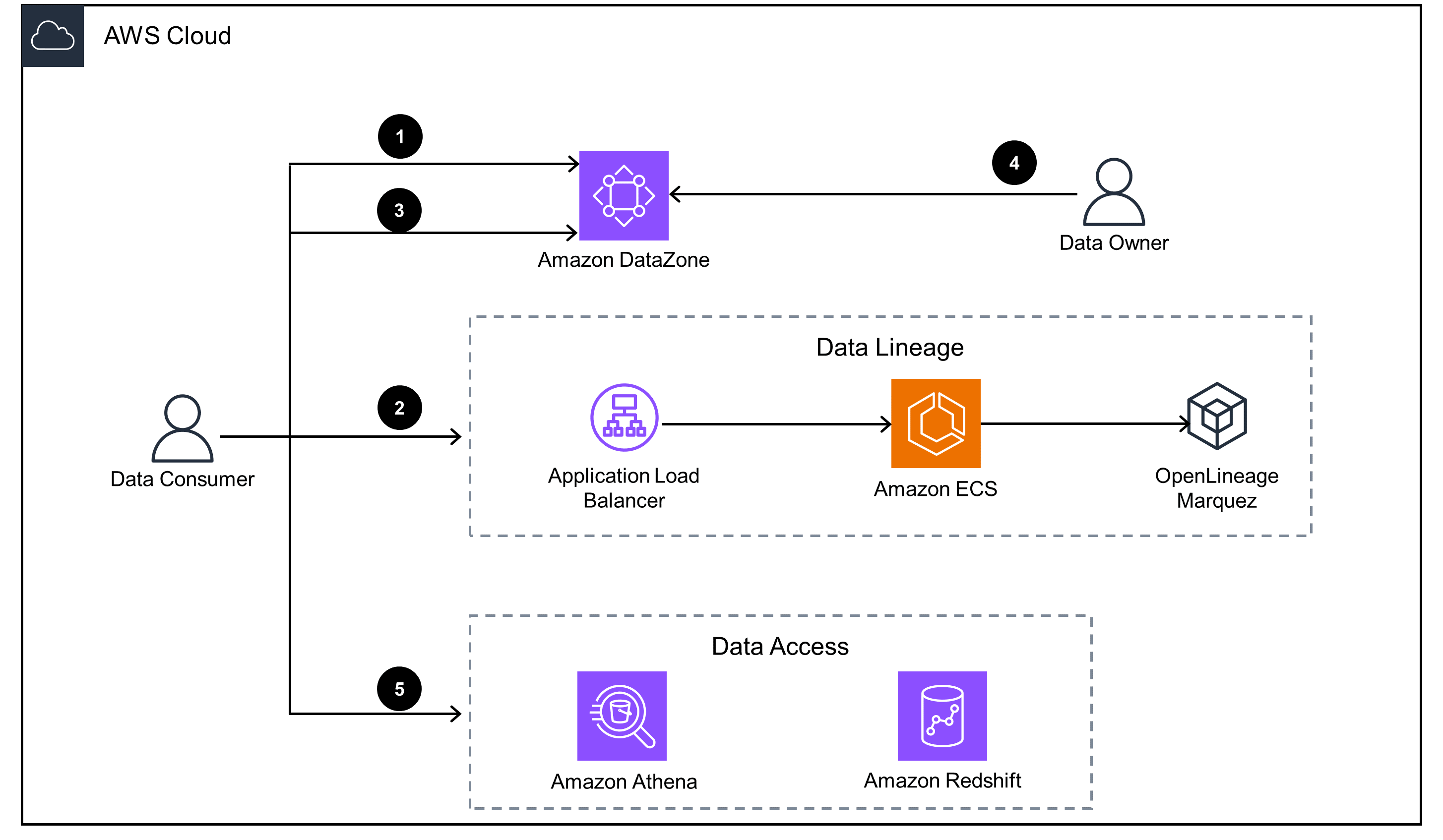
Data discovery
Search, discover, and request access to data assets in the data catalog.
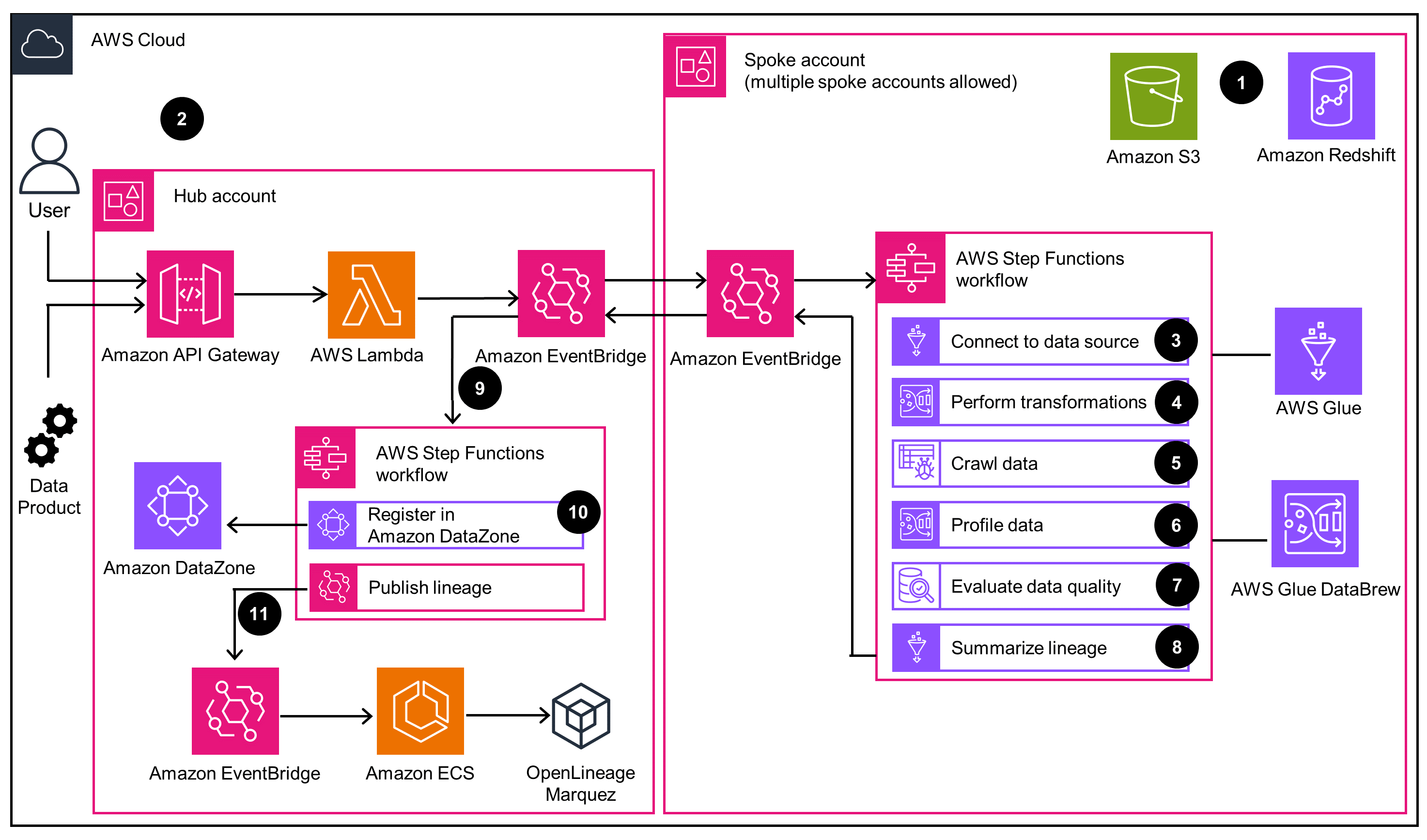
Automated data asset registration
Data asset registration with profiling, transformation, quality assertion, and lineage tracking.
Get Started
Try out this Guidance
Explore an interactive demo for a sneak peak at how this Guidance functions
Deploy this Guidance
Sample Code: Data Management Core
Sample Code: Sustainability Data Management
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
Amazon CloudWatch provides centralized monitoring and observability, which tracks operational metrics and logs across services. This integrated visibility into your workload health and performance helps you identify issues and troubleshoot problems, allowing you to continuously improve processes and procedures for efficient operations.
Cognito, AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), and IAM Identity Center help you implement secure authentication and authorization mechanisms. Cognito provides user authentication and authorization for the application APIs, while IAM policies and roles control access to resources based on the principle of least privilege. IAM Identity Center simplifies managing user identities across the components of this Guidance, enabling centralized identity management.
An Application Load Balancer, Lambda, EventBridge, and Amazon S3 work in tandem so that your workloads perform their intended functions correctly and consistently. For example, the Application Load Balancer distributes traffic to the application containers, providing high availability. EventBridge replicates events across accounts for reliable event delivery, while the automatic scaling of Lambda handles varying workloads without disruption. And as the root data source, Amazon S3 provides highly durable and available storage.
The services selected for this Guidance are optimal services to help you both the monitor performance and maintain efficient workloads. Specifically, Athena and the Amazon Redshift Data API provide efficient querying of data assets. AWS Glue DataBrew and crawlers automate data transformation and cataloging, improving overall efficiency. Amazon Redshift Serverless scales compute resources elastically, allowing high-performance data processing without over-provisioning resources. Lastly, Amazon S3 offers high data throughput for efficient querying.
To optimize costs, this Guidance uses serverless services that automatically scale based on demand, ensuring that you only pay for the resources you use. For example, EventBridge eliminates the need for polling-based architectures, reducing compute costs, and Amazon Redshift Serverless automatically scales compute based on demand, charging only for resources consumed during processing.
The serverless services of this Guidance work together to reduce the need for always-on infrastructure, lowering the overall environmental impact of the workload. For example, Amazon Redshift Serverless automatically scales to the required demand, provisioning only the necessary compute resources and minimizing idle resources and their associated energy usage.
Disclaimer
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages