- AWS Solutions Library›
- Guidance for Disaster Recovery Using Amazon Aurora
Guidance for Disaster Recovery Using Amazon Aurora
Overview
This Guidance shows how to deploy a comprehensive disaster recovery (DR) solution for Amazon Aurora. Different business requirements necessitate different ways of achieving your DR objectives, and finding the best option to meet your recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO) can be overwhelming. This Guidance evaluates the most common routes to take when developing the database portion of your DR plan. By spanning your database resources to a secondary AWS Region and using AWS Backup or Aurora global databases, you can restore your data more easily in the event of a disaster, minimizing interruptions to your business.
How it works
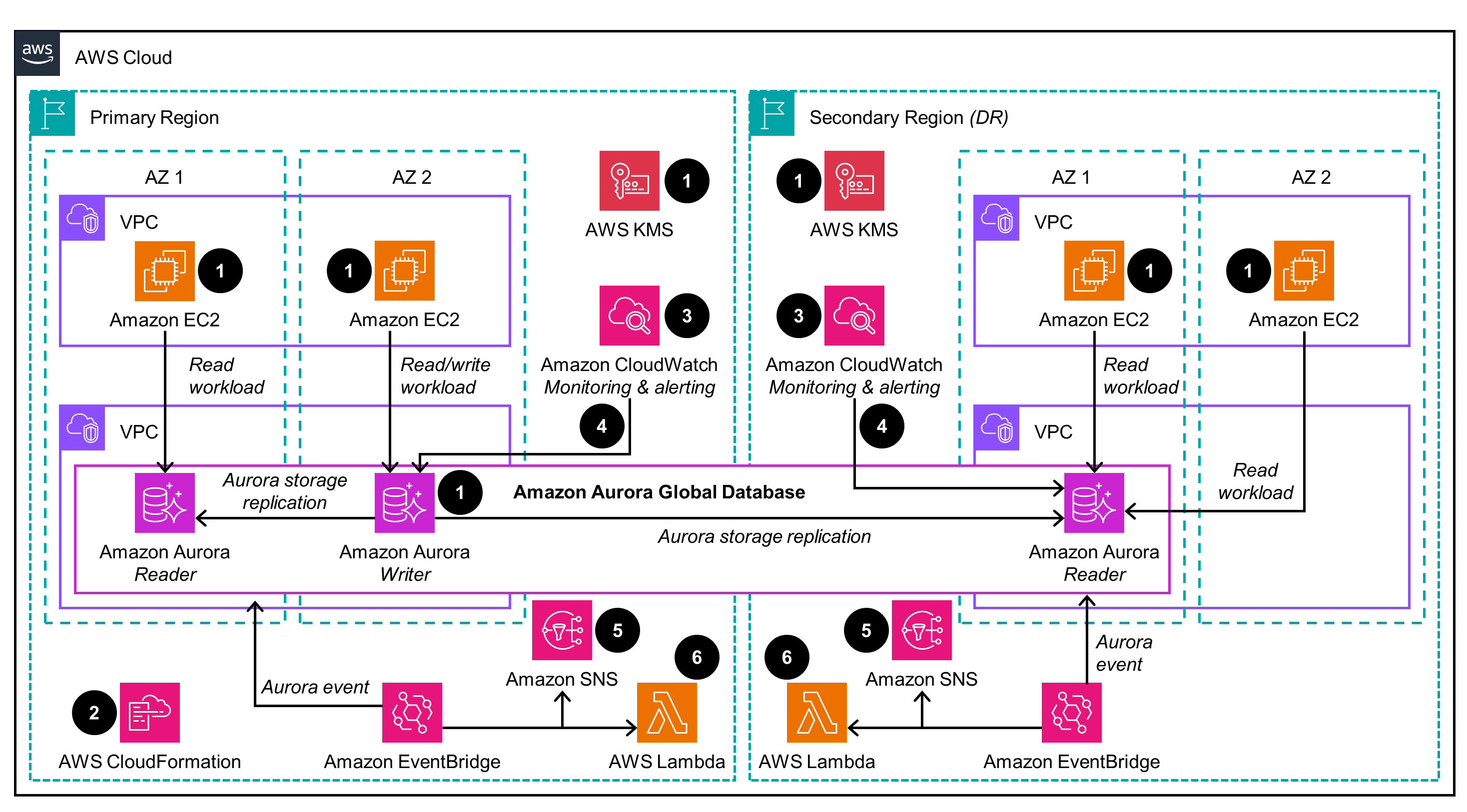
Replicate data
This architecture diagram shows how to implement an Aurora Global database to replicate data to a secondary Region.
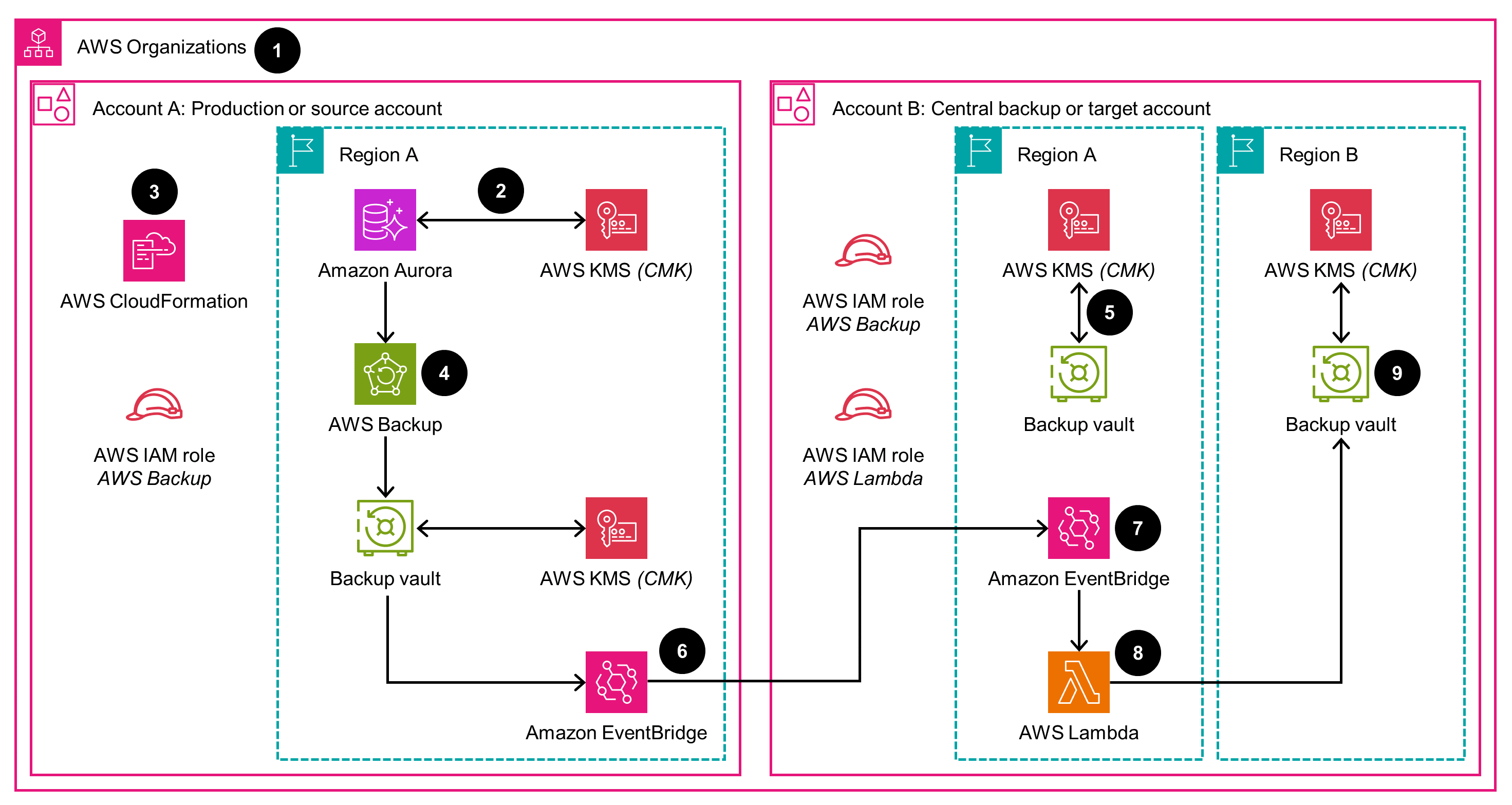
Backup data
Well-Architected Pillars
The architecture diagram above is an example of a Solution created with Well-Architected best practices in mind. To be fully Well-Architected, you should follow as many Well-Architected best practices as possible.
Aurora enables you to customize DR solutions based on your RPO and RTO needs to uphold operational continuity during disaster events. CloudWatch and AWS CloudTrail aid in tracking and reviewing logs and information. By contributing to operational visibility, these services enable quick and effective error review and incident response.
This Guidance uses AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) to enforce the least-privilege model, limiting access to resources. Private resources, protected by IAM identity-based policies, offer heightened security. Additionally, it uses AWS-managed roles in CloudFormation to control access. AWS KMS provides default encryption and the option to use custom keys to safeguard data. Encrypted DB clusters in Aurora offer an additional layer of data protection by encrypting underlying storage, backups, replicas, and snapshots, helping you meet compliance requirements.
Aurora supports data resilience by using replication across multiple AZs to maintain high availability. Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) offers durable storage for critical data, like Aurora snapshots and AWS Backup data. CloudFormation automates resource deployment, as well as rollbacks upon failures. CloudWatch dashboards and Amazon SNS notifications enable monitoring and alerts, and AWS Backup facilitates backup and restore operations for Aurora databases, all contributing to a highly reliable architecture.
This Guidance uses services selected to enhance performance. Aurora offers low-latency, storage-based replication, and Aurora global databases provide cross-Region replication, helping you minimize the impact on workload performance while maintaining data availability in the event of a failure. Additionally, CloudFormation enables you to customize values to meet service-level agreements and RPO and RTO requirements. Finally, AWS Backup uses Lambda and EventBridge for scalable backup frequency that you can optimize based on your business requirements.
Aurora global databases and AWS Backup offer a pay-as-you-go model that helps you avoid maintenance overhead. You can also choose a headless configuration for Aurora global databases, reducing costs to storage and replicated I/O. Additionally, AWS Backup lets you adjust configurations, such as for retention periods, to optimize costs based on your recovery objectives. As a result of using these services, you can reduce unnecessary expenses while maintaining data integrity and availability.
The services in this Guidance contribute to sustainability by scaling resources based on workload demands. Aurora enables dynamic resizing of storage space to achieve optimal resource utilization and minimize unnecessary consumption. Aurora global databases replicate these dynamic changes across Regions to maintain consistency. Additionally, AWS Backup offers incremental and continuous backups, reducing data redundancy and optimizing backup efficiency. By using this Guidance with Aurora serverless v2 clusters, you can enhance capacity adjustments, aligning resources with application needs and minimizing waste.
Deploy with confidence
Everything you need to launch this Guidance in your account is right here
We'll walk you through it
A detailed guide is provided to experiment and use within your AWS account. Each stage of building the Guidance, including deployment, usage, and cleanup, is examined to prepare it for deployment.
Let's make it happen
The sample code is a starting point. It is industry validated, prescriptive but not definitive, and a peek under the hood to help you begin.
Disclaimer
The sample code; software libraries; command line tools; proofs of concept; templates; or other related technology (including any of the foregoing that are provided by our personnel) is provided to you as AWS Content under the AWS Customer Agreement, or the relevant written agreement between you and AWS (whichever applies). You should not use this AWS Content in your production accounts, or on production or other critical data. You are responsible for testing, securing, and optimizing the AWS Content, such as sample code, as appropriate for production grade use based on your specific quality control practices and standards. Deploying AWS Content may incur AWS charges for creating or using AWS chargeable resources, such as running Amazon EC2 instances or using Amazon S3 storage.
References to third-party services or organizations in this Guidance do not imply an endorsement, sponsorship, or affiliation between Amazon or AWS and the third party. Guidance from AWS is a technical starting point, and you can customize your integration with third-party services when you deploy the architecture.
Did you find what you were looking for today?
Let us know so we can improve the quality of the content on our pages