AWS News Blog
EC2 Run Command Update – Now Available for Linux Instances
When we launched EC2 Run Command seven weeks ago (see my post, New EC2 Run Command – Remote Instance Management at Scale to learn more), I promised similar functionality for instances that run Linux. I am happy to be able to report that this functionality is available now and that you can start using it today.
Run Command for Linux
Like its Windows counterpart, this feature is designed to help you to administer your EC2 instances in an easy and secure fashion, regardless of how many you are running. You can install patches, alter configuration files, and more. To recap, we built this feature to serve the following management needs:
- A need to implement configuration changes across their instances on a consistent yet ad hoc basis.
- A need for reliable and consistent results across multiple instances.
- Control over who can perform changes and what can be done.
- A clear audit path of what actions were taken.
- A desire to be able to do all of the above without the need for unfettered SSH access.
This new feature makes command execution secure, reliable, convenient, and scalable. You can create your own commands and exercise fine-grained control over execution privileges using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). All of the commands are centrally logged to AWS CloudTrail for easy auditing.
Run Command Benefits
The Run Command feature was designed to provide you with the following benefits (these apply to both Linux and Windows):
Control / Security – You can use IAM policies and roles to regulate access to commands and to instances. This allows you to reduce the number of users who have direct access to the instances.
Reliability – You can increase the reliability of your system by creating templates for your configuration changes. This will give you more control while also increasing predictability and reducing configuration drift over time.
Visibility – You will have more visibility into configuration changes because Run Command supports command tracking and is also integrated with CloudTrail.
Ease of Use – You can choose from a set of predefined commands, run them, and then track their progress using the Console, CLI, or API.
Customizability – You can create custom commands to tailor Run Command to the needs of your organization.
Using Run Command on Linux
Run Command makes use of an agent (amazon-ssm-agent) that runs on each instance. It is available for the following Linux distributions:
- Amazon Linux AMI (64 bit) – 2015.09, 2015.03, 2014.09, and 2014.03.
- Ubuntu Server (64 bit) – 14.04 LTS, 12.04 LTS
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux (64 bit) – 7.x
Here are some of the things that you can do with Run Command:
- Run shell commands or scripts
- Add users or groups
- Configure user or group permissions
- View all running services
- Start or stop services
- View system resources
- View log files
- Install or uninstall applications
- Update a scheduled (cron) task
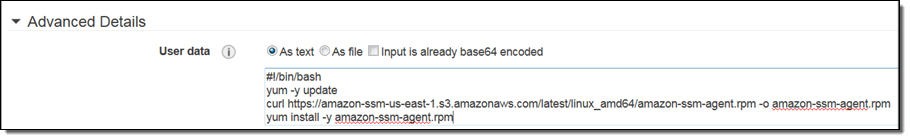
You can launch new Linux instances and bootstrap the agent by including a few lines in the UserData like this (to learn more, read Configure the SSM Agent in the EC2 Documentation):
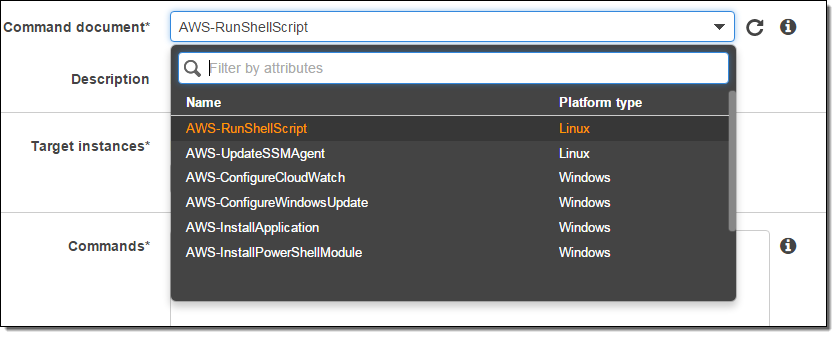
Here’s how I choose a command document (separate command documents are available for Linux and for Windows):
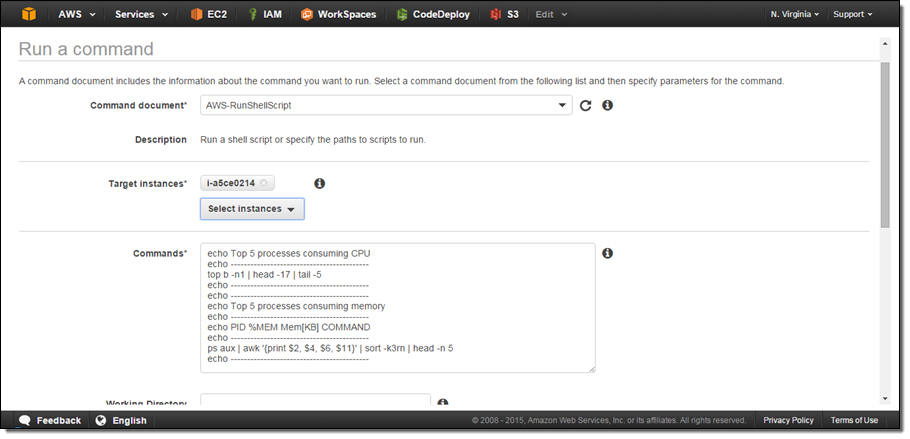
And here’s how I select the target instances and enter in a command or a set of commands to run:
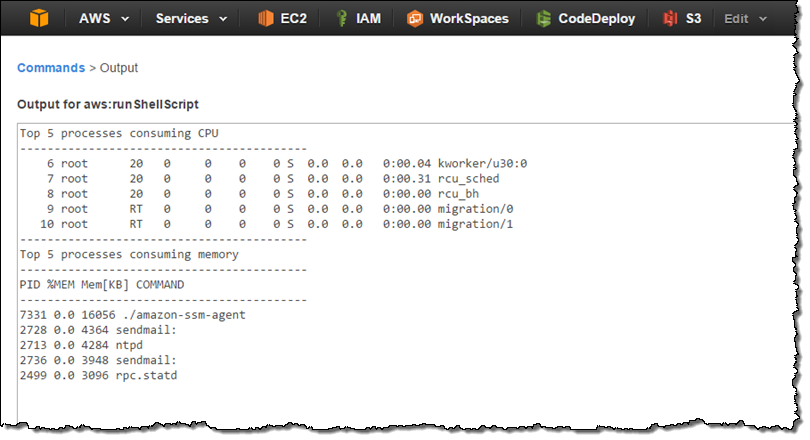
Here’s the output from the command:
Here’s how I review the output from commands that I have already run:
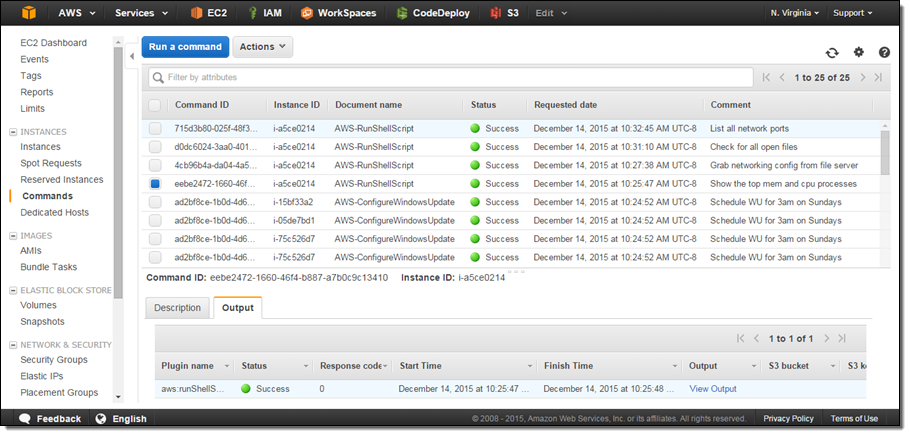
Run a Command Today
This feature is available now and you can start using it today in the US East (N. Virginia), US West (Oregon), and Europe (Ireland) regions. There’s no charge for the command, but you will be billed for other AWS resources that you consume.
To learn more, visit the Run Command page.
— Jeff;