AWS News Blog
Amazon EMR Update – Apache HBase 1.2 Is Now Available
Apache HBase is a distributed, scalable big data store designed to support tables with billions of rows and millions of columns. HBase runs on top of Hadoop and HDFS and can also be queried using MapReduce, Hive, and Pig jobs.
AWS customers use HBase for their ad tech, web analytics, and financial services workloads. They appreciate its scalability and the ease with which it handles time-series data.
HBase 1.2 on Amazon EMR
Today we are making version 1.2 of HBase available for use with Amazon EMR. Here are some of the most important and powerful features and benefits that you get when you run HBase:
Strongly Consistent Reads and Writes – When a writer returns, all of the readers will see the same value.
Scalability – Individual HBase tables can be comprised of billions of rows and millions of columns. HBase stores data in a sparse form in order to conserve space. You can use column families and column prefixes to organize your schemas and to indicate to HBase that the members of the family have a similar access pattern. You can also use timestamps and versioning to retain old versions of cells.
Backup to S3 – You can use the HBase Export Snapshot tool to backup your tables to Amazon S3. The backup operation is actually a MapReduce job and uses parallel processing to adeptly handle large tables.
Graphs And Timeseries – You can use HBase as the foundation for a more specialized data store. For example, you can use Titan for graph databases and OpenTSDB for time series.
Coprocessors – You can write custom business logic (similar to a trigger or a stored procedure) that runs within HBase and participates in query and update processing (read The How To of HBase Coprocessors to learn more).
You also get easy provisioning and scaling, access to a pre-configured installation of HDFS, and automatic node replacement for increased durability.
Getting Started with HBase
HBase 1.2 is available as part of Amazon EMR release 4.6. You can, as usual, launch it from the Amazon EMR Console, the Amazon EMR CLI, or through the Amazon EMR API. Here’s the command that I used:
$ aws --region us-east-1 emr create-cluster \
--name "MyCluster" --release-label "emr-4.6.0" \
--instance-type m3.xlarge --instance-count 3 --use-default-roles \
--ec2-attributes KeyName=keys-jbarr-us-east \
--applications Name=Hadoop Name=Hue Name=HBase Name=HiveThis command assumes that the EMR_DefaultRole and EMR_EC2_DefaultRole IAM roles already exist. They are created automatically when you launch an EMR cluster from the Console (read about Create and Use Roles for Amazon EMR and Create and Use Roles with the AWS CLI to learn more).
I found the master node’s DNS on the Cluster Details page and SSH’ed in as user hadoop. Then I ran a couple of HBase shell commands:
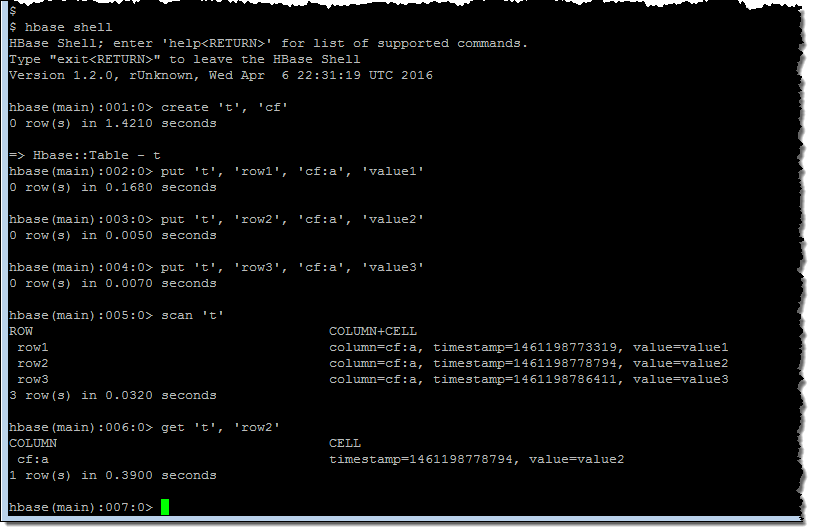
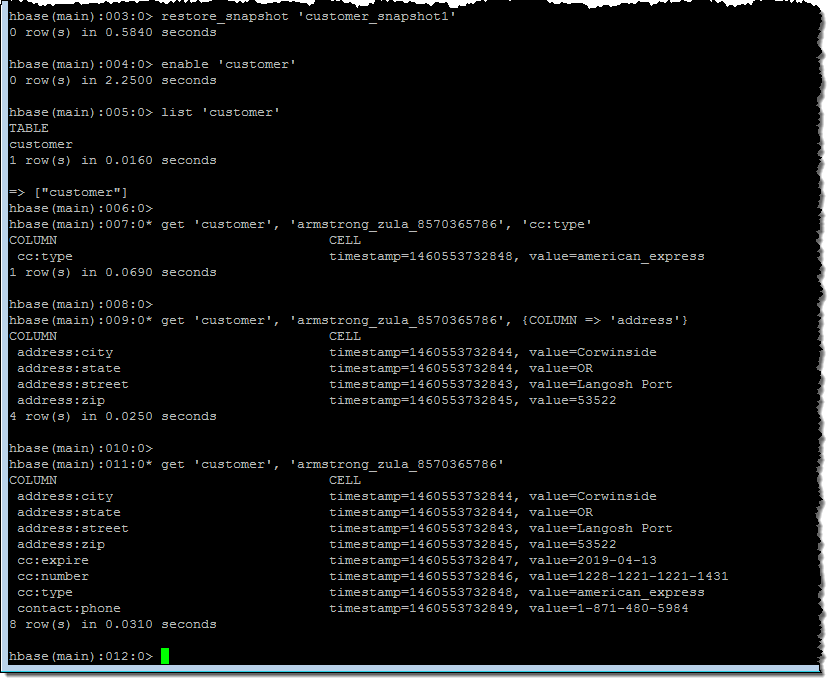
Following the directions in our new HBase Tutorial, I created a table called customer, restored a multi-million record snapshot from S3 into the table, and ran some simple queries:
Available Now
You can start using HBase 1.2 on Amazon EMR today. To learn more, read the Amazon EMR Documentation.
— Jeff;